Toxicodynamics explores how toxins interact with biological targets to produce harmful effects at the cellular and molecular levels. Understanding these mechanisms helps predict the severity and progression of toxic exposures in the body. Dive into the full article to uncover how toxicodynamics shapes your response to toxins and informs safety measures.
Table of Comparison
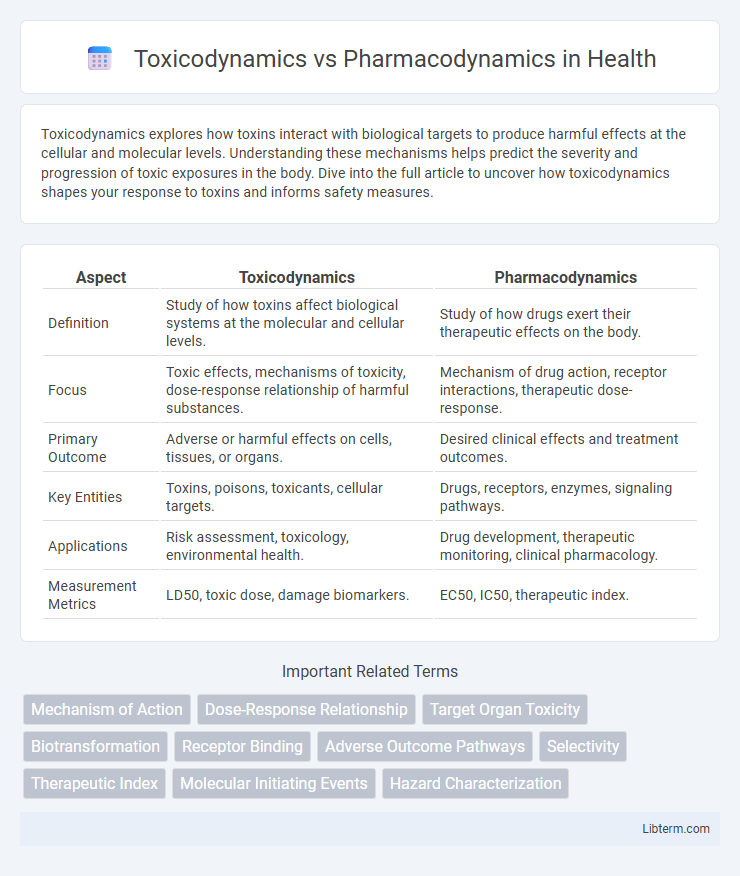
| Aspect | Toxicodynamics | Pharmacodynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how toxins affect biological systems at the molecular and cellular levels. | Study of how drugs exert their therapeutic effects on the body. |
| Focus | Toxic effects, mechanisms of toxicity, dose-response relationship of harmful substances. | Mechanism of drug action, receptor interactions, therapeutic dose-response. |
| Primary Outcome | Adverse or harmful effects on cells, tissues, or organs. | Desired clinical effects and treatment outcomes. |
| Key Entities | Toxins, poisons, toxicants, cellular targets. | Drugs, receptors, enzymes, signaling pathways. |
| Applications | Risk assessment, toxicology, environmental health. | Drug development, therapeutic monitoring, clinical pharmacology. |
| Measurement Metrics | LD50, toxic dose, damage biomarkers. | EC50, IC50, therapeutic index. |
Introduction to Toxicodynamics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics examines how drugs interact with biological receptors to produce therapeutic effects by influencing physiological functions and biochemical pathways. Toxicodynamics studies the adverse effects of chemical agents on biological systems, focusing on the mechanisms underlying toxicity at molecular, cellular, and organ levels. Understanding the distinct interaction profiles in pharmacodynamics versus toxicodynamics is essential for drug development and safety assessment.
Key Definitions: Toxicodynamics vs Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics refers to the study of drug effects on the body, focusing on mechanisms of action, receptor interactions, and dose-response relationships. Toxicodynamics examines the adverse effects of chemicals or drugs on biological systems, detailing mechanisms leading to toxicity and the dose-dependent progression of harmful outcomes. Both fields analyze biochemical and molecular interactions but differ in their emphasis on therapeutic versus toxic effects.
