Leukoplakia presents as white patches on the mucous membranes, often in the mouth, and can be a precancerous condition requiring medical evaluation. Leukemia is a group of blood cancers characterized by abnormal white blood cell production, affecting immunity and overall health. To understand the distinctions, symptoms, and treatment options for these conditions, continue reading the article.
Table of Comparison
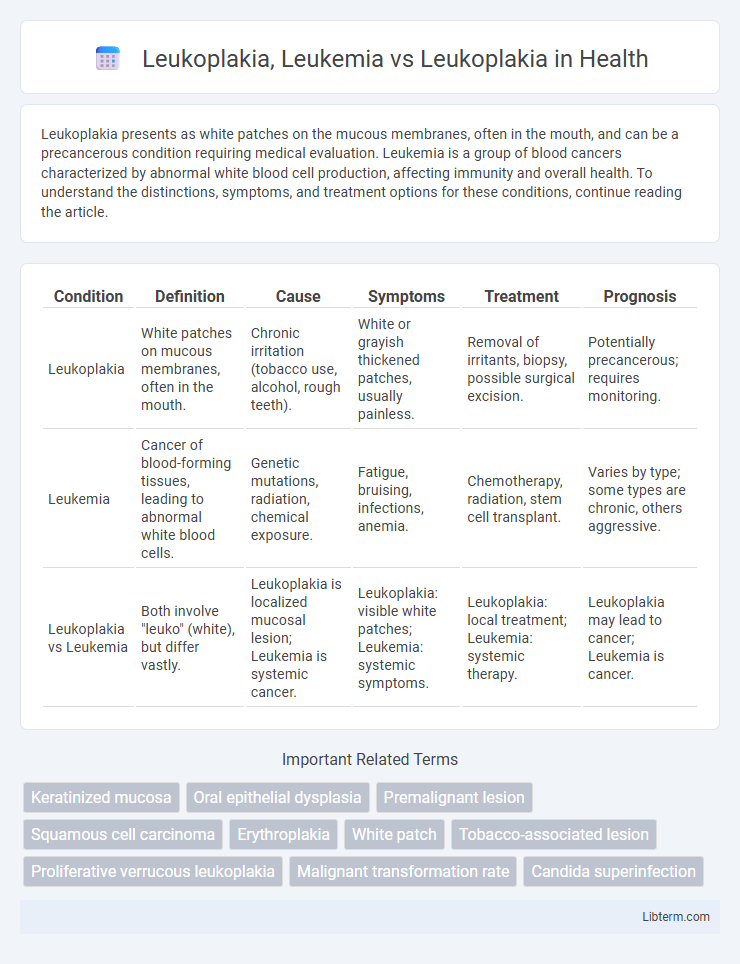
| Condition | Definition | Cause | Symptoms | Treatment | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leukoplakia | White patches on mucous membranes, often in the mouth. | Chronic irritation (tobacco use, alcohol, rough teeth). | White or grayish thickened patches, usually painless. | Removal of irritants, biopsy, possible surgical excision. | Potentially precancerous; requires monitoring. |
| Leukemia | Cancer of blood-forming tissues, leading to abnormal white blood cells. | Genetic mutations, radiation, chemical exposure. | Fatigue, bruising, infections, anemia. | Chemotherapy, radiation, stem cell transplant. | Varies by type; some types are chronic, others aggressive. |
| Leukoplakia vs Leukemia | Both involve "leuko" (white), but differ vastly. | Leukoplakia is localized mucosal lesion; Leukemia is systemic cancer. | Leukoplakia: visible white patches; Leukemia: systemic symptoms. | Leukoplakia: local treatment; Leukemia: systemic therapy. | Leukoplakia may lead to cancer; Leukemia is cancer. |
Understanding Leukoplakia: Definition and Causes
Leukoplakia is a condition characterized by white patches on the mucous membranes of the mouth, primarily caused by chronic irritation from tobacco use, alcohol consumption, or rough teeth surfaces. Unlike leukemia, which is a malignant cancer of blood-forming tissues affecting white blood cells, leukoplakia is a potentially precancerous lesion localized in the oral cavity. Early identification and management of leukoplakia are crucial to prevent progression to oral cancer.
