Spirometry and peak flow meters are essential tools for assessing lung function and monitoring respiratory conditions such as asthma and COPD. Spirometry measures the volume and speed of air you can exhale, providing detailed information about lung capacity and airway obstruction, while peak flow meters offer a quick and convenient way to track peak expiratory flow rates at home. Explore the rest of the article to learn how these tests can help you manage your respiratory health effectively.
Table of Comparison
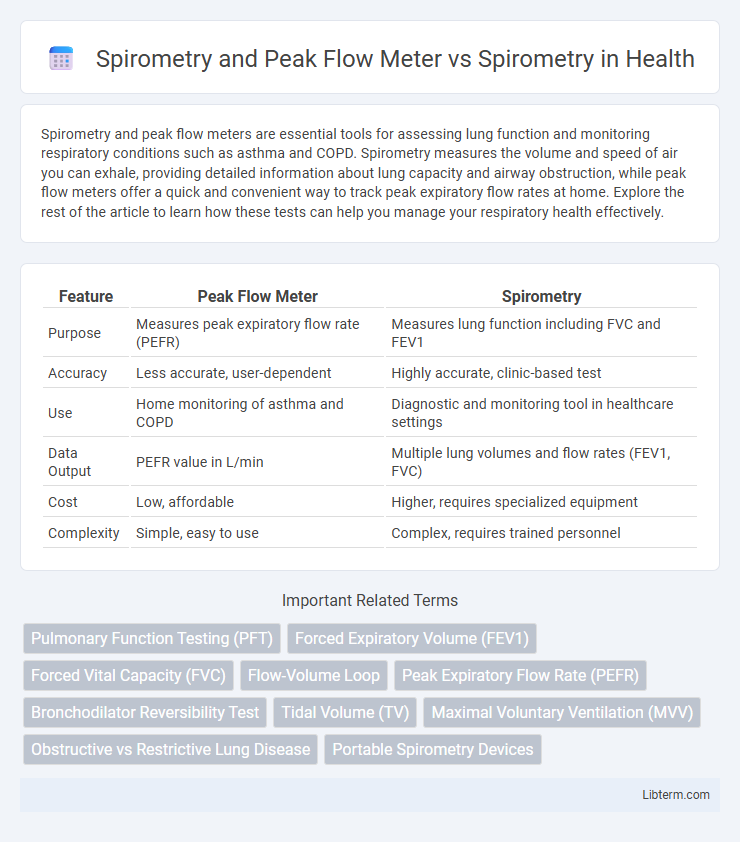
| Feature | Peak Flow Meter | Spirometry |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) | Measures lung function including FVC and FEV1 |
| Accuracy | Less accurate, user-dependent | Highly accurate, clinic-based test |
| Use | Home monitoring of asthma and COPD | Diagnostic and monitoring tool in healthcare settings |
| Data Output | PEFR value in L/min | Multiple lung volumes and flow rates (FEV1, FVC) |
| Cost | Low, affordable | Higher, requires specialized equipment |
| Complexity | Simple, easy to use | Complex, requires trained personnel |
Introduction: Understanding Spirometry and Peak Flow Meters
Spirometry measures lung function by assessing the volume and flow of air inhaled and exhaled, providing detailed insights into respiratory health. Peak flow meters record the maximum speed of expiration, offering a quick and simple way to monitor airway obstruction, particularly in asthma management. Both tools are essential for diagnosing and monitoring respiratory conditions but differ in complexity, precision, and clinical application.
What is Spirometry?
Spirometry is a diagnostic test that measures lung function by assessing the volume and flow of air inhaled and exhaled, providing critical data on respiratory health such as forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). Unlike a peak flow meter, which only measures the maximum speed of expiration, spirometry offers a comprehensive evaluation of lung volumes and airflow patterns essential for diagnosing conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung disease. Spirometry results guide treatment decisions by quantifying airway obstruction and lung capacity, making it a gold standard tool in pulmonary function testing.
