Survival skills are essential for overcoming emergencies and thriving in challenging environments by securing shelter, food, and water. Mastering techniques like fire-starting, navigation, and first aid can significantly increase your chances of staying safe and healthy. Explore the full article to learn practical tips and strategies that will empower your survival abilities.
Table of Comparison
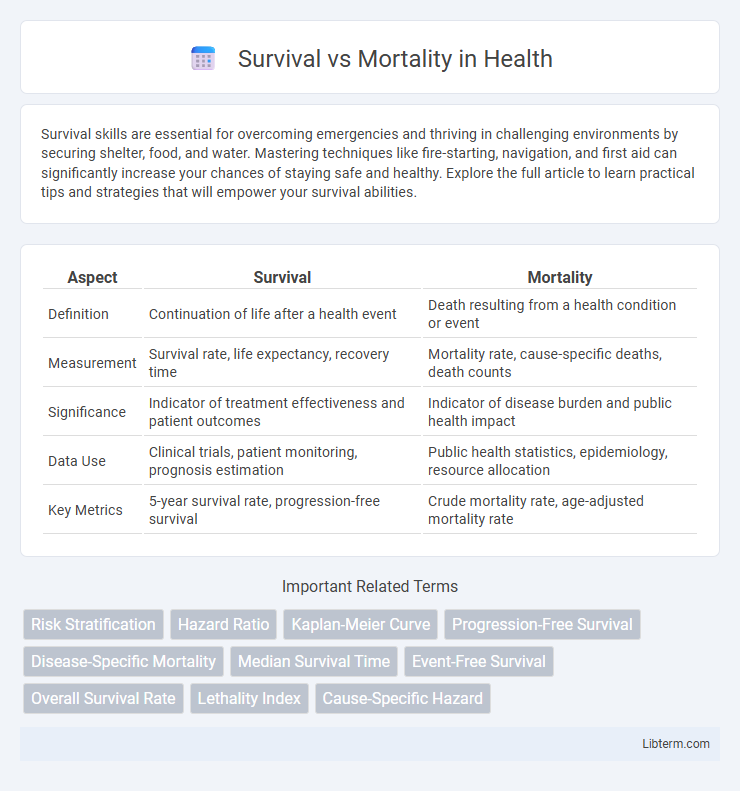
| Aspect | Survival | Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuation of life after a health event | Death resulting from a health condition or event |
| Measurement | Survival rate, life expectancy, recovery time | Mortality rate, cause-specific deaths, death counts |
| Significance | Indicator of treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes | Indicator of disease burden and public health impact |
| Data Use | Clinical trials, patient monitoring, prognosis estimation | Public health statistics, epidemiology, resource allocation |
| Key Metrics | 5-year survival rate, progression-free survival | Crude mortality rate, age-adjusted mortality rate |
Understanding Survival and Mortality
Survival refers to the duration a living organism continues to exist after exposure to a certain condition or event, often measured in clinical or biological studies to assess treatment efficacy. Mortality indicates the rate or occurrence of death within a specific population or timeframe, serving as a critical metric in public health and epidemiology. Understanding survival and mortality involves analyzing risk factors, intervention outcomes, and statistical survival analysis methods such as Kaplan-Meier estimates and hazard ratios to optimize healthcare strategies.
Key Differences between Survival and Mortality
Survival refers to the duration of life or the continued existence of an individual or population after exposure to a risk or adverse condition, while mortality denotes the incidence or rate of death within a specific population or time frame. Key differences include survival emphasizing life expectancy and the probability of living beyond a certain point, whereas mortality focuses on death occurrence and factors contributing to fatality. Survival analysis often uses metrics like survival rates and hazard ratios, contrasting with mortality statistics such as crude death rates and cause-specific mortality rates.
Factors Influencing Survival Rates
Survival rates are significantly influenced by factors such as age, stage of disease at diagnosis, and access to quality healthcare services. Biological variables like genetic predisposition and immune system strength also play crucial roles in determining mortality outcomes. Socioeconomic status and lifestyle behaviors, including diet and physical activity, further impact the likelihood of survival across different populations.
Determinants of Mortality Outcomes
Determinants of mortality outcomes include socioeconomic status, access to quality healthcare, and underlying health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Environmental factors like pollution exposure and lifestyle choices, including smoking and diet, significantly influence survival rates. Genetic predisposition and timely medical interventions also play critical roles in determining individual mortality risk.
Measuring Survival: Methods and Metrics
Measuring survival involves key methods such as Kaplan-Meier estimation, which calculates survival probabilities over time, and Cox proportional hazards models for analyzing the impact of covariates on survival rates. Common metrics include overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and progression-free survival (PFS), each quantifying different aspects of patient outcomes in clinical studies. Accurate survival analysis helps in comparing treatment efficacy and understanding long-term prognosis across various medical conditions.
Analyzing Mortality: Tools and Techniques
Analyzing mortality involves utilizing statistical tools such as Kaplan-Meier survival curves and Cox proportional hazards models to estimate survival probabilities and identify risk factors. Techniques include cause-specific mortality analysis and competing risks models to differentiate between various death causes. Advanced software like R and SAS facilitates comprehensive data analysis by integrating demographic, clinical, and temporal variables for accurate mortality assessments.
The Role of Healthcare in Survival vs Mortality
Healthcare significantly influences survival rates by providing timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive care that reduce mortality risks from chronic diseases and acute conditions. Access to advanced medical technologies, skilled healthcare professionals, and comprehensive public health initiatives improve life expectancy and quality of life across populations. Health systems that prioritize early intervention and equitable healthcare delivery demonstrate lower mortality rates and higher overall survival outcomes.
Survival Strategies in Life-Threatening Situations
Survival strategies in life-threatening situations rely heavily on quick decision-making, situational awareness, and resourcefulness to increase chances of survival. Techniques such as prioritizing shelter, securing clean water, and signal for rescue are essential components of effective survival plans. Mental resilience and adaptability further enhance an individual's ability to withstand extreme environmental challenges and improve mortality outcomes.
Global Trends in Survival and Mortality
Global trends in survival and mortality reveal significant improvements in life expectancy due to advances in healthcare, vaccination programs, and disease control, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer have become leading causes of mortality worldwide, while infectious diseases have declined. Data from the World Health Organization indicate a steady decrease in child mortality rates and maternal deaths, reflecting progress in medical interventions and public health initiatives.
Improving Survival and Reducing Mortality: Future Directions
Advancing personalized medicine and integrating artificial intelligence in health data analysis enhance early detection and tailored treatments, significantly improving survival rates. Expanding access to preventive care and promoting lifestyle interventions address underlying risk factors, effectively reducing mortality. Ongoing research into novel therapies and real-time patient monitoring technologies promises to transform clinical outcomes and decrease death rates.
Survival Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com