Hemiplegia is a neurological condition characterized by paralysis affecting one side of the body, often resulting from stroke or brain injury. This loss of motor function can significantly impact your daily activities, requiring specialized rehabilitation and therapy to regain strength and coordination. Explore the article to understand causes, symptoms, treatment options, and coping strategies for hemiplegia.
Table of Comparison
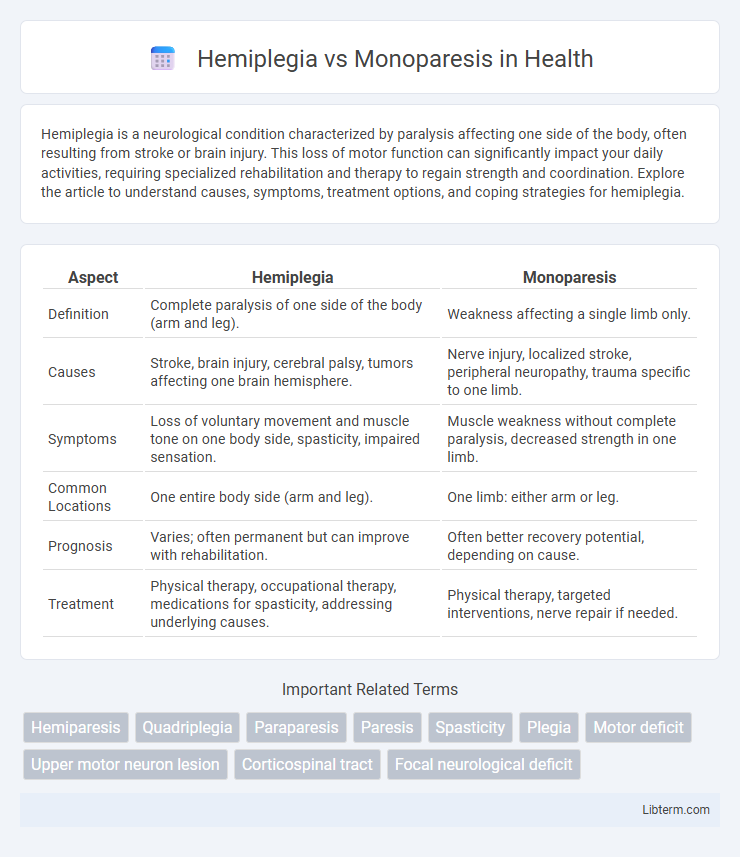
| Aspect | Hemiplegia | Monoparesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete paralysis of one side of the body (arm and leg). | Weakness affecting a single limb only. |
| Causes | Stroke, brain injury, cerebral palsy, tumors affecting one brain hemisphere. | Nerve injury, localized stroke, peripheral neuropathy, trauma specific to one limb. |
| Symptoms | Loss of voluntary movement and muscle tone on one body side, spasticity, impaired sensation. | Muscle weakness without complete paralysis, decreased strength in one limb. |
| Common Locations | One entire body side (arm and leg). | One limb: either arm or leg. |
| Prognosis | Varies; often permanent but can improve with rehabilitation. | Often better recovery potential, depending on cause. |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, occupational therapy, medications for spasticity, addressing underlying causes. | Physical therapy, targeted interventions, nerve repair if needed. |
Introduction to Hemiplegia and Monoparesis
Hemiplegia is a neurological condition characterized by complete paralysis affecting one side of the body, often resulting from stroke, traumatic brain injury, or cerebral palsy. In contrast, monoparesis involves weakness or partial paralysis confined to a single limb without total loss of movement. Understanding the distinct etiologies and clinical presentations of hemiplegia and monoparesis is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted rehabilitation strategies.
Defining Hemiplegia: Causes and Symptoms
Hemiplegia is a neurological condition characterized by complete paralysis on one side of the body, typically resulting from brain injuries such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or cerebral palsy. Symptoms include loss of motor function, muscle stiffness, and impaired coordination affecting the arm, leg, and sometimes the face on the affected side. Unlike monoparesis, which involves weakness in a single limb, hemiplegia causes profound impairment across half of the body due to damage in the brain's motor pathways.
