Diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy characterized by muscle stiffness and weakness primarily affecting both legs, leading to difficulties in walking and coordination. Treatment options focus on physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions to improve mobility and quality of life. Explore the full article to understand how different therapies can support your journey with diplegia.
Table of Comparison
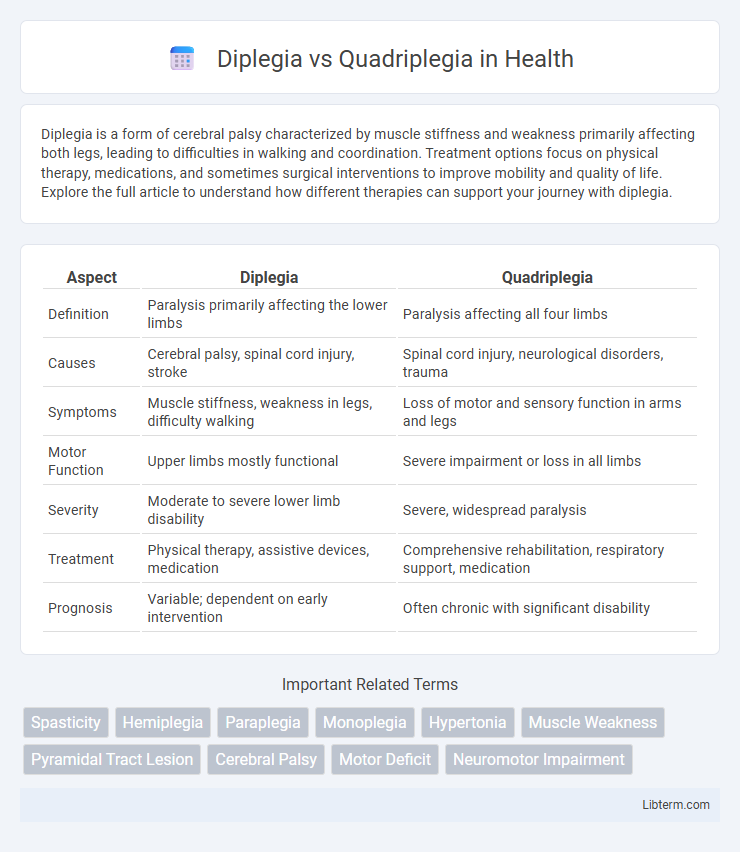
| Aspect | Diplegia | Quadriplegia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paralysis primarily affecting the lower limbs | Paralysis affecting all four limbs |
| Causes | Cerebral palsy, spinal cord injury, stroke | Spinal cord injury, neurological disorders, trauma |
| Symptoms | Muscle stiffness, weakness in legs, difficulty walking | Loss of motor and sensory function in arms and legs |
| Motor Function | Upper limbs mostly functional | Severe impairment or loss in all limbs |
| Severity | Moderate to severe lower limb disability | Severe, widespread paralysis |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, assistive devices, medication | Comprehensive rehabilitation, respiratory support, medication |
| Prognosis | Variable; dependent on early intervention | Often chronic with significant disability |
Understanding Diplegia: Definition and Overview
Diplegia is a form of cerebral palsy characterized by motor impairment predominantly affecting the lower limbs, resulting in muscle stiffness and difficulty with walking. Unlike quadriplegia, which impacts all four limbs and often includes trunk and facial muscles, diplegia primarily limits lower body movement while upper limbs maintain better function. Understanding diplegia involves recognizing its neurological basis in brain injury affecting motor control areas, typically leading to symmetrical muscle weakness and spasticity in the legs.
What is Quadriplegia? Key Characteristics
Quadriplegia, also known as tetraplegia, is a condition characterized by partial or complete paralysis of all four limbs and the torso, typically resulting from spinal cord injury or neurological disorders. Key characteristics include loss of motor function and sensation below the level of injury, impaired respiratory function, and reduced muscle control in both arms and legs. This condition often requires comprehensive medical management, including physical therapy, respiratory support, and adaptive devices to improve quality of life.
Causes of Diplegia and Quadriplegia
Diplegia primarily results from periventricular leukomalacia or prenatal brain injury affecting the motor cortex, frequently linked to prematurity and cerebral palsy. Quadriplegia is often caused by severe spinal cord injuries, traumatic brain injury, or neurological diseases leading to impairment in all four limbs. Both conditions involve disrupted neural pathways but differ significantly in the location and extent of motor function damage.
Differences in Affected Body Areas
Diplegia primarily affects the lower limbs, causing muscle stiffness or weakness predominantly in the legs, while the upper body remains largely unaffected or minimally impacted. Quadriplegia involves paralysis or significant impairment in all four limbs, including both arms and legs, often resulting from spinal cord injury or neurological conditions. The extent of motor function loss in quadriplegia is more widespread, affecting the body's ability to perform coordinated movements across multiple regions.
Symptoms: Diplegia vs Quadriplegia
Diplegia primarily affects symmetrical parts of the body, usually the legs, causing muscle stiffness, weakness, and difficulty walking, while the arms are less impaired or unaffected. Quadriplegia involves paralysis or severe weakness in all four limbs, both arms and legs, often accompanied by impaired trunk control and reduced respiratory function. The severity of motor dysfunction and sensory loss is generally more profound in quadriplegia compared to diplegia, impacting overall mobility and daily activities.
Diagnosis: Methods and Considerations
Diagnosis of diplegia and quadriplegia primarily involves clinical evaluation and neuroimaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans to identify brain or spinal cord abnormalities. Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies assist in assessing muscle and nerve function, while careful neurological examination helps differentiate the extent of limb involvement. Early and accurate diagnosis relies on detailed patient history, physical assessments, and the use of advanced imaging modalities to guide treatment planning.
Treatment and Therapy Options
Treatment for diplegia primarily involves physical therapy, occupational therapy, and muscle relaxants to improve motor function and reduce spasticity in the lower limbs. Quadriplegia therapy includes similar rehabilitation strategies but often requires more intensive respiratory support, assistive devices, and sometimes surgical interventions due to paralysis affecting all four limbs. Both conditions benefit from multidisciplinary approaches tailored to individual needs, emphasizing early intervention and continuous care for optimal outcomes.
Prognosis and Long-term Outcomes
Diplegia primarily affects the lower limbs and generally offers a more favorable prognosis with higher potential for mobility improvements through physical therapy, compared to quadriplegia which involves all four limbs and often results in more severe functional impairments. Long-term outcomes for diplegia include increased independence in ambulation and self-care, while quadriplegia patients frequently require comprehensive assistive devices and full-time care support. Early intervention and multidisciplinary rehabilitation play critical roles in optimizing neurodevelopmental progress and quality of life for both conditions.
Daily Living and Support Needs
Diplegia primarily affects the lower limbs, allowing individuals to retain greater upper body mobility, which facilitates more independence in daily activities such as eating, dressing, and personal hygiene. Quadriplegia involves paralysis of all four limbs and the torso, significantly increasing dependency on caregivers for most daily living tasks, including feeding, mobility, and personal care. Support needs for diplegia often focus on mobility aids like walkers or braces, while quadriplegia requires comprehensive assistance including wheelchair use, specialized medical care, and extensive adaptive equipment.
Coping Strategies and Resources
Coping strategies for diplegia and quadriplegia emphasize physical therapy, assistive technologies, and psychological support tailored to the severity of motor impairments. Resources such as occupational therapy, adaptive equipment, and specialized rehabilitation centers enhance mobility and independence for both conditions. Peer support groups and counseling services provide essential emotional resilience and community connection for individuals managing these forms of cerebral palsy.
Diplegia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com