Empyema and abscess are both collections of pus but differ significantly in location and treatment approach. Empyema refers specifically to pus accumulation within a naturally existing body cavity, such as the pleural space around the lungs, while an abscess forms in tissue or organs, creating a localized infection. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective management, so continue reading to learn how to recognize and treat each condition appropriately.
Table of Comparison
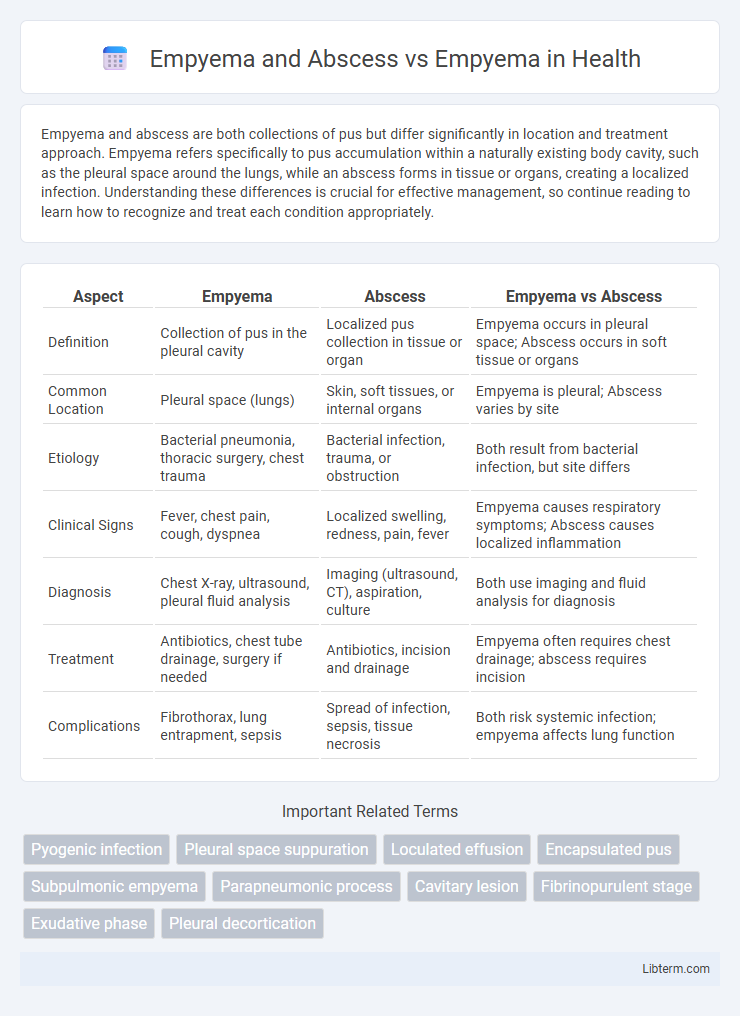
| Aspect | Empyema | Abscess | Empyema vs Abscess |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collection of pus in the pleural cavity | Localized pus collection in tissue or organ | Empyema occurs in pleural space; Abscess occurs in soft tissue or organs |
| Common Location | Pleural space (lungs) | Skin, soft tissues, or internal organs | Empyema is pleural; Abscess varies by site |
| Etiology | Bacterial pneumonia, thoracic surgery, chest trauma | Bacterial infection, trauma, or obstruction | Both result from bacterial infection, but site differs |
| Clinical Signs | Fever, chest pain, cough, dyspnea | Localized swelling, redness, pain, fever | Empyema causes respiratory symptoms; Abscess causes localized inflammation |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, ultrasound, pleural fluid analysis | Imaging (ultrasound, CT), aspiration, culture | Both use imaging and fluid analysis for diagnosis |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, chest tube drainage, surgery if needed | Antibiotics, incision and drainage | Empyema often requires chest drainage; abscess requires incision |
| Complications | Fibrothorax, lung entrapment, sepsis | Spread of infection, sepsis, tissue necrosis | Both risk systemic infection; empyema affects lung function |
Understanding Empyema: Definition and Causes
Empyema refers to the accumulation of pus within a naturally existing anatomical cavity, most commonly the pleural space surrounding the lungs, resulting from infections such as bacterial pneumonia or thoracic surgery complications. Unlike an abscess, which is a localized collection of pus in a newly formed cavity within tissue, empyema occurs in pre-formed spaces and often requires chest tube drainage or surgical intervention. Key causes include bacterial infections like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus, which trigger inflammation and pus accumulation in the pleural cavity.
