Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is a condition characterized by partial or total loss of use of all four limbs and torso, typically resulting from spinal cord injury. This condition affects motor and sensory functions below the site of the injury, impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. Explore this article to understand the causes, treatments, and support options available for managing tetraplegia.
Table of Comparison
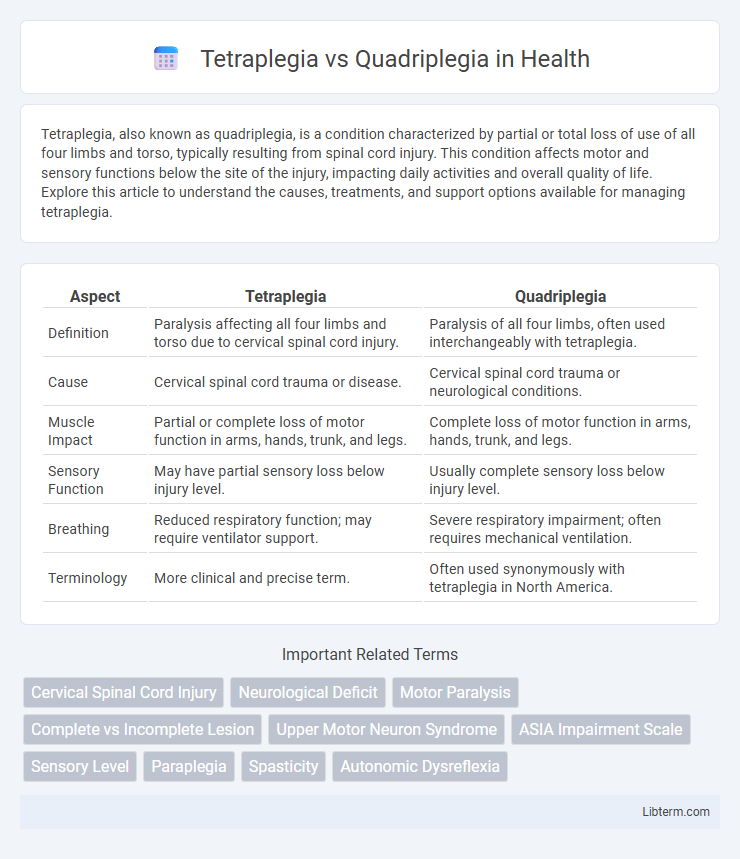
| Aspect | Tetraplegia | Quadriplegia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paralysis affecting all four limbs and torso due to cervical spinal cord injury. | Paralysis of all four limbs, often used interchangeably with tetraplegia. |
| Cause | Cervical spinal cord trauma or disease. | Cervical spinal cord trauma or neurological conditions. |
| Muscle Impact | Partial or complete loss of motor function in arms, hands, trunk, and legs. | Complete loss of motor function in arms, hands, trunk, and legs. |
| Sensory Function | May have partial sensory loss below injury level. | Usually complete sensory loss below injury level. |
| Breathing | Reduced respiratory function; may require ventilator support. | Severe respiratory impairment; often requires mechanical ventilation. |
| Terminology | More clinical and precise term. | Often used synonymously with tetraplegia in North America. |
Understanding Tetraplegia and Quadriplegia
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia both refer to paralysis affecting all four limbs and the torso, typically caused by spinal cord injury or neurological conditions. Tetraplegia is often used interchangeably with quadriplegia, but some medical sources distinguish tetraplegia as paralysis resulting from cervical spinal cord damage, emphasizing impairment in both sensory and motor functions. Understanding the specific level and severity of spinal cord injury is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, as these factors determine the extent of functional limitations and potential recovery.
Defining Tetraplegia: Key Characteristics
Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, involves partial or complete paralysis of all four limbs and the torso, typically resulting from injury to the cervical spinal cord segments C1-C8. Key characteristics include loss of motor function and sensation below the level of injury, with varying degrees of impairment depending on the specific spinal segments affected. Unlike paraplegia, tetraplegia affects both arm and leg mobility, requiring comprehensive medical management and rehabilitation.
