Bursitis is the inflammation of the small fluid-filled sacs called bursae that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near your joints, causing pain and swelling. Commonly affecting the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees, it often results from repetitive motions or prolonged pressure on the joints. Discover effective treatments and prevention tips by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
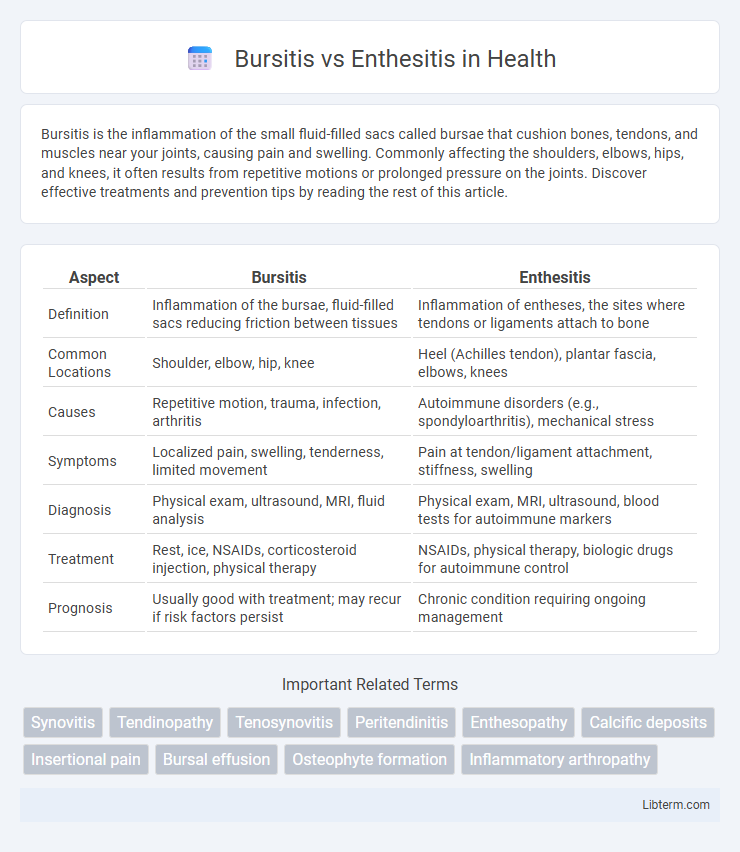
| Aspect | Bursitis | Enthesitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs reducing friction between tissues | Inflammation of entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments attach to bone |
| Common Locations | Shoulder, elbow, hip, knee | Heel (Achilles tendon), plantar fascia, elbows, knees |
| Causes | Repetitive motion, trauma, infection, arthritis | Autoimmune disorders (e.g., spondyloarthritis), mechanical stress |
| Symptoms | Localized pain, swelling, tenderness, limited movement | Pain at tendon/ligament attachment, stiffness, swelling |
| Diagnosis | Physical exam, ultrasound, MRI, fluid analysis | Physical exam, MRI, ultrasound, blood tests for autoimmune markers |
| Treatment | Rest, ice, NSAIDs, corticosteroid injection, physical therapy | NSAIDs, physical therapy, biologic drugs for autoimmune control |
| Prognosis | Usually good with treatment; may recur if risk factors persist | Chronic condition requiring ongoing management |
Understanding Bursitis and Enthesitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints, primarily causing pain and swelling in areas such as the shoulders, elbows, and hips. Enthesitis refers to inflammation at the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, commonly associated with conditions like ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Understanding the distinct anatomical locations and typical symptoms of bursitis and enthesitis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, as bursitis involves fluid-filled sacs while enthesitis affects connective tissue insertion points.
Key Differences Between Bursitis and Enthesitis
Bursitis is inflammation of the bursae, the small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints, commonly causing localized pain and swelling, especially in the shoulders, hips, and knees. Enthesitis involves inflammation at the entheses, the sites where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, frequently associated with spondyloarthropathies and often manifesting as pain at tendon insertions like the Achilles tendon or plantar fascia. The key differences lie in their anatomical locations--bursae versus entheses--and their typical clinical contexts, with bursitis often resulting from repetitive motion or trauma, while enthesitis is linked to autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Causes of Bursitis
Bursitis is primarily caused by repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on a joint, leading to inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. Common causes include overuse injuries from activities such as running or gardening, trauma from a direct blow, and underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or infection. Unlike enthesitis, which involves inflammation at tendon or ligament attachment sites, bursitis specifically affects the bursa, resulting in localized pain and swelling.
Causes of Enthesitis
Enthesitis primarily results from inflammation at the entheses, where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, often triggered by autoimmune conditions such as psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. Mechanical stress and repetitive trauma can also contribute to the development of enthesitis by causing microdamage to the connective tissue. Unlike bursitis, which involves inflammation of fluid-filled sacs cushioning joints, enthesitis specifically targets the tendon-bone junction, leading to localized pain and stiffness.
Symptoms Comparison: Bursitis vs Enthesitis
Bursitis presents with localized pain, swelling, and tenderness around the affected bursa, often exacerbated by joint movement or pressure. Enthesitis is characterized by pain and stiffness at the site where tendons or ligaments attach to the bone, frequently accompanied by swelling and reduced mobility in adjacent joints. While both conditions involve inflammation, bursitis symptoms primarily affect bursae near joints, whereas enthesitis specifically targets entheses, leading to distinct patterns of discomfort and functional limitation.
Diagnosis: Bursitis vs Enthesitis
Bursitis diagnosis involves clinical evaluation of localized pain, swelling, and tenderness near joints, supported by imaging techniques such as ultrasound or MRI to detect inflamed bursae. Enthesitis diagnosis relies on physical examination for pain at tendon or ligament insertions, with ultrasound revealing thickening or erosions and MRI showing bone marrow edema at entheses. Laboratory tests may assist in differentiating inflammatory causes, particularly in enthesitis associated with spondyloarthropathies.
Treatment Options for Bursitis
Bursitis treatment primarily includes rest, ice application, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation and pain. Physical therapy and corticosteroid injections may be recommended for persistent cases to improve mobility and further decrease inflammation. Severe or chronic bursitis could require aspiration or surgical intervention to remove the inflamed bursa.
Treatment Options for Enthesitis
Enthesitis treatment primarily involves nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation at tendon or ligament insertion sites. Physical therapy is crucial for maintaining joint flexibility and strengthening surrounding muscles, while corticosteroid injections may be used in severe cases to provide targeted relief. Biologic therapies, such as TNF inhibitors, are effective for chronic or autoimmune-related enthesitis, particularly in conditions like psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
Prevention Strategies for Both Conditions
Preventing bursitis involves minimizing repetitive joint stress and ensuring proper ergonomics during physical activities, alongside regular stretching and strengthening exercises. Enthesitis prevention emphasizes managing underlying inflammatory conditions like spondyloarthritis through medication and maintaining joint flexibility with targeted physical therapy. Both conditions benefit from weight management to reduce joint load and avoiding prolonged immobilization to preserve joint function.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for bursitis if you experience severe pain, swelling, redness, or limited joint movement, especially when symptoms persist beyond a few days or worsen rapidly. For enthesitis, consult a healthcare professional if localized tenderness, stiffness, or inflammation around tendon or ligament attachment sites does not improve with rest or over-the-counter treatments, or if it is associated with underlying conditions like spondyloarthritis. Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent complications and improve outcomes for both bursitis and enthesitis.
Bursitis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com