Migraine is a neurological condition characterized by intense, pulsating headaches often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light, and visual disturbances. Understanding the triggers and effective treatment options can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the frequency of attacks. Discover comprehensive strategies and insights to manage migraines in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
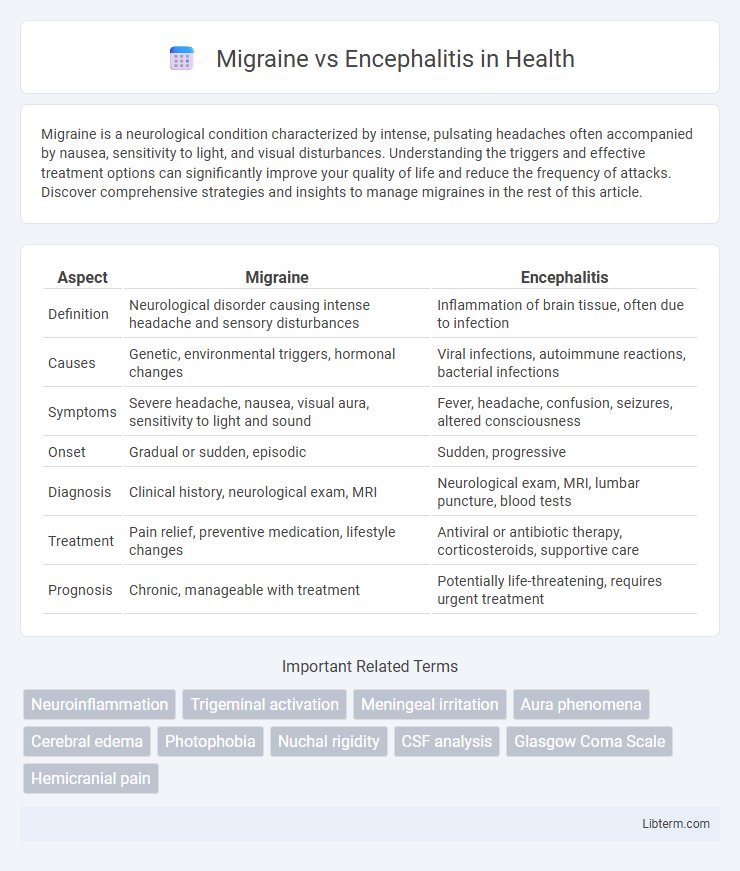
| Aspect | Migraine | Encephalitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Neurological disorder causing intense headache and sensory disturbances | Inflammation of brain tissue, often due to infection |
| Causes | Genetic, environmental triggers, hormonal changes | Viral infections, autoimmune reactions, bacterial infections |
| Symptoms | Severe headache, nausea, visual aura, sensitivity to light and sound | Fever, headache, confusion, seizures, altered consciousness |
| Onset | Gradual or sudden, episodic | Sudden, progressive |
| Diagnosis | Clinical history, neurological exam, MRI | Neurological exam, MRI, lumbar puncture, blood tests |
| Treatment | Pain relief, preventive medication, lifestyle changes | Antiviral or antibiotic therapy, corticosteroids, supportive care |
| Prognosis | Chronic, manageable with treatment | Potentially life-threatening, requires urgent treatment |
Introduction to Migraine and Encephalitis
Migraine is a neurological disorder characterized by intense, recurrent headaches often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light, and visual disturbances. Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain tissue, usually caused by viral infections, leading to symptoms such as fever, headache, confusion, and seizures. Differentiating between migraine and encephalitis is critical because encephalitis can cause serious neurological damage without prompt treatment.
Definitions and Key Differences
Migraine is a neurological disorder characterized by intense, recurring headaches often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound, while encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain typically caused by viral infections leading to symptoms like fever, confusion, seizures, and altered consciousness. Migraines primarily involve episodic pain and sensory disturbances without infection, whereas encephalitis presents with acute neurological dysfunction due to brain tissue inflammation. Diagnosis of migraine relies on clinical history and symptom patterns, but encephalitis requires imaging and cerebrospinal fluid analysis to detect inflammation and potential infectious causes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Migraine is primarily caused by genetic and environmental factors influencing brain activity and blood vessel regulation, often triggered by stress, hormonal changes, or certain foods. Encephalitis results from viral infections, autoimmune responses, or bacterial infections leading to brain inflammation. Risk factors for migraine include family history and hormonal fluctuations, while encephalitis risk increases with exposure to infectious agents, compromised immune systems, and age extremes.
