Disorder disrupts the natural balance and orderliness of systems, leading to confusion and inefficiency in both physical and mental environments. Understanding the causes and effects of disorder can help you develop strategies to restore harmony and improve overall functionality. Explore the following article to learn how to manage and transform disorder into order effectively.
Table of Comparison
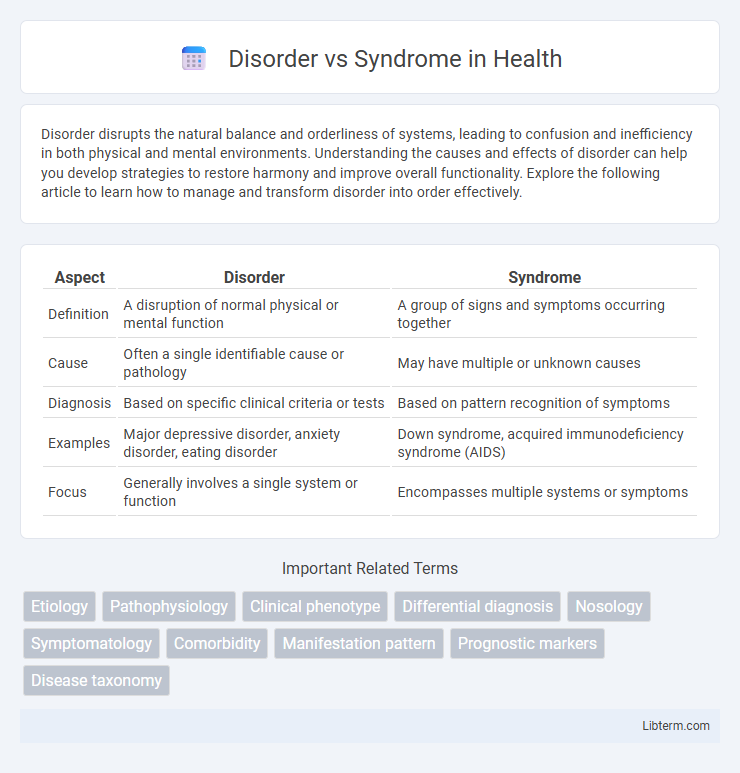
| Aspect | Disorder | Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A disruption of normal physical or mental function | A group of signs and symptoms occurring together |
| Cause | Often a single identifiable cause or pathology | May have multiple or unknown causes |
| Diagnosis | Based on specific clinical criteria or tests | Based on pattern recognition of symptoms |
| Examples | Major depressive disorder, anxiety disorder, eating disorder | Down syndrome, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) |
| Focus | Generally involves a single system or function | Encompasses multiple systems or symptoms |
Understanding the Terms: Disorder vs Syndrome
A disorder refers to a disruption of normal physical or mental functions, often characterized by a set of symptoms and signs that impair health or quality of life. A syndrome, on the other hand, is a collection of symptoms and clinical features that consistently occur together, indicating a particular abnormal condition but not necessarily pointing to a single cause. Understanding the distinction between disorder and syndrome is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and communication in medical and psychological contexts.
Defining "Disorder": Key Characteristics
A disorder is characterized by a disruption in normal physical or mental functions, typically identifiable through consistent symptoms and diagnostic criteria. It often involves a defined etiology or underlying cause, such as genetic, biochemical, or environmental factors. Unlike a syndrome, a disorder usually implies a pathological process affecting an individual's health or behavior.
What Constitutes a "Syndrome"?
A syndrome constitutes a set of medical signs, symptoms, and phenomena that occur together and characterize a particular abnormality or condition. Unlike a disorder, which refers broadly to any disruption of normal physical or mental functions, a syndrome specifically defines a recognizable pattern of symptoms that may have a known or unknown cause. Accurate identification of a syndrome is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and understanding its underlying pathology.
Differences in Diagnosis and Classification
Disorder refers to a disruption of normal physical or mental functions characterized by specific symptoms and signs, often diagnosed through standardized criteria such as the DSM-5 or ICD-11. Syndrome describes a collection of symptoms and clinical features that consistently occur together, but may not point to a specific underlying cause, making diagnosis more symptom-based and less definitive. Classification of disorders typically involves identifying distinct pathological mechanisms, while syndromes are grouped phenomenologically, emphasizing symptom patterns over etiology.
Underlying Causes: Disorder vs Syndrome
A disorder refers to a disruption in normal physical or mental functioning typically linked to identifiable underlying causes such as genetic mutations, infections, or environmental factors. Syndromes consist of a collection of symptoms and signs that occur together but may not have a clearly defined cause, often serving as a clinical pattern rather than a specific diagnosis. Understanding the etiological differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies in medical practice.
Common Examples: Disorders and Syndromes
Disorders such as anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, and bipolar disorder involve specific patterns of symptoms affecting mental health and behavior, often with identifiable causes and diagnostic criteria. Syndromes like Down syndrome, metabolic syndrome, and irritable bowel syndrome represent clusters of signs and symptoms that commonly occur together but may have varied underlying causes. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, highlighting the importance of comprehensive clinical evaluation.
Medical Perspectives: How Professionals Distinguish
Medical professionals distinguish between disorder and syndrome based on specificity and diagnostic criteria, where a disorder refers to a recognized set of symptoms with a known cause or pathology, while a syndrome represents a collection of symptoms that occur together without a fully understood etiology. Disorders often have established diagnostic tests or biomarkers, enabling precise identification, whereas syndromes require clinicians to interpret symptom clusters and patterns for diagnosis. This differentiation guides treatment planning and prognosis by framing the underlying mechanisms and clinical expectations.
Implications for Treatment and Management
Disorders often reflect a broader range of symptoms with variable causes, requiring personalized treatment approaches tailored to underlying factors such as genetics or environment. Syndromes consist of a specific set of symptoms that consistently appear together, allowing for more standardized management protocols based on established clinical patterns. Treatment for disorders may involve multifaceted strategies addressing mental, physical, and social aspects, whereas syndromes typically benefit from targeted therapies aimed at the defined symptom cluster.
Misconceptions and Overlaps
Disorder and syndrome are often mistakenly used interchangeably, though a disorder typically refers to a specific medical or psychological condition with defined symptoms and causes, while a syndrome denotes a collection of symptoms that may arise from various conditions. Misconceptions arise because syndromes can encompass multiple disorders or conditions, leading to overlap and confusion in diagnosis and treatment. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate clinical assessments and effective patient management.
Key Takeaways: Choosing the Right Term
Disorder refers to a disruption of normal physical or mental functions, often with identifiable causes, while syndrome describes a group of symptoms that consistently occur together without a singular known cause. Choosing the right term depends on the clarity of underlying pathology and symptom patterns, with disorders typically having more defined diagnostic criteria. Accurate usage enhances communication in medical diagnosis, research, and treatment planning.
Disorder Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com