Aversion is a psychological response characterized by an intense dislike or avoidance of certain stimuli, situations, or behaviors that cause discomfort or distress. Understanding the underlying causes and manifestations of aversion can help you manage and reduce its impact on daily life. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective strategies for overcoming aversion and improving your well-being.
Table of Comparison
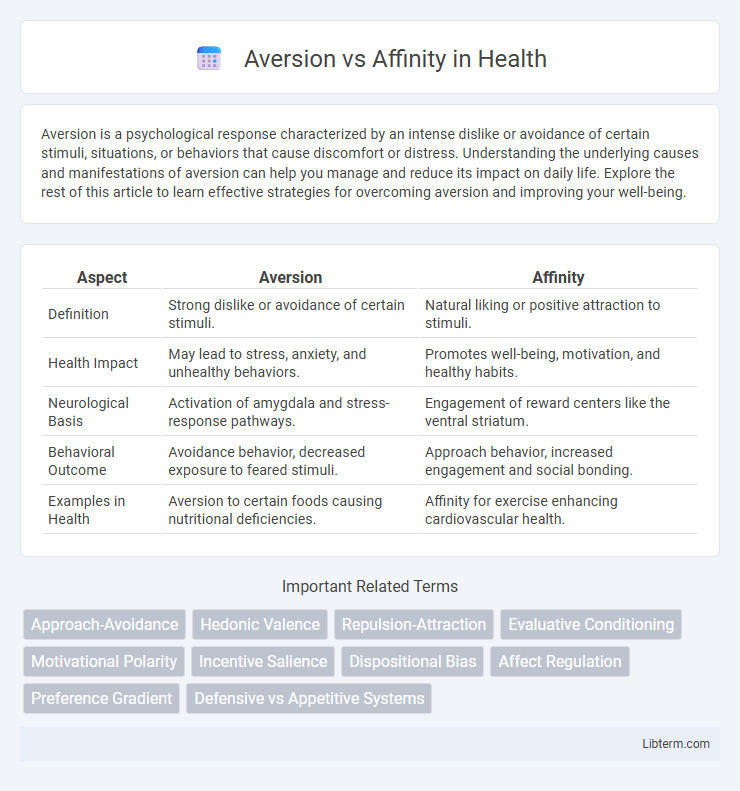
| Aspect | Aversion | Affinity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong dislike or avoidance of certain stimuli. | Natural liking or positive attraction to stimuli. |
| Health Impact | May lead to stress, anxiety, and unhealthy behaviors. | Promotes well-being, motivation, and healthy habits. |
| Neurological Basis | Activation of amygdala and stress-response pathways. | Engagement of reward centers like the ventral striatum. |
| Behavioral Outcome | Avoidance behavior, decreased exposure to feared stimuli. | Approach behavior, increased engagement and social bonding. |
| Examples in Health | Aversion to certain foods causing nutritional deficiencies. | Affinity for exercise enhancing cardiovascular health. |
Understanding Aversion and Affinity
Aversion and affinity represent opposite emotional responses toward people, objects, or ideas, where aversion involves feelings of dislike or avoidance, and affinity signifies attraction or a strong positive connection. These responses are driven by complex psychological and neurological processes, influencing behavior and decision-making. Understanding aversion and affinity enables better management of interpersonal relationships and enhances emotional intelligence in various social and professional contexts.
Defining Aversion: Causes and Manifestations
Aversion originates from negative experiences, fear, or discomfort linked to specific stimuli, leading to avoidance behaviors and emotional distress. Common causes include traumatic events, learned associations, and innate predispositions that trigger physiological responses such as increased heart rate and sweating. Manifestations of aversion often appear as physical withdrawal, verbal rejection, or psychological resistance towards particular objects, situations, or individuals.
Exploring Affinity: Roots and Expressions
Affinity originates from shared values, interests, or experiences that foster strong emotional connections and mutual understanding between individuals or groups. Expressions of affinity include collaborative efforts, positive communication, and empathetic behaviors that enhance social bonding and group cohesion. Neuroscientific studies highlight increased activation in reward-related brain regions when individuals engage with those they feel affinity toward, reinforcing these social connections.
Psychological Factors Influencing Aversion
Psychological factors influencing aversion include negative past experiences, cognitive biases, and emotional responses that shape an individual's avoidance behavior. Neurobiological mechanisms, such as heightened amygdala activity, enhance sensitivity to perceived threats, reinforcing aversion patterns. Understanding these factors provides insight into behavioral tendencies and informs therapeutic interventions targeting maladaptive aversions.
Social Dynamics Shaping Affinity
Social dynamics shaping affinity revolve around shared values, mutual interests, and reciprocal trust, which foster strong interpersonal connections. Group affiliations, cultural norms, and positive interactions enhance emotional bonding and collective identity, reinforcing a sense of belonging. These factors drive affinity by creating environments where individuals feel understood, accepted, and valued within social networks.
Aversion and Affinity in Decision-Making
Aversion and affinity significantly influence decision-making by shaping preferences and risk assessments. Aversion drives individuals to avoid options that pose potential losses or discomfort, often leading to conservative choices, while affinity encourages selection based on positive associations and emotional appeal, facilitating risk-taking or preference for familiar alternatives. Understanding the balance between aversion and affinity enhances predictions of consumer behavior and strategic decision outcomes.
Impacts on Relationships and Communication
Aversion can create barriers in relationships by fostering mistrust and reducing openness, leading to miscommunication and conflict escalation. Affinity, on the other hand, enhances rapport and emotional connection, facilitating clearer and more empathetic communication. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for improving interpersonal interactions and achieving effective dialogue.
Cultural Perspectives on Aversion and Affinity
Cultural perspectives on aversion and affinity influence social interactions and emotional responses across societies, shaping collective behaviors and values. In collectivist cultures, affinity often emphasizes group harmony and social cohesion, while aversion may arise from behaviors perceived as disrespectful or disruptive to communal norms. Contrarily, individualistic cultures may prioritize personal preferences and aversions, reflecting autonomy and self-expression over collective agreement.
Managing Aversion: Practical Strategies
Managing aversion involves identifying triggers and employing cognitive restructuring techniques to reduce negative reactions. Mindfulness practices help increase awareness of aversive feelings, enabling individuals to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Exposure therapy and gradual desensitization also serve as effective methods to lessen avoidance behavior and build affinity towards previously avoided stimuli.
Enhancing Affinity for Positive Outcomes
Enhancing affinity involves building strong emotional connections and trust between individuals or groups, which leads to improved collaboration and positive outcomes. Techniques such as active listening, empathy, and consistent positive reinforcement significantly increase affinity, fostering a supportive environment. Organizations that prioritize affinity experience higher employee engagement, customer loyalty, and overall better performance.
Aversion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com