Ulceration is the process in which an open sore forms on the skin or mucous membrane due to tissue breakdown and inflammation. This condition can result from various causes, including infections, chronic diseases, or prolonged pressure, and requires prompt care to prevent complications. Discover more about ulceration causes, symptoms, and effective treatment methods in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
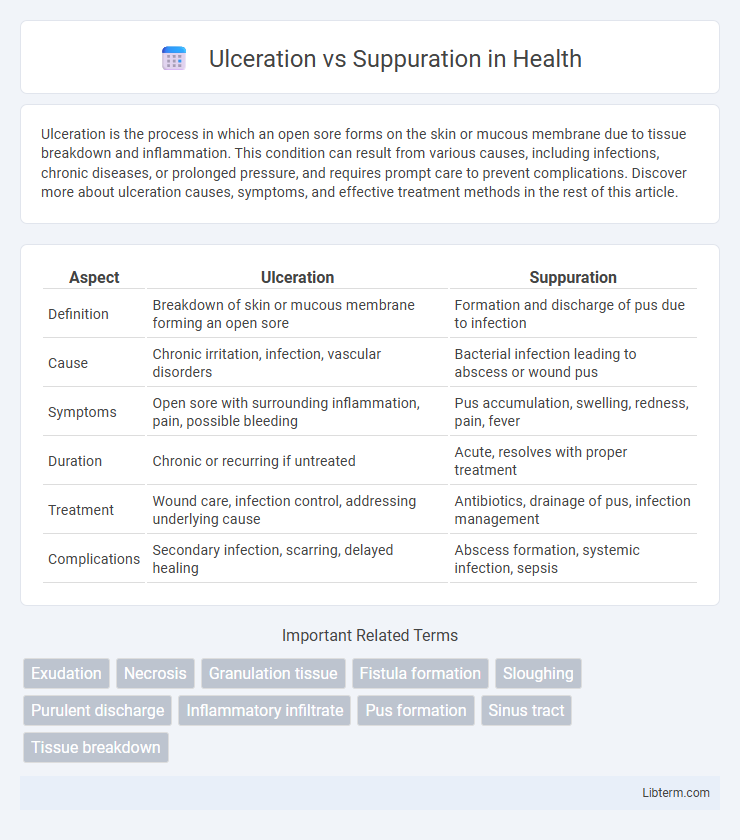
| Aspect | Ulceration | Suppuration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Breakdown of skin or mucous membrane forming an open sore | Formation and discharge of pus due to infection |
| Cause | Chronic irritation, infection, vascular disorders | Bacterial infection leading to abscess or wound pus |
| Symptoms | Open sore with surrounding inflammation, pain, possible bleeding | Pus accumulation, swelling, redness, pain, fever |
| Duration | Chronic or recurring if untreated | Acute, resolves with proper treatment |
| Treatment | Wound care, infection control, addressing underlying cause | Antibiotics, drainage of pus, infection management |
| Complications | Secondary infection, scarring, delayed healing | Abscess formation, systemic infection, sepsis |
Understanding Ulceration: Definition and Characteristics
Ulceration refers to the formation of an open sore on the skin or mucous membrane, characterized by tissue loss and inflammation. It typically results from prolonged irritation, infection, or injury, leading to the breakdown of the epithelial surface. Key features include a well-demarcated lesion with exposed underlying tissue, often accompanied by redness, swelling, and sometimes pain.
What is Suppuration? Key Features and Process
Suppuration is the biological process of pus formation as a result of the body's response to infection, characterized by the accumulation of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Key features include localized swelling, redness, warmth, and the presence of thick, yellowish or greenish pus at the infection site. The process begins with tissue injury and immune activation, followed by white blood cell infiltration, bacterial proliferation, and eventual pus discharge as the body attempts to eliminate the infection.
Etiology: Causes of Ulceration vs Suppuration
Ulceration primarily results from tissue ischemia, chronic inflammation, infections such as bacterial or viral agents, and autoimmune disorders that disrupt mucosal integrity. Suppuration is caused by bacterial infections, commonly involving pyogenic bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species, which trigger pus formation through the accumulation of dead neutrophils and necrotic tissue. Both conditions involve inflammatory processes, but ulceration emphasizes tissue breakdown while suppuration centers on purulent exudate due to active infection.
Pathophysiology: How Ulcers and Suppuration Develop
Ulceration develops through tissue necrosis caused by persistent inflammation, ischemia, or infection leading to the breakdown of the epithelial or mucosal surface. Suppuration results from an acute inflammatory response to bacterial infection where neutrophils accumulate and release enzymes, causing localized tissue destruction and pus formation. Both processes involve immune cell recruitment and release of proteolytic enzymes that degrade tissue, but ulceration primarily reflects chronic tissue loss, whereas suppuration signifies active purulent inflammation.
Clinical Presentation: Signs and Symptoms Compared
Ulceration presents as a localized loss of the epithelial surface with a clean base, often accompanied by redness, pain, and sometimes bleeding, typically indicating tissue breakdown due to chronic irritation or infection. Suppuration is characterized by the accumulation of pus within tissues, manifesting clinically with swelling, warmth, tenderness, and fluctuant masses, often signifying active bacterial infection. Both conditions may cause localized discomfort, but suppuration frequently involves systemic signs like fever and malaise, distinguishing it from the usually localized symptoms of ulceration.
Diagnostic Approaches: Distinguishing Ulceration from Suppuration
Diagnostic approaches to distinguish ulceration from suppuration primarily involve clinical evaluation and imaging techniques. Ulceration is identified by the presence of tissue loss with exposed subepithelial structures, whereas suppuration is characterized by pus formation due to localized infection and inflammation. Laboratory analysis, including culture and histopathology, aids in differentiating the underlying causes and guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Common Conditions Associated with Ulceration and Suppuration
Ulceration commonly occurs in conditions such as diabetic foot ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, and pressure sores, where tissue breakdown results from poor circulation or prolonged pressure. Suppuration is typically associated with infections like abscesses, cellulitis, and infected wounds, characterized by pus formation due to bacterial invasion and immune response. Both processes can coexist in chronic wounds, complicating healing and requiring targeted medical management.
Treatment Modalities: Managing Ulceration vs Suppuration
Treatment modalities for ulceration primarily involve wound cleaning, debridement, and application of topical antimicrobial agents to promote tissue regeneration and prevent infection. Suppuration management centers on drainage of pus, use of systemic antibiotics, and addressing the underlying infection to reduce inflammation and facilitate healing. Both conditions benefit from accurate diagnosis and tailored therapy to optimize outcomes and minimize complications.
Potential Complications: Risks and Outcomes
Ulceration can lead to complications such as secondary infections, delayed wound healing, and potential progression to chronic wounds, increasing the risk of tissue necrosis and scarring. Suppuration involves pus formation that may result in abscess development, systemic infection like sepsis, and impaired immune response if untreated. Both conditions require prompt medical intervention to prevent severe outcomes like gangrene or systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS).
Prevention and Prognosis: Improving Patient Outcomes
Ulceration prevention involves maintaining skin integrity through proper hygiene, nutrition, and early treatment of underlying conditions such as diabetes or vascular diseases. Suppuration management requires prompt intervention with appropriate antibiotics and drainage to prevent abscess formation and systemic infection. Effective prevention and timely treatment of both ulceration and suppuration significantly enhance prognosis by reducing complications and promoting faster healing.
Ulceration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com