Pharmaceutics focuses on the design, formulation, and delivery of medications to ensure their safety, efficacy, and patient compliance. Understanding the principles of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion is crucial for developing effective pharmaceutical products. Explore the rest of the article to discover how pharmaceutics transforms scientific knowledge into life-saving therapies tailored for your health needs.
Table of Comparison
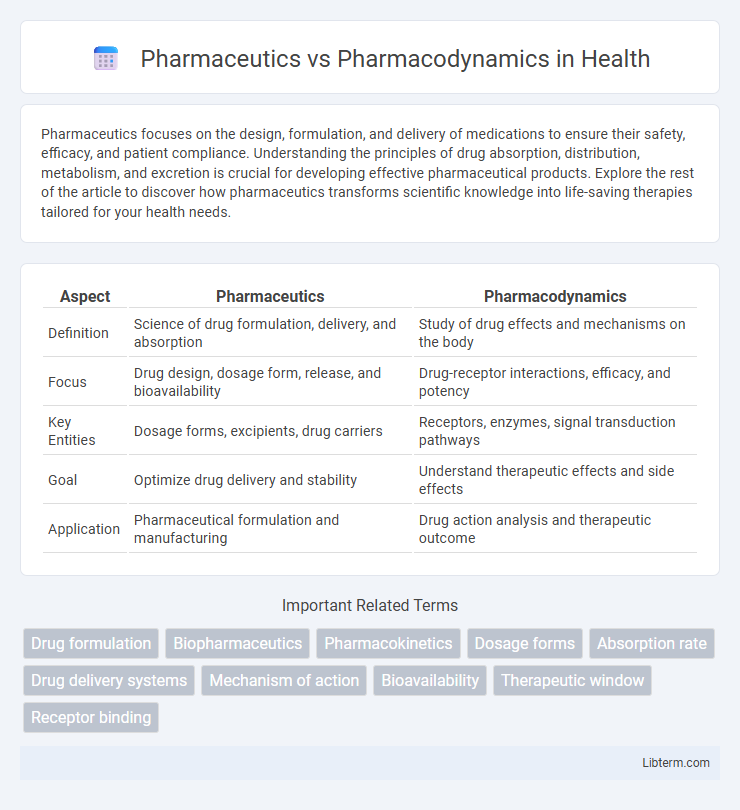
| Aspect | Pharmaceutics | Pharmacodynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Science of drug formulation, delivery, and absorption | Study of drug effects and mechanisms on the body |
| Focus | Drug design, dosage form, release, and bioavailability | Drug-receptor interactions, efficacy, and potency |
| Key Entities | Dosage forms, excipients, drug carriers | Receptors, enzymes, signal transduction pathways |
| Goal | Optimize drug delivery and stability | Understand therapeutic effects and side effects |
| Application | Pharmaceutical formulation and manufacturing | Drug action analysis and therapeutic outcome |
Introduction to Pharmaceutics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmaceutics involves the formulation, design, and delivery of drugs, focusing on the physical and chemical properties that affect drug absorption and bioavailability. Pharmacodynamics studies how drugs interact with biological targets to produce therapeutic effects, emphasizing mechanisms of action, receptor binding, and dose-response relationships. Understanding pharmaceutics is crucial for optimizing drug delivery systems, while pharmacodynamics provides insight into the drug's efficacy and safety profiles.
Defining Pharmaceutics
Pharmaceutics is the science of designing, formulating, and manufacturing drug delivery systems to ensure optimal therapeutic efficacy and patient safety. It encompasses drug formulation, dosage form design, and the controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredients to achieve desired absorption and bioavailability. In contrast, pharmacodynamics studies the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body and their mechanisms of action.
Understanding Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics explores how drugs interact with biological receptors to produce therapeutic effects and side effects by analyzing dose-response relationships and mechanisms of action. Understanding pharmacodynamics is crucial for predicting drug efficacy, optimizing dosing regimens, and minimizing adverse reactions. This field integrates receptor binding, signal transduction, and physiological responses, distinguishing it from pharmaceutics, which concentrates on drug formulation and delivery.
Key Differences between Pharmaceutics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmaceutics focuses on the formulation, preparation, and delivery of drugs, emphasizing drug dosage forms and their stability, absorption, and bioavailability. Pharmacodynamics studies the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, highlighting drug-receptor interactions and mechanisms of action. The key difference lies in pharmaceutics addressing how drugs are administered and absorbed, while pharmacodynamics analyzes what drugs do to the body at the molecular and systemic levels.
Role of Pharmaceutics in Drug Development
Pharmaceutics plays a crucial role in drug development by designing and formulating drug delivery systems that ensure optimal bioavailability, stability, and patient compliance. It involves the study of drug dosage forms, release mechanisms, and manufacturing processes to transform active pharmaceutical ingredients into safe and effective medications. This field bridges the gap between pharmacodynamics and clinical application by optimizing drug absorption and therapeutic efficacy.
Role of Pharmacodynamics in Clinical Practice
Pharmacodynamics plays a crucial role in clinical practice by elucidating the mechanisms through which drugs exert their effects on the body, including receptor interactions, dose-response relationships, and drug efficacy. Understanding pharmacodynamics enables clinicians to tailor drug therapy based on individual patient responses and optimize therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects. This knowledge guides dosage adjustments, drug selection, and monitoring strategies essential for personalized medicine and effective treatment protocols.
Interrelationship between Pharmaceutics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmaceutics involves the formulation and delivery of drugs, directly influencing the drug's bioavailability and absorption rate which are critical parameters for pharmacodynamics--the study of a drug's biochemical and physiological effects. The interrelationship between pharmaceutics and pharmacodynamics is evident as optimized drug formulation ensures proper drug concentration at the target site, thereby defining the onset, intensity, and duration of drug action. Understanding this connection allows for precise control over therapeutic outcomes and minimization of adverse effects.
Impact on Drug Efficacy and Safety
Pharmaceutics focuses on the formulation, delivery, and absorption of drugs, directly influencing drug bioavailability and ensuring consistent therapeutic levels for optimal efficacy and safety. Pharmacodynamics examines the drug's biochemical and physiological effects on the body, determining the drug's mechanism of action, potency, and receptor interactions that drive therapeutic outcomes and adverse effects. Understanding the interplay between pharmaceutics and pharmacodynamics is crucial for optimizing drug design, maximizing efficacy, and minimizing toxicity in clinical therapy.
Applications in Personalized Medicine
Pharmaceutics involves the formulation and delivery of drugs tailored to individual patients, optimizing therapeutic effectiveness and minimizing side effects through personalized dosage forms and controlled-release systems. Pharmacodynamics studies the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body, enabling the prediction of individual responses based on genetic, molecular, and cellular variations. Integrating pharmaceutics and pharmacodynamics enhances personalized medicine by ensuring precise drug targeting and efficacy, adjusted for patient-specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
Future Trends in Pharmaceutics and Pharmacodynamics
Future trends in pharmaceutics emphasize personalized medicine through advanced drug delivery systems such as nanotechnology and 3D printing, enhancing targeted therapy and controlled release. Pharmacodynamics is increasingly guided by computational modeling and biomarker identification to predict drug-receptor interactions and optimize therapeutic efficacy. Integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics accelerates drug discovery and individual response prediction in both fields.
Pharmaceutics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com