Healing is a natural process where your body repairs itself after injury or illness, restoring health and function over time. Factors like nutrition, rest, and mental well-being significantly influence the speed and effectiveness of healing. Discover deeper insights into how you can support your body's recovery by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
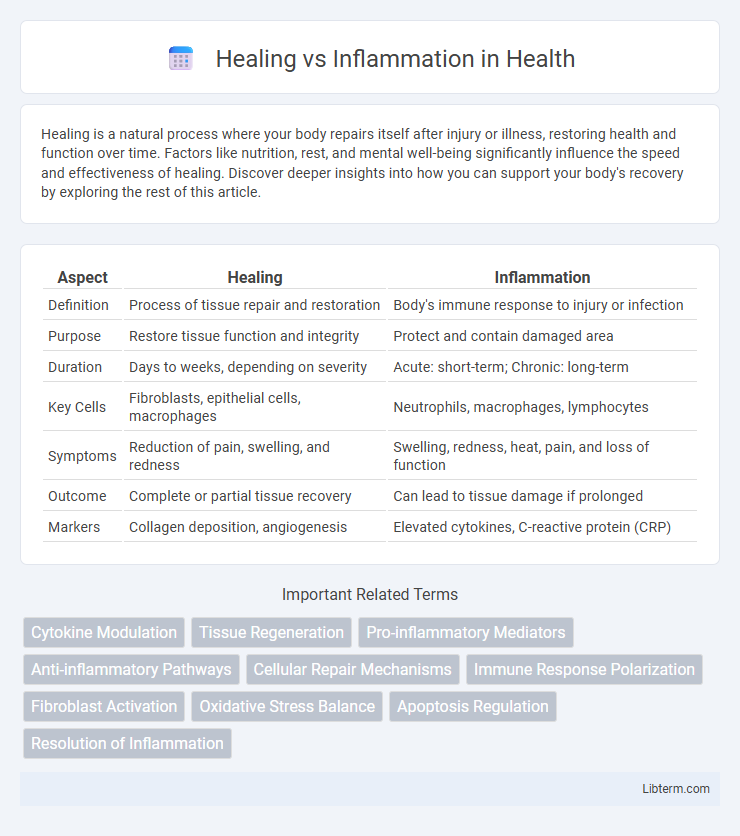
| Aspect | Healing | Inflammation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of tissue repair and restoration | Body's immune response to injury or infection |
| Purpose | Restore tissue function and integrity | Protect and contain damaged area |
| Duration | Days to weeks, depending on severity | Acute: short-term; Chronic: long-term |
| Key Cells | Fibroblasts, epithelial cells, macrophages | Neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes |
| Symptoms | Reduction of pain, swelling, and redness | Swelling, redness, heat, pain, and loss of function |
| Outcome | Complete or partial tissue recovery | Can lead to tissue damage if prolonged |
| Markers | Collagen deposition, angiogenesis | Elevated cytokines, C-reactive protein (CRP) |
Understanding Healing and Inflammation
Healing involves a complex biological process where tissues repair after injury, restoring function and integrity through stages like hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Inflammation is an essential part of the healing process, characterized by immune cell activation, release of cytokines, and increased blood flow to remove pathogens and damaged tissue. Understanding the balance between beneficial inflammation and chronic inflammation is critical to promoting effective tissue repair and preventing excessive damage or fibrosis.
The Body’s Natural Response: Inflammation Explained
Inflammation is the body's natural defense mechanism triggered by injury or infection, characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain. This immune response mobilizes white blood cells and biochemical mediators to eliminate harmful agents and initiate tissue repair. Proper regulation of inflammation is crucial for effective healing, as unresolved or chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and impaired recovery.
Stages of the Healing Process
The healing process consists of three primary stages: inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. During the inflammation stage, immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages eliminate pathogens and debris to prepare the wound for repair. The proliferation stage involves tissue regeneration and angiogenesis, followed by remodeling, where collagen is reorganized to restore tissue strength and function.
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a short-term immune response that promotes healing by removing harmful stimuli and initiating tissue repair, typically resolving within days. Chronic inflammation persists over longer periods, often weeks to years, contributing to tissue damage and impaired healing due to continuous immune activation. Understanding the balance between acute and chronic inflammation is crucial for developing treatments that minimize tissue destruction while enhancing regenerative processes.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Inflammation
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, promoting healing by eliminating harmful stimuli and initiating tissue repair. Benefits of inflammation include enhanced immune defense and removal of damaged cells, which accelerates recovery. However, prolonged or excessive inflammation can lead to chronic pain, tissue damage, and increased risk of diseases such as arthritis and cardiovascular conditions.
Factors Influencing Healing and Inflammation
Healing and inflammation are influenced by various factors including age, nutrition, and immune function. Chronic inflammation can impair tissue repair by prolonging the inflammatory phase, while proper nutrition supports collagen synthesis and cellular regeneration. Environmental factors such as infection and stress also modulate the balance between effective healing and excessive inflammation.
Nutrition’s Role in Healing and Inflammation
Nutrition plays a critical role in modulating inflammation and promoting healing by providing essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins A, C, and E, which help regulate the immune response and reduce oxidative stress. Adequate protein intake supports tissue repair and the synthesis of enzymes and collagen crucial for wound healing. Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can minimize chronic inflammation, thereby accelerating recovery and improving overall immune function.
Medical Treatments: Supporting Healing, Reducing Inflammation
Medical treatments for supporting healing often involve the use of growth factors, wound dressings, and regenerative therapies that stimulate tissue repair and cell proliferation. Anti-inflammatory medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and biologics specifically target inflammatory pathways to reduce swelling, pain, and tissue damage. Combining these therapies can optimize recovery by controlling inflammation while promoting the body's natural healing processes.
Lifestyle Strategies for Optimal Healing
Effective healing requires managing inflammation through lifestyle strategies such as a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, regular moderate exercise, and adequate sleep which supports immune function and tissue repair. Stress reduction techniques including mindfulness and meditation help lower chronic inflammation, promoting faster recovery. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption further reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, enhancing the body's natural healing processes.
Preventing Chronic Inflammation for Long-Term Health
Effective healing depends on controlling inflammation to prevent chronic inflammation, which is linked to diseases like arthritis, heart disease, and diabetes. Strategies for preventing chronic inflammation include maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, managing stress, and regular physical activity to support the immune system. Monitoring inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) helps in early detection and intervention for better long-term health outcomes.
Healing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com