Hepatostasis refers to the medical condition where the liver's blood flow is significantly reduced or obstructed, leading to impaired liver function. This condition can result from various causes such as liver congestion, thrombosis, or external compression of hepatic vessels. Discover detailed information on the causes, symptoms, and treatment options of hepatostasis in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
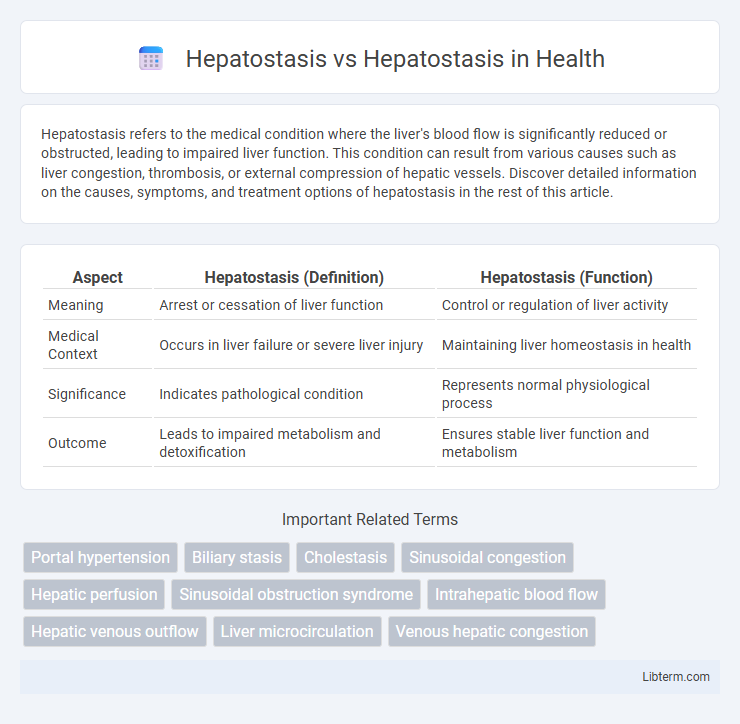
| Aspect | Hepatostasis (Definition) | Hepatostasis (Function) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Arrest or cessation of liver function | Control or regulation of liver activity |
| Medical Context | Occurs in liver failure or severe liver injury | Maintaining liver homeostasis in health |
| Significance | Indicates pathological condition | Represents normal physiological process |
| Outcome | Leads to impaired metabolism and detoxification | Ensures stable liver function and metabolism |
Understanding Hepatostasis: Definition and Overview
Hepatostasis refers to the process of maintaining liver function and preventing liver cell damage through various physiological mechanisms. It involves the regulation of liver enzymes, bile production, and detoxification pathways, ensuring metabolic homeostasis within hepatic tissues. Understanding hepatostasis is crucial for diagnosing and managing liver diseases, as disruptions can lead to conditions such as fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Common Causes of Hepatostasis
Hepatostasis, often confused with hepatostasis, primarily refers to the stagnation of bile flow within the liver, leading to conditions such as cholestasis. Common causes of hepatostasis include viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and drug-induced liver injury, which disrupt normal liver function and bile secretion. Understanding these etiologies is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment of liver function disorders.
Signs and Symptoms of Hepatostasis
Hepatostasis is characterized by impaired bile flow leading to symptoms such as jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, and pruritus due to bile salt accumulation. Patients may also experience right upper quadrant abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, and fatigue as liver function becomes compromised. Laboratory findings typically include elevated serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase levels indicating cholestasis.
Hepatostasis Diagnosis: Key Methods and Tools
Hepatostasis diagnosis relies on advanced imaging techniques such as ultrasound elastography and liver biopsy to assess liver stiffness and fibrosis accurately. Blood tests measuring liver enzymes, bilirubin levels, and coagulation profiles provide essential data for identifying hepatostasis severity. Emerging tools like transient elastography and magnetic resonance elastography enhance non-invasive evaluation, enabling precise monitoring of disease progression.
Hepatostasis vs. Hepatostasis: Exploring the Confusion
Hepatostasis and hepatostasis are often mistakenly used interchangeably despite their distinct meanings in medical terminology; hepatostasis refers to the cessation or suppression of liver function, while hepatostasis is a non-standard term sometimes confused with hepatostasis or misused in clinical contexts. This confusion arises due to the similarity in spelling and pronunciation, leading to potential miscommunication in diagnosis and treatment plans. Clear differentiation based on clinical context and accurate terminology improves understanding and patient care in hepatology.
Pathophysiology: How Hepatostasis Impacts Liver Function
Hepatostasis refers to the maintenance of liver cell stability, crucial for optimal hepatic metabolism, detoxification, and regeneration processes. Disruption in hepatostasis leads to impaired hepatocyte function, resulting in accumulation of toxins, altered bile secretion, and compromised synthesis of essential proteins such as albumin and clotting factors. Understanding the pathophysiology of hepatostasis highlights its impact on liver homeostasis, underscoring the importance of cellular repair mechanisms and inflammatory responses in preserving liver function and preventing chronic liver diseases.
Treatment Approaches for Hepatostasis
Treatment approaches for hepatostasis focus on restoring normal liver function by addressing underlying causes such as bile duct obstruction or hepatic inflammation. Therapies may include bile acid sequestrants, ursodeoxycholic acid, and interventions like endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to alleviate bile flow. Supportive care emphasizes maintaining liver health through dietary modifications and managing symptoms to prevent progression to liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Preventive Strategies for Hepatostasis
Preventive strategies for hepatostasis primarily involve maintaining liver health through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption to reduce the risk of liver congestion and impaired bile flow. Incorporating antioxidants, such as vitamins E and C, and promoting hydration support liver detoxification processes essential for preventing hepatostasis. Regular medical check-ups to monitor liver function and early intervention in underlying conditions like hepatitis and fatty liver disease are critical in managing and preventing hepatostasis-related complications.
Complications Associated with Untreated Hepatostasis
Untreated hepatostasis can lead to severe complications such as biliary cirrhosis, liver fibrosis, and portal hypertension due to prolonged bile acid accumulation causing hepatocellular damage. Persistent bile flow obstruction increases the risk of bacterial cholangitis and hepatic encephalopathy, significantly impairing liver function. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent irreversible liver injury and associated systemic complications.
Future Directions in Hepatostasis Research
Future directions in hepatostasis research emphasize the development of advanced molecular therapies targeting liver fibrosis and regeneration pathways. Cutting-edge gene editing techniques and stem cell-based regenerative medicine show promise for restoring hepatic function in chronic liver diseases. Enhanced biomarkers for early detection and personalized treatment strategies aim to improve patient outcomes in hepatostasis management.
Hepatostasis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com