What is a Peak Flow Meter?
A Peak Flow Meter is a portable device used to measure the maximum speed of expiration, helping monitor lung function in asthma patients by assessing airway obstruction. Spirometry, in contrast, provides a comprehensive evaluation of lung volumes and airflow rates during forced breathing maneuvers, offering detailed diagnostic insights for respiratory conditions. Peak Flow Meters are ideal for daily home monitoring, while spirometry is typically performed in clinical settings for thorough respiratory assessment.
Key Differences Between Spirometry and Peak Flow Meter
Spirometry measures multiple lung volumes and capacities, providing detailed information on lung function and airway obstruction, while a peak flow meter solely measures peak expiratory flow rate to assess airway narrowing. Spirometry requires calibrated equipment and trained personnel for accurate testing, whereas peak flow meters are portable, inexpensive, and designed for daily self-monitoring by patients. The comprehensive data from spirometry aids in diagnosing and managing respiratory diseases like asthma and COPD, whereas peak flow meters help monitor asthma control and detect early signs of exacerbation.
Advantages of Using Spirometry
Spirometry offers comprehensive measurements of lung function, including forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), enabling precise diagnosis and monitoring of respiratory diseases like asthma and COPD. Spirometry provides detailed data on airflow obstruction and restriction, which cannot be captured by peak flow meters that only measure peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR). This detailed functional assessment allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans more effectively and track disease progression with higher accuracy.
Benefits of Peak Flow Meters for Asthma Management
Peak flow meters provide quick, convenient, and cost-effective monitoring of airway obstruction, allowing asthma patients to track their lung function daily and detect exacerbations early. Unlike spirometry, peak flow measurements can be performed at home without specialized training or equipment, facilitating timely intervention and personalized asthma action plans. Regular use of peak flow meters improves asthma control by helping patients and healthcare providers identify triggers and adjust medications promptly.
Limitations of Spirometry and Peak Flow Meters
Spirometry provides comprehensive measurements of lung function but requires proper patient cooperation and skilled technicians, making it less practical for frequent home monitoring. Peak flow meters offer simplicity and portability for daily asthma management but only measure peak expiratory flow, limiting their ability to detect early or subtle changes in airway obstruction. Both tools may produce variable results influenced by user effort, leading to potential inaccuracies in diagnosing and monitoring respiratory conditions.
When to Choose Spirometry Over Peak Flow
Spirometry provides comprehensive measurements of lung function, including forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), making it ideal for diagnosing and monitoring chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD. Peak flow meters offer quick, daily monitoring of airway obstruction but lack the detailed assessment available in spirometry. Choose spirometry over peak flow when precise evaluation of lung function, detection of restrictive or obstructive patterns, and accurate diagnosis are required.
Clinical Applications: Spirometry vs Peak Flow Meter
Spirometry provides comprehensive lung function assessment by measuring volumes such as FEV1 and FVC, essential for diagnosing and monitoring chronic respiratory diseases like asthma and COPD. Peak flow meters offer rapid, daily monitoring of peak expiratory flow rates, useful for asthma self-management and detecting airflow variations at home. Clinicians rely on spirometry for detailed, diagnostic evaluation while peak flow meters serve as practical tools for patient-driven symptom tracking and early intervention.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Test for Respiratory Assessment
Spirometry provides a comprehensive evaluation of lung function by measuring volumes and airflow rates critical for diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions such as asthma, COPD, and restrictive lung diseases. Peak flow meters offer a convenient, portable method for monitoring airway obstruction and daily variability, particularly useful in asthma self-management but lack the detailed diagnostic capability of spirometry. Selecting the appropriate test depends on clinical needs, with spirometry preferred for detailed pulmonary assessment and diagnosis, while peak flow meters serve well for ongoing self-monitoring and control of known respiratory conditions.
Spirometry and Peak Flow Meter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com