Mechanisms of Action: Toxic and Therapeutic Agents
Toxicodynamics and pharmacodynamics both explore mechanisms of action, but toxicodynamics focuses on harmful interactions of toxic agents at molecular or cellular targets causing adverse effects, while pharmacodynamics centers on therapeutic agents binding to receptors or enzymes to elicit desired physiological responses. Toxic agents often disrupt normal biochemical pathways or induce oxidative stress, whereas therapeutic drugs modulate receptor activity or enzyme function to restore homeostasis. Understanding these mechanisms aids in predicting toxicity risks and optimizing drug efficacy.
Dose–Response Relationships in Toxicodynamics and Pharmacodynamics
Dose-response relationships in toxicodynamics describe the correlation between toxin exposure levels and adverse biological effects, emphasizing the threshold at which harmful outcomes manifest. Pharmacodynamics focuses on the interaction between drug concentrations and therapeutic effects, highlighting the receptor binding, efficacy, and potency that determine drug action. Understanding these dose-response curves is crucial for assessing safety margins, therapeutic windows, and toxic thresholds in both toxicology and pharmacology.
Molecular Targets and Biological Pathways
Toxicodynamics and pharmacodynamics both examine molecular targets and biological pathways but differ in their outcomes and mechanisms of action; pharmacodynamics studies drug interactions with specific receptors, enzymes, or ion channels to elicit therapeutic effects, while toxicodynamics focuses on how toxicants disrupt cellular signaling pathways, such as oxidative stress or inflammation cascades, leading to adverse biological responses. Key molecular targets in pharmacodynamics include G-protein coupled receptors and transporters that regulate physiological functions, whereas toxicodynamics often involves reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial dysfunction, or DNA damage pathways. Understanding the distinct molecular interactions and downstream signaling events is crucial for differentiating therapeutic efficacy from toxicity during drug development and safety assessments.
Factors Influencing Drug and Toxin Effects
Drug and toxin effects in toxicodynamics and pharmacodynamics are influenced by factors such as dose, route of administration, and individual metabolic variations impacting absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Genetic polymorphisms in metabolic enzymes and receptor sensitivity significantly modify the intensity and duration of these effects. Environmental conditions and co-exposure to other substances also alter the pharmacokinetic and toxicodynamic responses, affecting overall efficacy and toxicity profiles.
Clinical Relevance and Applications
Toxicodynamics examines the harmful effects and mechanisms of toxins at molecular and cellular levels, guiding risk assessment and management in clinical toxicology. Pharmacodynamics studies drug interactions with biological targets to optimize therapeutic efficacy and minimize adverse effects, critical for personalized medicine and dose adjustment. Understanding both disciplines improves clinical decision-making, balancing drug benefits against potential toxicities for safer patient outcomes.
Assessment and Measurement Techniques
Toxicodynamics involves assessing the molecular and cellular mechanisms affected by toxic substances, often utilizing biomarker analysis, dose-response curves, and in vitro assays to measure toxic effects. Pharmacodynamics focuses on the drug-receptor interactions, employing techniques such as receptor binding assays, functional assays, and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling to evaluate therapeutic efficacy and drug action. Both fields rely heavily on quantitative methods like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry to precisely measure drug and toxin concentrations in biological systems.
Implications for Risk Assessment and Drug Development
Toxicodynamics studies the harmful effects and mechanisms of toxic substances on biological systems, while pharmacodynamics examines the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of drugs. Understanding toxicodynamic parameters aids in predicting adverse effects and safety margins, which is crucial for risk assessment during drug development. Integrating both toxicodynamic and pharmacodynamic data enhances the prediction of drug efficacy and toxicity, leading to safer and more effective therapeutic agents.
Future Perspectives in Toxicodynamics and Pharmacodynamics
Emerging advancements in toxicodynamics and pharmacodynamics emphasize integrating high-throughput screening and artificial intelligence to enhance predictive modeling of drug and toxin interactions at molecular and systemic levels. Future research focuses on personalized medicine approaches, leveraging genomic and proteomic data to tailor therapeutic interventions while minimizing adverse effects. Innovations in organ-on-a-chip technology and real-time biomarker monitoring aim to refine the understanding of dynamic dose-response relationships, improving safety and efficacy profiles in drug development.
Toxicodynamics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com