What Is Leukemia? Key Facts and Overview
Leukemia is a type of cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow, characterized by the uncontrolled production of abnormal white blood cells. It leads to symptoms such as fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bleeding due to impaired blood cell function. Unlike leukoplakia, which involves white patches on mucous membranes often caused by irritation or precancerous changes, leukemia is a systemic malignancy requiring specialized hematologic treatment.
Leukoplakia Symptoms: Recognizing Early Signs
Leukoplakia is characterized by white or gray patches on the tongue, inside cheeks, or gums, often without pain, making early detection challenging. Common symptoms include thickened, slightly raised lesions with a hard texture and possible redness or inflammation around the patches. Differentiating leukoplakia from leukemia is crucial since leukemia involves abnormal white blood cell proliferation causing systemic symptoms like fatigue, fever, and bleeding, while leukoplakia primarily affects the oral mucosa with localized signs.
Leukemia Signs and Symptoms Explained
Leukoplakia is a white patch or plaque that forms on the mucous membranes, often in the mouth, and is considered a potentially precancerous lesion, whereas leukemia is a type of cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow characterized by the abnormal proliferation of white blood cells. Leukemia signs and symptoms include persistent fatigue, frequent infections, unexplained bruising or bleeding, swollen lymph nodes, and bone or joint pain due to the disruption of normal blood cell production. Early diagnosis of leukemia relies on recognizing these clinical features alongside laboratory tests such as complete blood count and bone marrow biopsy.
Leukoplakia vs Leukemia: Key Differences
Leukoplakia presents as white patches on mucous membranes, primarily in the oral cavity, often caused by chronic irritation or tobacco use and considered potentially precancerous. Leukemia is a group of blood cancers originating in bone marrow, characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal white blood cells, leading to symptoms like fatigue, infections, and bleeding. Key differences include leukoplakia's localized mucosal appearance with malignant potential versus leukemia's systemic impact on blood and immune function.
Risk Factors: Who Is Most at Risk for Each Condition?
Leukoplakia primarily affects smokers and individuals who use tobacco or consume excessive alcohol, with risk factors including chronic irritation from tobacco, alcohol, or dental issues; it is most common in middle-aged and older adults. Leukemia risk factors differ significantly, with exposure to high doses of radiation, certain chemicals like benzene, a family history of leukemia, and previous chemotherapy treatments increasing susceptibility, often impacting both children and adults. While leukoplakia is linked to localized mucosal changes often preceding cancer, leukemia is a systemic blood cancer with distinct genetic and environmental risk profiles.
Diagnosis: How Leukoplakia and Leukemia Are Identified
Leukoplakia is diagnosed primarily through a clinical oral examination followed by a biopsy to rule out dysplasia or malignancy, with white plaques appearing on mucous membranes as a key indicator. Leukemia diagnosis involves blood tests showing abnormal white blood cell counts, bone marrow biopsy, and flow cytometry to detect leukemic cells. Accurate differentiation between leukoplakia and leukemia relies on tissue histopathology for leukoplakia and hematologic parameters for leukemia identification.
Treatment Options for Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia treatment primarily involves eliminating risk factors like tobacco and alcohol use, with topical antioxidants and retinoids showing promising results in reducing lesion size. In some cases, laser therapy, cryotherapy, or surgical excision is necessary to remove persistent or dysplastic patches to prevent malignant transformation. Regular monitoring by oral health specialists is crucial for early detection of any progression towards oral cancer.
Leukemia Treatment Approaches
Leukoplakia is a white patch on mucous membranes often linked to tobacco use, whereas leukemia is a malignant blood cancer characterized by abnormal white blood cell proliferation. Leukemia treatment approaches include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, each tailored to the specific leukemia subtype such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Advances in immunotherapy, including CAR-T cell therapy and monoclonal antibodies, have significantly improved treatment outcomes for various leukemia patients.
Prevention and Outlook: Managing Leukoplakia and Leukemia
Effective prevention of leukoplakia involves avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption, alongside regular dental check-ups to detect precancerous lesions early. Leukemia prevention is less defined but maintaining a healthy lifestyle and minimizing exposure to radiation and toxic chemicals may reduce risk. The outlook for leukoplakia depends on early identification and treatment to prevent malignant transformation, whereas leukemia prognosis varies by subtype and treatment responsiveness, with advances in targeted therapies improving survival rates.
Leukoplakia, Leukemia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com