Balance is essential for maintaining physical stability and preventing injuries during daily activities or exercise. Your core strength and coordination play crucial roles in achieving better balance and overall body control. Discover effective tips to improve your balance and enhance your wellbeing in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
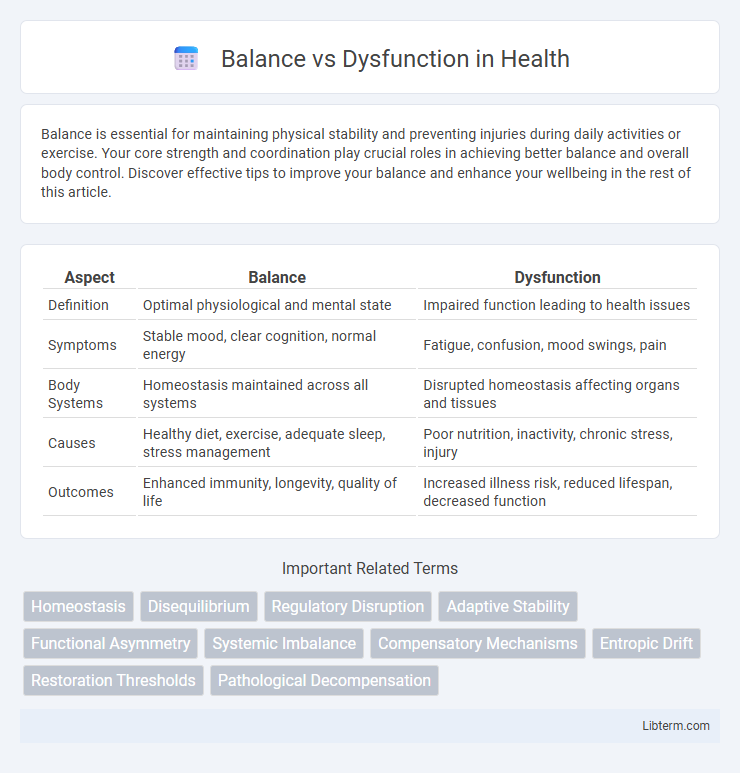
| Aspect | Balance | Dysfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimal physiological and mental state | Impaired function leading to health issues |
| Symptoms | Stable mood, clear cognition, normal energy | Fatigue, confusion, mood swings, pain |
| Body Systems | Homeostasis maintained across all systems | Disrupted homeostasis affecting organs and tissues |
| Causes | Healthy diet, exercise, adequate sleep, stress management | Poor nutrition, inactivity, chronic stress, injury |
| Outcomes | Enhanced immunity, longevity, quality of life | Increased illness risk, reduced lifespan, decreased function |
Understanding Balance and Dysfunction
Balance in biological systems refers to the optimal state where physiological processes function harmoniously, maintaining homeostasis necessary for health. Dysfunction occurs when this balance is disrupted, leading to impaired cellular or organ function and potential disease development. Understanding the mechanisms of balance and dysfunction is crucial for diagnosing conditions and designing effective therapeutic interventions.
The Importance of Balance in Daily Life
Maintaining balance in daily life is crucial for overall well-being, as it promotes physical health, mental clarity, and emotional stability. Imbalance often leads to dysfunction, manifesting as stress, fatigue, and decreased productivity. Prioritizing balance through proper nutrition, regular exercise, and restful sleep enhances resilience and supports optimal functioning.
Signs and Symptoms of Dysfunction
Dysfunction is characterized by signs such as chronic fatigue, persistent pain, hormonal imbalances, and impaired cognitive function, indicating that the body's natural balance is disrupted. Symptoms often include irregular sleep patterns, mood instability, digestive issues, and decreased immune response, reflecting systemic stress and breakdown in homeostasis. Identifying these clinical manifestations early helps target interventions that restore physiological equilibrium and prevent progression to more severe conditions.
Causes of Imbalance in the Mind and Body
Stress, poor nutrition, and lack of sleep are primary causes of imbalance in the mind and body, disrupting hormonal and neural regulation. Chronic inflammation and sedentary lifestyle contribute to dysfunction by impairing immune response and decreasing physical resilience. Mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression further exacerbate the imbalance by altering neurotransmitter levels and cognitive processes.
Physical Health: Balance vs Dysfunction
Maintaining physical balance is crucial for preventing dysfunction in musculoskeletal and neurological health, as impaired balance often leads to increased risk of falls and chronic pain conditions. Dysfunction in physical health manifests through symptoms such as muscle weakness, joint instability, and reduced proprioception, which impede mobility and overall functionality. Effective interventions include targeted physical therapy and balance training exercises that enhance neuromuscular control and restore functional stability.
Emotional Well-being: Maintaining Stability
Emotional well-being thrives on a balanced state where stress levels are managed, and positive coping mechanisms are reinforced, supporting mental stability and resilience. Dysfunction often arises from chronic emotional imbalance, leading to anxiety, depression, and impaired decision-making that disrupt daily functioning. Consistent emotional regulation fosters psychological health, enhancing life satisfaction and overall stability.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Balance
Lifestyle choices directly influence the body's ability to maintain balance by affecting muscle strength, coordination, and sensory perception. Poor habits such as sedentary behavior, inadequate nutrition, and lack of sleep contribute to dysfunction in the vestibular system and proprioception, increasing the risk of falls and injuries. Conversely, regular physical activity, proper hydration, and a balanced diet enhance neuromuscular control and postural stability, promoting overall balance and reducing dysfunction.
Strategies to Restore Balance
Restoring balance in biological or psychological systems involves targeted strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness practices, and nutritional adjustments that enhance homeostasis and reduce dysfunction symptoms. Neuroplasticity-based interventions and hormone regulation therapies also play critical roles in reestablishing optimal functioning by correcting imbalances in neural pathways and endocrine responses. Implementing personalized treatment plans that integrate these approaches increases the likelihood of sustained recovery and improved systemic equilibrium.
Consequences of Prolonged Dysfunction
Prolonged dysfunction in biological systems disrupts homeostasis, leading to chronic inflammation, impaired organ function, and increased susceptibility to diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disorders. Cellular imbalances cause oxidative stress, DNA damage, and metabolic disturbances that accelerate aging and reduce overall physiological resilience. Persistent imbalance also compromises immune responses, resulting in a higher risk of infections and prolonged recovery periods.
Achieving Lasting Balance for Optimal Health
Achieving lasting balance in health involves harmonizing physical, mental, and emotional well-being through consistent lifestyle choices such as proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management. Dysfunction arises when one or more of these components are neglected, leading to chronic conditions like inflammation, hormonal imbalances, or mental health disorders. Integrating holistic practices and personalized interventions promotes optimal health by restoring equilibrium and preventing long-term disease progression.
Balance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com