What is an Abscess? Key Differences from Empyema
An abscess is a localized collection of pus within tissues, often caused by bacterial infection, characterized by swelling, redness, and pain. Unlike empyema, which specifically refers to pus accumulation within a body cavity such as the pleural space, abscesses are confined to soft tissues or organs. The key difference lies in the anatomical location and the presence of a well-defined capsule in abscesses, whereas empyemas are typically associated with infected fluid collections in natural body cavities.
Empyema vs Abscess: Clinical Presentation
Empyema typically presents with pleuritic chest pain, fever, and productive cough, often following pneumonia, whereas abscess presents as a localized collection of pus with swelling, redness, and tenderness in soft tissues or organs. In empyema, imaging shows pleural fluid accumulation with loculations, while abscess imaging reveals a well-defined fluid-filled cavity within the affected tissue. Laboratory findings in empyema often demonstrate elevated inflammatory markers and positive pleural fluid cultures, contrasting with abscesses that usually yield pus cultures from the involved site.
Pathophysiology: Empyema Compared to Abscess
Empyema involves the accumulation of pus within a naturally existing anatomical cavity, such as the pleural space, whereas an abscess is a localized collection of pus in newly formed tissue resulting from infection. The pathophysiology of empyema includes persistent inflammation of the pleural membranes, leading to fibrin deposition, pleural thickening, and potential septation, which impairs lung expansion. In contrast, abscess formation is characterized by necrosis of tissue, encapsulation by a fibrous capsule, and localized immune response aimed at containing the infection.
Diagnosis: Differentiating Empyema and Abscess
Diagnosis of empyema primarily relies on imaging techniques such as chest X-ray, ultrasound, and computed tomography (CT) to detect pus accumulation in the pleural space, while abscess diagnosis often involves CT or MRI to identify localized pus collections within tissue. Thoracentesis with fluid analysis confirms empyema by revealing purulent fluid and positive microbial cultures, whereas abscesses require biopsy or aspiration to differentiate from other masses. Precise differentiation is crucial as empyema involves pleural infection requiring drainage and antibiotics, whereas abscesses may necessitate surgical intervention depending on location and severity.
Imaging Features: Empyema versus Abscess
Empyema typically presents on imaging as a lentiform, pleural-based collection with split pleura sign and smooth inner margins, often causing adjacent lung compression, while abscesses appear as rounded, thick-walled cavities within lung parenchyma featuring central necrosis and air-fluid levels. Contrast-enhanced CT distinguishes empyema by peripheral rim enhancement and loculated fluid, whereas abscesses show more irregular, thick walls with possible surrounding consolidation. Ultrasound aids in detecting septations within empyema, contrasting with the more homogeneous fluid content generally seen in abscesses.
Treatment Strategies: Empyema and Abscess
Treatment strategies for empyema and abscess differ based on the infection's location and severity; empyema often requires chest tube drainage combined with targeted antibiotics to evacuate pus from the pleural space. In contrast, abscess management typically involves incision and drainage alongside systemic antimicrobial therapy to control localized purulent collections. Both conditions demand prompt intervention to prevent complications such as sepsis or tissue necrosis.
Complications: Empyema vs Abscess
Empyema involves the accumulation of pus within a naturally existing anatomical cavity, such as the pleural space, leading to complications like pleural thickening, fibrosis, and potential lung entrapment. In contrast, an abscess represents a localized pus collection within tissue, often causing tissue necrosis, systemic sepsis, and fistula formation if untreated. Empyema complications frequently include respiratory distress and impaired lung function, whereas abscess complications typically involve localized tissue destruction and potential spread of infection to adjacent structures.
Prognosis and Outcomes: Comparative Analysis
Empyema typically involves pus accumulation within a pleural cavity, leading to more severe respiratory complications and requiring prompt drainage and antibiotics, whereas abscesses can occur in various tissues with variable prognosis depending on location and treatment. Prognosis for empyema worsens with delayed intervention, often resulting in prolonged hospitalization, pleural thickening, or chronic lung impairment, while abscess outcomes improve significantly with timely surgical or percutaneous drainage combined with targeted antimicrobial therapy. Comparative analyses indicate that empyema carries a higher risk of morbidity and mortality than localized abscesses due to systemic infection potential and respiratory compromise.
Prevention and Risk Factors: Empyema and Abscess
Empyema and abscess both involve localized collections of pus caused by bacterial infections, with empyema specifically referring to pus accumulation in body cavities such as the pleural space, while abscesses occur in tissues. Prevention focuses on timely treatment of infections like pneumonia or skin infections, maintaining good hygiene, and managing underlying conditions such as diabetes or immunosuppression that increase susceptibility. Risk factors for empyema include respiratory infections, thoracic surgery, and trauma, whereas abscess risk factors prominently include skin breaches, poor wound care, and intravenous drug use.
Empyema and Abscess Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com