An allergen is a substance that triggers an immune response in sensitive individuals, causing symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe reactions. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods, which can significantly impact your daily life if exposure is not managed. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify, avoid, and treat allergens effectively.
Table of Comparison
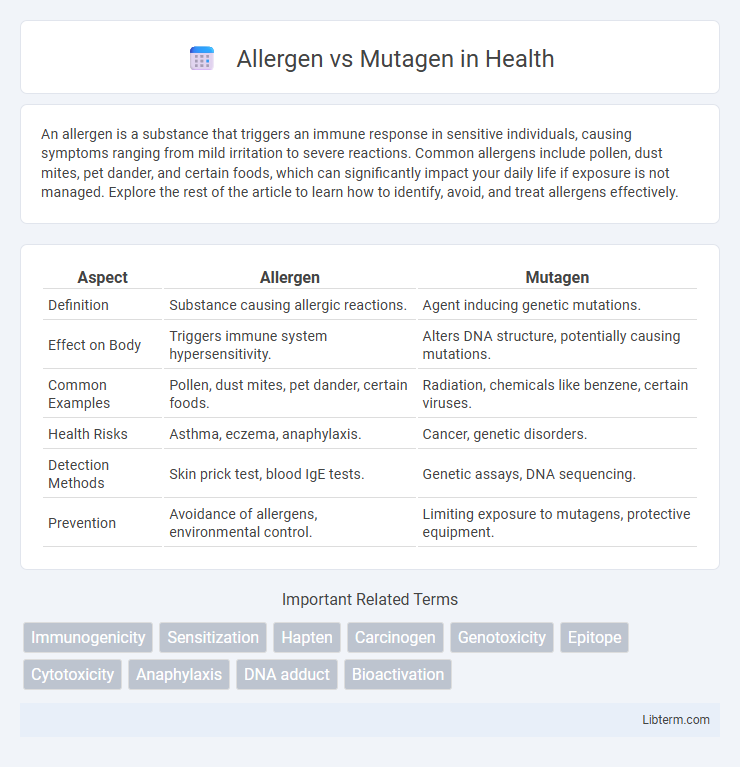
| Aspect | Allergen | Mutagen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substance causing allergic reactions. | Agent inducing genetic mutations. |
| Effect on Body | Triggers immune system hypersensitivity. | Alters DNA structure, potentially causing mutations. |
| Common Examples | Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods. | Radiation, chemicals like benzene, certain viruses. |
| Health Risks | Asthma, eczema, anaphylaxis. | Cancer, genetic disorders. |
| Detection Methods | Skin prick test, blood IgE tests. | Genetic assays, DNA sequencing. |
| Prevention | Avoidance of allergens, environmental control. | Limiting exposure to mutagens, protective equipment. |
Introduction to Allergens and Mutagens
Allergens are substances that trigger immune responses resulting in allergic reactions, commonly found in pollen, dust mites, and certain foods. Mutagens are agents, such as radiation, chemicals, or viruses, that cause genetic mutations, potentially leading to cancer or hereditary diseases. Understanding the distinct biological impacts of allergens and mutagens is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Defining Allergens: What They Are
Allergens are substances that trigger immune system responses, causing allergic reactions in sensitive individuals by mistakenly identifying these substances as harmful. Common allergens include pollen, pet dander, certain foods, and insect stings, which can lead to symptoms such as itching, swelling, respiratory issues, or anaphylaxis. Unlike mutagens that cause genetic mutations, allergens specifically provoke hypersensitivity in the immune system without altering DNA.
Understanding Mutagens: A Brief Overview
Mutagens are agents that cause changes or mutations in DNA sequences, potentially leading to genetic disorders or cancer. Unlike allergens, which trigger immune responses, mutagens directly alter the genetic material, increasing the risk of hereditary or cellular abnormalities. Common examples of mutagens include ultraviolet radiation, certain chemicals like benzo[a]pyrene, and some viruses.
Sources of Allergens in Daily Life
Common sources of allergens in daily life include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and certain foods such as nuts, shellfish, and dairy products. Household products like detergents, fragrances, and latex can also trigger allergic reactions. Understanding these sources helps in managing exposure and reducing the risk of allergic responses effectively.
Common Sources of Mutagens
Mutagens are agents that cause genetic mutations by altering DNA sequences, commonly found in substances like tobacco smoke, ultraviolet radiation, certain chemicals in pesticides, and some industrial pollutants. Unlike allergens that trigger immune responses, mutagens directly impact cellular genetics leading to potential cancer or hereditary diseases. Identifying common sources such as benzene, aflatoxins, and ionizing radiation is critical for minimizing exposure and preventing genetic damage.
How Allergens Affect the Human Body
Allergens trigger immune system responses by stimulating the production of IgE antibodies, leading to symptoms such as inflammation, itching, and respiratory distress. These substances cause hypersensitivity reactions, ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis in susceptible individuals. Unlike mutagens, allergens do not alter DNA but primarily affect immune function through antigen recognition and histamine release.
Mutagenic Effects on DNA and Health
Mutagens induce changes in the DNA sequence, causing mutations that can disrupt genetic integrity and lead to various health issues such as cancer and hereditary disorders. Unlike allergens, which trigger immune responses, mutagenic effects involve direct interaction with genetic material, leading to permanent alterations in nucleotide sequences. Exposure to mutagenic agents like radiation, chemicals, or certain viruses increases the risk of genetic instability, highlighting the importance of monitoring and minimizing contact with such substances to protect human health.
Key Differences Between Allergens and Mutagens
Allergens trigger immune system responses causing allergic reactions, typically involving proteins or substances like pollen, dust mites, or certain foods. Mutagens induce genetic mutations by directly damaging DNA or interfering with replication, often linked to chemicals, radiation, or environmental toxins. The key difference lies in allergens activating hypersensitivity reactions without altering genetic material, whereas mutagens cause hereditary changes and potential long-term genetic damage.
Preventive Measures Against Allergens and Mutagens
Preventive measures against allergens include minimizing exposure by using air purifiers, maintaining clean environments, and avoiding known allergenic substances such as pollen, dust mites, and pet dander. To prevent mutagen exposure, it is essential to use protective equipment when handling chemicals like benzene and formaldehyde, follow safety guidelines for radiation exposure, and consume antioxidants-rich foods that help repair DNA damage. Implementing strict workplace safety protocols and promoting awareness about potential allergenic and mutagenic agents reduce risks and safeguard health.
Conclusion: Importance of Awareness and Safety
Understanding the distinction between allergens and mutagens is critical for maintaining health and safety, as allergens trigger immune responses while mutagens cause DNA damage that can lead to genetic mutations. Awareness of these hazards enables individuals and industries to implement appropriate protective measures, such as using allergen-free materials or minimizing exposure to mutagenic chemicals. Prioritizing safety protocols and continuous education reduces the risk of adverse health effects, promoting safer environments in workplaces and public spaces.
Allergen Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com