Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, commonly in a fallopian tube, posing serious health risks. Early detection through symptoms like abdominal pain and bleeding is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications. Discover more about ectopic pregnancy symptoms, causes, and management in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
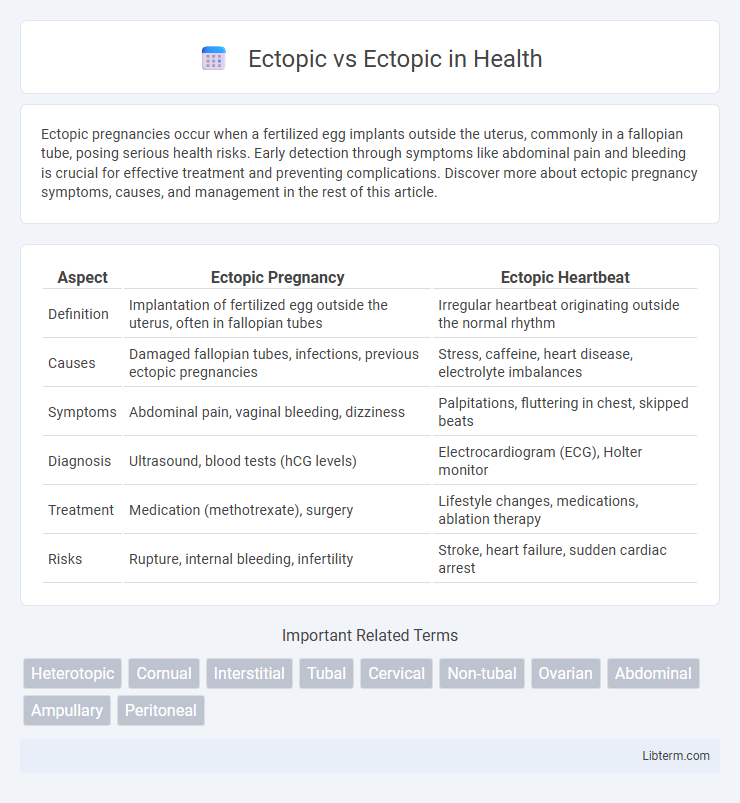
| Aspect | Ectopic Pregnancy | Ectopic Heartbeat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Implantation of fertilized egg outside the uterus, often in fallopian tubes | Irregular heartbeat originating outside the normal rhythm |
| Causes | Damaged fallopian tubes, infections, previous ectopic pregnancies | Stress, caffeine, heart disease, electrolyte imbalances |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, dizziness | Palpitations, fluttering in chest, skipped beats |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, blood tests (hCG levels) | Electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor |
| Treatment | Medication (methotrexate), surgery | Lifestyle changes, medications, ablation therapy |
| Risks | Rupture, internal bleeding, infertility | Stroke, heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest |
Understanding the Term: What Does "Ectopic" Mean?
Ectopic refers to the abnormal location of an organ or tissue outside its usual position, commonly used in medical contexts such as ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. Understanding ectopic is crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions like ectopic thyroid, ectopic kidney, or ectopic hormone secretion, which can lead to significant clinical implications. The term highlights displacement from normal anatomical sites, emphasizing the importance of identifying ectopic occurrences for effective treatment and prognosis.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Definition and Overview
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most commonly in the fallopian tubes, leading to a potentially life-threatening condition. Early diagnosis through transvaginal ultrasound and serum hCG levels is critical for managing ectopic pregnancies and preventing complications like tubal rupture. Treatment options include medical management with methotrexate or surgical intervention, depending on the gestational age and patient stability.
Ectopic Beats: Cardiac Context of "Ectopic
Ectopic beats are premature heartbeats originating from abnormal electrical impulses outside the sinoatrial node, disrupting the normal cardiac rhythm. These beats often occur in the atria or ventricles and can be detected through electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, indicating underlying cardiac irritability or stress. Understanding ectopic beats is crucial for diagnosing arrhythmias such as premature atrial contractions (PACs) or premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), which may signify heart disease or electrolyte imbalances.
Key Differences: Ectopic Pregnancy vs. Ectopic Heartbeat
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube, posing serious health risks and requiring immediate medical attention. An ectopic heartbeat refers to an irregular or premature heartbeat originating outside the heart's normal rhythm, often detected through ECG and typically less urgent but monitored for cardiac health. The key differences lie in ectopic pregnancy being a reproductive complication with surgical implications, while an ectopic heartbeat involves cardiac arrhythmia and is managed through cardiological evaluation and treatment.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most commonly in the fallopian tubes, causing significant health risks. Causes include damaged or blocked fallopian tubes due to pelvic inflammatory disease, previous surgeries, or endometriosis, which hinder the egg's movement to the uterus. Other risk factors involve hormonal imbalances, assisted reproductive technologies, and smoking, which can impair tubal function and increase ectopic pregnancy chances.
Causes of Ectopic Heartbeats
Ectopic heartbeats occur due to abnormal electrical impulses originating outside the heart's normal pacemaker, often triggered by stress, caffeine, or electrolyte imbalances. Causes include underlying heart conditions like ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, or inflammation such as myocarditis. Other contributors are stimulants, hormonal changes, and structural heart abnormalities that disrupt normal rhythm.
Symptoms: How Ectopic Conditions Present
Ectopic conditions primarily manifest through localized pain, abnormal bleeding, or swelling depending on the affected site, such as the fallopian tubes or thyroid gland. Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy often include sharp pelvic pain, vaginal spotting, and dizziness, signaling possible internal bleeding. In contrast, ectopic thyroid tissue may present as a painless neck mass or dysphagia, with few systemic symptoms but potential hormonal imbalances.
Risks and Complications of Ectopic Manifestations
Ectopic manifestations, particularly ectopic pregnancies, pose significant risks including tubal rupture, severe hemorrhage, and potential infertility if not promptly diagnosed. Complications can escalate to life-threatening internal bleeding and shock, necessitating urgent medical intervention. Early detection through ultrasound and beta-hCG monitoring is critical to prevent these severe outcomes.
Diagnostic Methods for Ectopic Conditions
Diagnostic methods for ectopic conditions primarily include transvaginal ultrasound, which offers high-resolution imaging to locate ectopic pregnancies within the fallopian tubes or other abnormal sites. Serum beta-hCG levels are measured quantitatively to differentiate between viable intrauterine pregnancies and ectopic gestations, often showing slower-than-expected rise or plateau. Laparoscopy remains the gold standard for definitive diagnosis and treatment in uncertain cases, allowing direct visualization and management of ectopic tissues.
Treatment and Management: Comparing Approaches
Treatment and management of ectopic pregnancy primarily involve medication with methotrexate or surgical intervention such as laparoscopy to remove the ectopic tissue. In contrast, an ectopic beat, a premature cardiac contraction, is typically managed with lifestyle changes, beta-blockers, or antiarrhythmic drugs depending on symptom severity and underlying cardiac health. Accurate diagnosis using ultrasound imaging or electrocardiograms is crucial to tailor treatment approaches effectively for these distinct medical conditions.
Ectopic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com