Tinnitus is the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears without an external source, often caused by exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or age-related hearing loss. Understanding the triggers and treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life. Discover effective strategies to alleviate tinnitus and protect your hearing in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
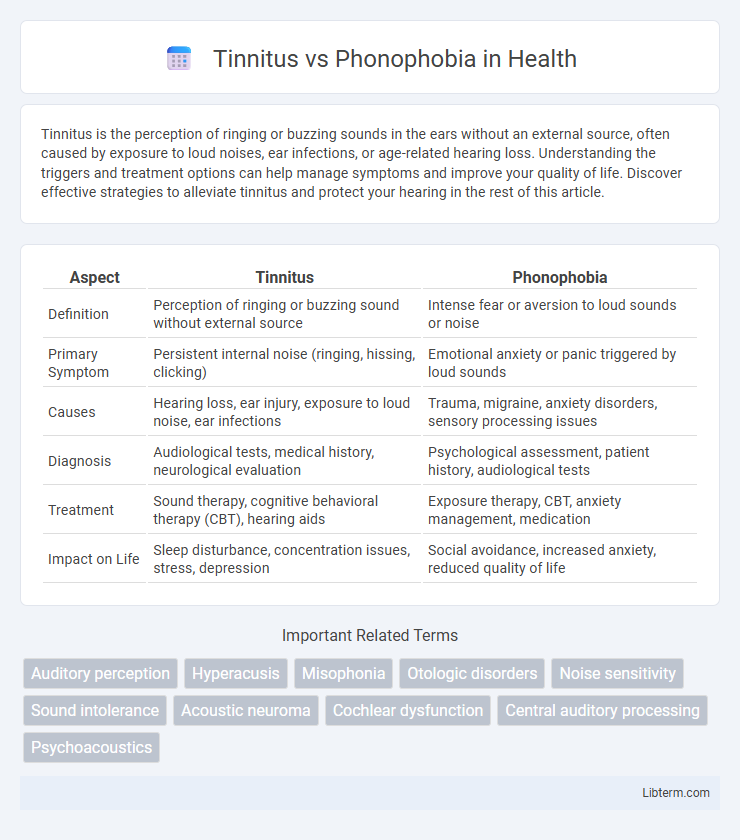
| Aspect | Tinnitus | Phonophobia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Perception of ringing or buzzing sound without external source | Intense fear or aversion to loud sounds or noise |
| Primary Symptom | Persistent internal noise (ringing, hissing, clicking) | Emotional anxiety or panic triggered by loud sounds |
| Causes | Hearing loss, ear injury, exposure to loud noise, ear infections | Trauma, migraine, anxiety disorders, sensory processing issues |
| Diagnosis | Audiological tests, medical history, neurological evaluation | Psychological assessment, patient history, audiological tests |
| Treatment | Sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), hearing aids | Exposure therapy, CBT, anxiety management, medication |
| Impact on Life | Sleep disturbance, concentration issues, stress, depression | Social avoidance, increased anxiety, reduced quality of life |
Understanding Tinnitus: Definition and Causes
Tinnitus is the perception of ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears without external stimuli, often caused by exposure to loud noise, ear infections, or age-related hearing loss. Phonophobia refers to a fear or aversion to loud sounds, frequently associated with migraine or anxiety disorders. Understanding the underlying causes of tinnitus involves identifying auditory system damage or neurological disruptions contributing to the persistent internal noise sensation.
What is Phonophobia? Symptoms and Triggers
Phonophobia is an anxiety disorder characterized by an intense fear or aversion to loud sounds or certain noises, often leading to severe discomfort or panic attacks. Symptoms include heightened sensitivity to everyday noises, increased heart rate, sweating, and avoidance behavior. Common triggers encompass sudden loud noises, crowded environments, and specific pitch frequencies, distinguishing phonophobia from tinnitus, which primarily involves persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears without fear response.
Key Differences Between Tinnitus and Phonophobia
Tinnitus is characterized by the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears without an external source, while phonophobia involves an intense fear or aversion to loud sounds. Tinnitus is a sensory condition often linked to hearing loss or ear damage, whereas phonophobia is a psychological response commonly associated with anxiety or migraine disorders. Understanding these key differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies in auditory and mental health care.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Tinnitus and phonophobia both involve auditory sensitivities but differ significantly in causes and risk factors. Tinnitus commonly arises from noise-induced hearing loss, ear infections, or ototoxic medications, while phonophobia is frequently linked to migraine disorders, anxiety, and hyperacusis. Risk factors for tinnitus include prolonged exposure to loud sounds and age-related hearing degeneration, whereas phonophobia risk is elevated in individuals with neurological conditions and heightened sensory processing sensitivity.
Diagnosing Tinnitus vs Phonophobia
Diagnosing tinnitus involves assessing the presence of persistent or intermittent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears without external stimuli, often through audiometric tests and patient history. Phonophobia diagnosis centers on identifying an abnormal fear or aversion to loud sounds, typically evaluated via psychological assessment and behavioral observations. Differentiation relies on distinguishing auditory perception symptoms in tinnitus from anxiety-driven reactions to noise in phonophobia.
Impact on Daily Life and Mental Health
Tinnitus, characterized by persistent ringing or buzzing in the ears, often leads to difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, and heightened stress levels, significantly affecting daily functioning and mental well-being. Phonophobia, an intense fear or aversion to loud sounds, can cause avoidance behaviors, social withdrawal, and anxiety, impairing social interactions and overall quality of life. Both conditions contribute to increased risks of depression and anxiety disorders, highlighting the necessity for targeted psychological interventions and sound management therapies.
Treatment Options for Tinnitus
Tinnitus treatment options primarily focus on managing symptoms through sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and pharmacological approaches such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications. Advanced treatments include tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT) and neuromodulation techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) aimed at reducing neural hyperactivity. Unlike phonophobia, which often requires behavioral desensitization and anxiety management, tinnitus therapies target auditory perception and neural plasticity to alleviate persistent ringing or buzzing sensations.
Managing Phonophobia: Strategies and Therapies
Managing phonophobia involves cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sound therapy, and gradual desensitization techniques to reduce sensitivity to specific sounds. Use of ear protection devices, combined with stress management strategies, helps alleviate anxiety-triggered reactions. Professional audiological support and personalized treatment plans significantly improve patient outcomes in phonophobia management.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Preventive measures for tinnitus include avoiding prolonged exposure to loud noises, using ear protection in noisy environments, and managing stress levels through relaxation techniques. For phonophobia, limiting exposure to sudden or intense sounds, establishing a calm and quiet environment, and seeking cognitive behavioral therapy can be effective. Both conditions benefit from regular hearing check-ups, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding caffeine and nicotine to reduce symptom severity.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help for tinnitus if persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears disrupt daily life, especially when accompanied by hearing loss or dizziness. Phonophobia requires medical attention when intense fear or anxiety triggered by certain sounds leads to avoidance behaviors or impairs social functioning. Early consultation with an audiologist or otolaryngologist ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies for both conditions.
Tinnitus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com