Common Symptoms Comparison
Migraine and encephalitis both present with severe headaches, but migraine headaches are often accompanied by visual disturbances, nausea, and sensitivity to light or sound, whereas encephalitis symptoms typically include fever, confusion, seizures, and neurological deficits. Common symptoms such as headache and fatigue overlap, though encephalitis usually involves more acute cognitive impairment and altered consciousness. Differentiating these conditions relies on identifying signs of infection and inflammation in encephalitis versus the recurrent, episodic nature and aura often seen in migraines.
Diagnosis: Methods and Challenges
Diagnosing migraine versus encephalitis involves distinct clinical evaluations and diagnostic tools, with migraines primarily identified through patient history and symptom patterns including unilateral headache, nausea, and photophobia, while encephalitis requires neuroimaging such as MRI, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis via lumbar puncture, and sometimes EEG to detect brain inflammation. Challenges arise due to overlapping symptoms like headache, fever, and neurological deficits, complicating differentiation without advanced testing. Timely, accurate diagnosis is critical as encephalitis demands urgent treatment to prevent severe neurological damage, whereas migraine management focuses on symptomatic relief and prevention.
Treatment Options for Migraine
Migraine treatment primarily involves analgesics such as NSAIDs and triptans to alleviate pain and prevent migraine attacks, while lifestyle modifications including stress management and regular sleep patterns play key roles in reducing frequency. Preventive medications like beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, and CGRP inhibitors are prescribed for chronic or severe migraine cases to decrease attack intensity and duration. Unlike encephalitis, which requires antiviral or antibiotic therapies targeting infection and often necessitates hospitalization, migraine management is largely outpatient and symptom-focused.
Treatment Options for Encephalitis
Encephalitis treatment primarily involves antiviral or antibiotic medications depending on the underlying cause, with acyclovir commonly prescribed for herpes simplex virus encephalitis. Supportive care such as corticosteroids to reduce brain inflammation, anticonvulsants for seizure management, and intensive care monitoring are critical components. Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment significantly improve outcomes, contrasting with migraine treatments that focus mainly on pain relief and prevention through medications like triptans or beta-blockers.
Prognosis and Possible Complications
Migraine typically has a favorable prognosis with proper management, although frequent attacks can impact quality of life and may lead to chronic migraine or medication overuse headache. Encephalitis carries a more serious prognosis due to potential brain inflammation, which can result in complications like seizures, cognitive impairment, neurological deficits, or even death if untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in encephalitis to reduce the risk of long-term sequelae, whereas migraine complications are generally less severe but can significantly affect daily functioning.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention for encephalitis if symptoms include high fever, severe headache, confusion, seizures, or loss of consciousness, as these indicate potentially life-threatening brain inflammation requiring urgent treatment. Migraines, while extremely painful and debilitating, typically warrant medical evaluation if headaches suddenly become more severe, frequent, or are accompanied by neurological deficits such as vision loss, weakness, or speech difficulties. Differentiating between migraine and encephalitis symptoms is crucial; encephalitis often presents with systemic signs of infection and altered mental status, whereas migraines commonly involve recurrent unilateral headaches with photophobia and nausea.
Prevention and Lifestyle Management
Preventing migraines involves identifying and avoiding individual triggers such as stress, certain foods, and irregular sleep patterns, while maintaining a consistent daily routine and staying hydrated. Encephalitis prevention centers on reducing risks of infections through vaccinations, proper hygiene, and avoiding vectors like mosquitoes. Lifestyle management for migraines includes regular exercise, balanced diet, and stress management techniques, whereas encephalitis requires prompt medical treatment and supportive care to minimize neurological damage.
Migraine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com