Homeopathy offers a natural approach to health by using highly diluted substances to trigger the body's self-healing mechanisms. This alternative medicine emphasizes individualized treatment based on your unique symptoms and constitution. Discover how homeopathy can complement your wellness routine by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
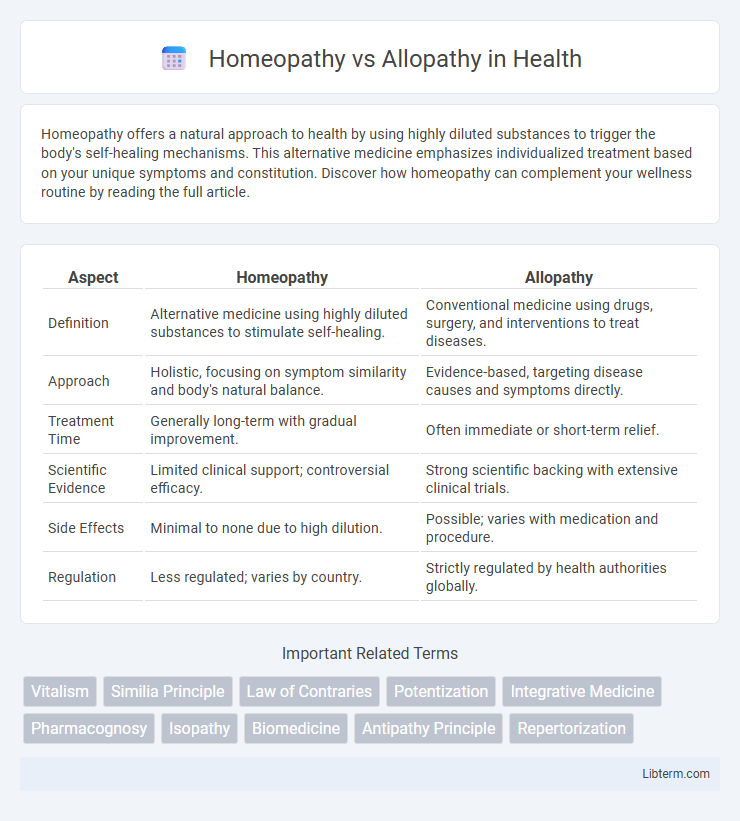
| Aspect | Homeopathy | Allopathy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alternative medicine using highly diluted substances to stimulate self-healing. | Conventional medicine using drugs, surgery, and interventions to treat diseases. |
| Approach | Holistic, focusing on symptom similarity and body's natural balance. | Evidence-based, targeting disease causes and symptoms directly. |
| Treatment Time | Generally long-term with gradual improvement. | Often immediate or short-term relief. |
| Scientific Evidence | Limited clinical support; controversial efficacy. | Strong scientific backing with extensive clinical trials. |
| Side Effects | Minimal to none due to high dilution. | Possible; varies with medication and procedure. |
| Regulation | Less regulated; varies by country. | Strictly regulated by health authorities globally. |
Introduction to Homeopathy and Allopathy
Homeopathy is a holistic medical system introduced by Samuel Hahnemann in the late 18th century, emphasizing the "like cures like" principle and using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing. Allopathy, also known as conventional medicine, relies on evidence-based treatments, pharmaceutical drugs, and surgical interventions to directly target and counteract specific symptoms or diseases. Both approaches differ fundamentally in methodology, with homeopathy focusing on individualized patient care and allopathy emphasizing standardized protocols and clinical trials.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Homeopathy originated in the late 18th century through the work of Samuel Hahnemann, emphasizing the principle of "like cures like" and highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing. Allopathy, developed alongside conventional medicine, is rooted in evidence-based practices and germ theory, evolving rapidly through advances in pharmacology and surgical techniques since the 19th century. Both systems have distinct historical trajectories, with homeopathy maintaining a holistic approach while allopathy expanded into modern biomedical sciences.
