Scotophobia, or the fear of darkness, can significantly impact your daily life by causing anxiety and avoidance behaviors during nighttime or in dimly lit environments. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective coping strategies is essential for managing this common phobia. Explore the rest of the article to learn how you can overcome scotophobia and regain your confidence in the dark.
Table of Comparison
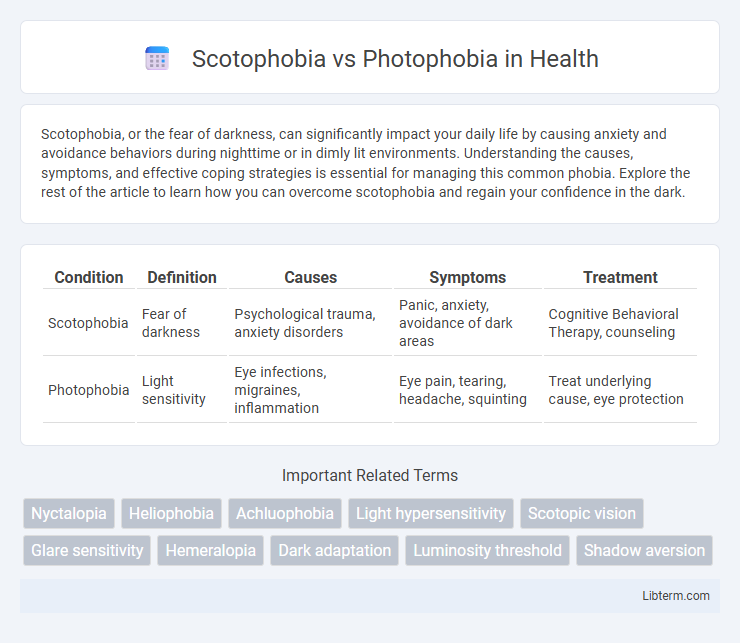
| Condition | Definition | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scotophobia | Fear of darkness | Psychological trauma, anxiety disorders | Panic, anxiety, avoidance of dark areas | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, counseling |
| Photophobia | Light sensitivity | Eye infections, migraines, inflammation | Eye pain, tearing, headache, squinting | Treat underlying cause, eye protection |
Understanding Scotophobia: Definition and Origins
Scotophobia is a specific fear or aversion to darkness, often rooted in psychological or developmental factors, distinguishing it from photophobia, which is a medical condition characterized by light sensitivity. Scotophobia originates from the Greek words "skotos" meaning darkness and "phobia" meaning fear, reflecting an intense discomfort or anxiety experienced in dark environments. Understanding scotophobia involves recognizing its emotional and cognitive impacts, which can lead to avoidance behaviors and affect daily activities in low-light situations.
What is Photophobia? Medical Context Explained
Photophobia is a medical symptom characterized by an abnormal sensitivity to light, causing discomfort or pain in the eyes when exposed to bright environments. It is often associated with conditions such as migraines, meningitis, eye injuries, or inflammation like uveitis and conjunctivitis. Unlike Scotophobia, which is a fear of darkness, photophobia specifically refers to the physical reaction and sensitivity to light stimuli.
Key Differences Between Scotophobia and Photophobia
Scotophobia is the fear of darkness, causing anxiety or panic in dim or dark environments, whereas photophobia is a medical symptom characterized by an abnormal sensitivity or discomfort to bright light or glare. Scotophobia primarily involves psychological responses triggered by darkness, while photophobia is associated with neurological or ocular conditions such as migraines, meningitis, or eye inflammation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment, with scotophobia often addressed through therapy and photophobia managed based on underlying medical causes.
Psychological vs Physiological Roots
Scotophobia, an intense fear of darkness, originates primarily from psychological factors such as anxiety disorders or traumatic childhood experiences. Photophobia, characterized by hypersensitivity to light, stems from physiological causes including migraines, eye inflammation, or neurological conditions. Distinguishing between the psychological roots of Scotophobia and the physiological basis of Photophobia is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment strategies.
Symptoms of Scotophobia vs Photophobia
Scotophobia is characterized by intense fear or anxiety associated with darkness, leading to symptoms such as panic attacks, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and avoidance of dark environments. Photophobia, on the other hand, manifests as heightened sensitivity to light, causing symptoms like eye pain, squinting, excessive tearing, headaches, and discomfort in well-lit settings. Differentiating between scotophobia and photophobia is essential for targeted treatment, as the former involves psychological distress while the latter results from physiological light intolerance.
Causes and Risk Factors
Scotophobia, the fear of darkness, often stems from traumatic childhood experiences, anxiety disorders, or underlying phobias, while photophobia, sensitivity to light, is commonly caused by eye conditions such as migraines, meningitis, or corneal abrasions. Risk factors for scotophobia include a history of anxiety, PTSD, or specific traumatic events related to darkness, whereas photophobia risk factors encompass neurological disorders, eye infections, and chronic inflammation. Understanding these distinct causes and risk factors is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Diagnosis and Assessment Methods
Scotophobia, the fear of darkness, is primarily diagnosed through psychological evaluations, including clinical interviews and standardized anxiety or phobia questionnaires to assess symptom severity and impact on daily functioning. Photophobia, characterized by light sensitivity, is assessed using ophthalmologic examinations such as slit-lamp biomicroscopy, pupillary light reflex tests, and detailed patient history to identify underlying causes like migraines or ocular inflammation. Accurate differentiation between scotophobia and photophobia relies on combining mental health assessments with targeted eye examinations to guide appropriate treatment strategies.
Available Treatment Options
Available treatment options for Scotophobia, the fear of darkness, primarily include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and anti-anxiety medications to address underlying psychological causes. Photophobia, or light sensitivity, is managed by treating the underlying conditions such as migraines, eye infections, or corneal abrasions and using tinted glasses, artificial tears, or prescribed medications like antihistamines. Customized treatment plans combining psychological interventions for Scotophobia and medical management for Photophobia improve patient outcomes effectively.
Coping Strategies and Management Tips
Coping with Scotophobia involves gradual exposure therapy and relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety associated with darkness, while Photophobia requires managing light sensitivity through the use of tinted lenses, controlled lighting environments, and avoiding glare. Both conditions benefit from professional medical evaluation to address underlying causes, complemented by supportive behavioral adjustments like practicing mindfulness and using assistive devices. Consistent adherence to tailored management plans improves quality of life by mitigating symptoms and enhancing daily functioning.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help for Scotophobia if persistent fear of darkness disrupts daily life, causes intense anxiety, or leads to avoidance behaviors. Consult a healthcare provider for Photophobia when light sensitivity results in severe headaches, eye pain, blurred vision, or significantly impairs vision. Early diagnosis by a specialist can prevent complications and guide effective treatment for both conditions.
Scotophobia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com