Understanding Monoparesis: Key Characteristics
Monoparesis refers to weakness affecting a single limb, often caused by localized nerve injury, stroke, or trauma, differentiating it from hemiplegia, which involves paralysis of one entire side of the body. Key characteristics of monoparesis include partial motor impairment without complete paralysis, usually confined to one arm or leg, enabling some retained movement and function. Diagnosis often relies on clinical examination and neuroimaging to identify underlying causes such as peripheral neuropathy or focal brain lesions.
Differences in Motor Impairment Patterns
Hemiplegia involves paralysis affecting one entire side of the body, typically resulting from brain injuries like stroke or cerebral palsy, and leads to severe motor impairment with loss of voluntary movement on the affected side. Monoparesis, in contrast, refers to weakness or partial paralysis confined to a single limb, often caused by peripheral nerve damage or localized brain lesions, resulting in less extensive motor dysfunction. The key difference lies in the distribution and severity of motor impairment: hemiplegia presents with complete or near-complete paralysis of half the body, while monoparesis shows limited weakness in one limb without widespread involvement.
Common Causes: Hemiplegia vs Monoparesis
Hemiplegia commonly results from stroke, traumatic brain injury, or cerebral palsy, causing paralysis on one side of the body due to brain or spinal cord damage. Monoparesis typically stems from peripheral nerve injury, localized trauma, or nerve compression, leading to weakness in a single limb without widespread neurological impairment. Understanding these distinct etiologies is crucial for targeted diagnosis and treatment strategies in neurological care.
Diagnostic Approaches and Assessment
Diagnostic approaches for hemiplegia commonly involve comprehensive neurological examinations, brain imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans to identify stroke or brain injury, and electromyography (EMG) to assess muscle activity. Monoparesis assessment focuses on targeted neurological tests to evaluate localized muscle weakness, nerve conduction studies, and MRI to detect peripheral nerve damage or localized lesions. Both conditions require detailed patient history, physical exam, and use of diagnostic tools to differentiate central nervous system involvement in hemiplegia from peripheral or focal causes in monoparesis.
Treatment Options for Hemiplegia
Treatment options for hemiplegia primarily include physical therapy to improve motor function and muscle strength on the affected side, occupational therapy to enhance daily living skills, and speech therapy if language or swallowing is impaired. Medications such as muscle relaxants, antispastic agents, and botulinum toxin injections help reduce muscle spasticity and improve mobility. In some cases, surgical interventions or electrical stimulation therapies are considered to restore movement and prevent muscle contractures.
Treatment Strategies for Monoparesis
Treatment strategies for monoparesis often involve targeted physical therapy to strengthen specific muscle groups affected by partial paralysis, alongside occupational therapy to improve functional independence. In some cases, medications such as muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to alleviate underlying causes like nerve inflammation or muscle spasticity. Advanced interventions may include nerve stimulation techniques or surgical options, depending on the severity and etiology of the monoparesis.
Rehabilitation and Prognosis Comparison
Rehabilitation for hemiplegia typically involves intensive multidisciplinary approaches including physical, occupational, and speech therapy to address extensive muscle weakness on one side of the body, with prognosis often depending on stroke severity and timely intervention. Monoparesis rehabilitation focuses on targeted strengthening and functional training of a single limb, generally resulting in a more favorable prognosis due to localized impairment and less extensive neural damage. Early and consistent therapy improves outcomes in both conditions, but hemiplegia patients face longer recovery periods and higher risks of complications such as spasticity and contractures.
Quality of Life: Living with Hemiplegia or Monoparesis
Living with hemiplegia often involves significant challenges in mobility and daily functioning due to paralysis on one side of the body, impacting independence and requiring extensive rehabilitation and assistive devices. Monoparesis, characterized by weakness in a single limb, typically allows greater preservation of function, enabling patients to maintain more autonomy and engage in daily activities with fewer limitations. Quality of life differences hinge on the severity of impairment, access to therapy, and social support, as effective management can improve physical capabilities and emotional well-being in both conditions.
Hemiplegia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com