Principles and Philosophies Explained
Homeopathy operates on the principle of "like cures like," using highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms, emphasizing individualization and holistic treatment. Allopathy follows a biomedical approach focused on diagnosing and treating symptoms or diseases through pharmacological agents, surgery, or other interventions, prioritizing evidence-based medicine. The philosophical contrast lies in homeopathy's vital force concept and minimal doses versus allopathy's targeted, dose-specific therapies designed to counteract pathologies directly.
Diagnostic Approaches: Homeopathy vs Allopathy
Homeopathy employs individualized diagnostic approaches centered on detailed patient interviews to identify unique symptom patterns for customized remedies. Allopathy relies on standardized diagnostic methods, including laboratory tests, imaging, and clinical examinations to detect specific diseases or abnormalities. The contrasting diagnostic philosophies highlight homeopathy's holistic, symptom-based assessment versus allopathy's objective, pathology-focused evaluation.
Treatment Modalities and Techniques
Homeopathy employs highly diluted substances to stimulate the body's self-healing mechanisms, using individualized remedies based on the principle of "like cures like." Allopathy relies on pharmacologically active agents and surgical procedures to target specific symptoms and pathologies directly, often providing faster symptomatic relief. Treatment modalities in homeopathy emphasize holistic assessment and minimal dosing, whereas allopathy focuses on evidence-based protocols and standardized drug regimens for disease management.
Effectiveness and Evidence-Based Research
Homeopathy's effectiveness remains controversial, with systematic reviews and meta-analyses generally indicating no conclusive evidence that it performs better than placebo in treating medical conditions. Allopathy, or conventional medicine, relies heavily on evidence-based research, with treatments undergoing rigorous clinical trials and regulatory approvals to establish safety and efficacy. Comparative studies consistently show that allopathic treatments provide measurable health benefits validated by scientific methods, contrasting with the limited empirical support available for homeopathic remedies.
Safety, Side Effects, and Controversies
Homeopathy is often praised for its minimal side effects due to highly diluted substances, contrasting with allopathy, which uses pharmaceutical drugs that may cause more significant adverse reactions. Safety concerns in allopathy arise from the potent chemical compositions and possible drug interactions, whereas homeopathy's efficacy and safety profile remain contentious within the medical community. Controversies center on allopathy's evidence-based approach versus homeopathy's reliance on principles like "like cures like," with critics highlighting the lack of rigorous scientific validation for homeopathy.
Global Acceptance and Regulations
Homeopathy and allopathy differ significantly in global acceptance and regulatory frameworks, with allopathy widely recognized and regulated by most national health authorities due to its evidence-based approach and standardized clinical trials. Homeopathy, though popular in countries such as India, Germany, and Brazil, faces more varied regulation, ranging from official recognition and integration into national health systems to skepticism and restriction in nations prioritizing conventional medicine. The World Health Organization highlights the need for stringent evaluation of homeopathic treatments, emphasizing that global health policies predominantly favor allopathic medicine for safety, efficacy, and consistency in patient care.
Patient Experiences and Success Stories
Patients report varied experiences with homeopathy and allopathy, highlighting the personalized approach of homeopathy that emphasizes holistic healing and minimal side effects. Success stories in homeopathy often involve chronic conditions like allergies and asthma, where conventional allopathic treatments may provide symptomatic relief but with potential side effects. Many allopathy patients share success in acute and emergency care due to evidence-based protocols and advanced diagnostics, underscoring the importance of integrating both systems for comprehensive healthcare.
Choosing the Right Therapy: Factors to Consider
Choosing between homeopathy and allopathy involves evaluating factors such as the severity of the condition, evidence-based treatment efficacy, and individual patient response. Homeopathy is often preferred for chronic, mild, or preventive care with minimal side effects, while allopathy is recommended for acute, severe, or emergency conditions due to its faster and scientifically validated results. Patient preferences, safety profile, and clinical consultation with healthcare professionals play critical roles in determining the most suitable therapy.
Homeopathy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com