What is Quadriplegia? Essential Overview
Quadriplegia, also known as tetraplegia, is a condition characterized by partial or complete paralysis of all four limbs, typically resulting from spinal cord injury at the cervical (neck) level. This paralysis affects motor function and sensation in both the arms and legs, often accompanied by impaired respiratory and autonomic functions depending on the injury's severity and location. Quadriplegia requires comprehensive medical management including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes adaptive technologies to enhance mobility and quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors for Both Conditions
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia primarily result from spinal cord injuries at the cervical level, often caused by traumatic incidents such as motor vehicle accidents, falls, or sports injuries. Risk factors include high-impact trauma, osteoporosis, and conditions like multiple sclerosis or transverse myelitis that damage spinal nerves. Both conditions share similar etiologies but may vary in severity depending on the extent and location of the spinal cord damage.
Comparing Symptoms: Tetraplegia vs Quadriplegia
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia both involve partial or total loss of sensory and motor function in all four limbs and the torso, but tetraplegia specifically results from cervical spinal cord injuries leading to varying degrees of paralysis and loss of sensation. Symptoms of tetraplegia often include impaired respiratory function and loss of bladder or bowel control, whereas quadriplegia is generally used interchangeably but may emphasize complete paralysis below the neck. Understanding the subtle differences in symptom severity and affected areas is crucial for tailored rehabilitation and medical management.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment Differences
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia both involve paralysis of all four limbs, but diagnosis and medical assessment differ in terminology and clinical context. Tetraplegia is more commonly used in Europe and in neurological diagnoses, focusing on impairment level after cervical spinal cord injury or brain damage, while quadriplegia is the term often used in North America and in rehabilitation settings. Medical assessments for tetraplegia typically emphasize precise neurological level and extent of sensory and motor function loss using the ASIA Impairment Scale, whereas quadriplegia assessments prioritize functional abilities and spasticity management in physical therapy evaluations.
Treatment Approaches for Tetraplegia and Quadriplegia
Treatment approaches for tetraplegia and quadriplegia primarily focus on maximizing patient independence and improving quality of life through multidisciplinary rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive technology. Medical interventions such as respiratory support, spasticity management with medications like baclofen, and surgical options including tendon transfers or nerve grafts are tailored to the severity and location of spinal cord injury. Emerging treatments involve functional electrical stimulation (FES) and stem cell research aiming to restore motor function and nerve regeneration for both tetraplegic and quadriplegic patients.
Rehabilitation and Therapy Options
Rehabilitation for tetraplegia and quadriplegia focuses on maximizing functional independence through tailored physical and occupational therapy programs that emphasize muscle strengthening, range of motion exercises, and adaptive techniques. Advanced therapies such as functional electrical stimulation (FES) and robotic-assisted training have shown significant improvements in motor recovery and wheelchair mobility. Comprehensive care also includes respiratory therapy and psychosocial support to address the complex needs of individuals with cervical spinal cord injuries.
Daily Living and Adaptations for Patients
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia both result in paralysis affecting all four limbs, but tetraplegia often involves partial loss of function in the arms and hands, whereas quadriplegia typically indicates complete paralysis. Daily living adaptations for these patients include specialized assistive devices such as customized wheelchairs, environmental control systems, and voice-activated technology to enhance independence. Occupational therapy and home modifications like adjustable beds and accessible bathrooms are essential to support personal care and mobility for individuals managing these conditions.
Outlook and Quality of Life Considerations
Tetraplegia and quadriplegia both result in significant motor and sensory impairments due to spinal cord injuries, but advances in medical care and assistive technologies have improved outlook and quality of life for affected individuals. Rehabilitation programs emphasizing physical therapy, adaptive equipment, and psychological support contribute to increased independence and community participation. Individual prognosis depends on the injury level and severity, with ongoing research in neuroregeneration and functional electrical stimulation offering promising pathways for enhanced recovery and life satisfaction.
Tetraplegia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com