Ear tube insertion is a common surgical procedure used to treat chronic ear infections or persistent fluid buildup in the middle ear, improving hearing and reducing discomfort. The procedure involves placing small tubes in the eardrum to allow air to enter the middle ear and fluid to drain out. Discover more about the benefits, risks, and recovery process to understand if this treatment is right for you.
Table of Comparison
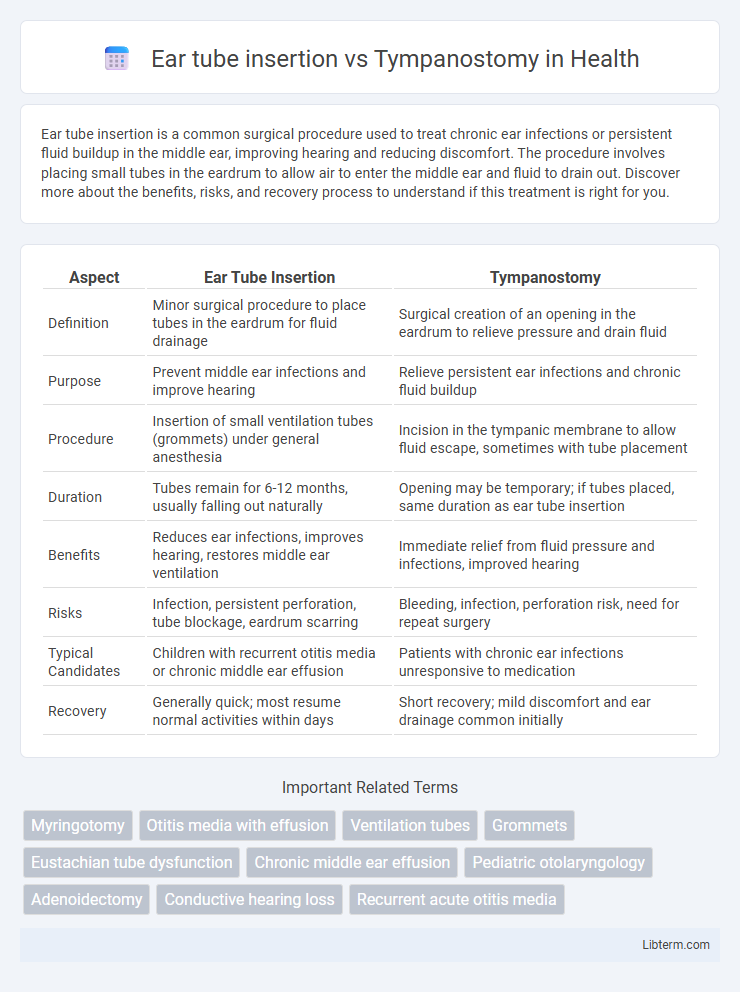
| Aspect | Ear Tube Insertion | Tympanostomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minor surgical procedure to place tubes in the eardrum for fluid drainage | Surgical creation of an opening in the eardrum to relieve pressure and drain fluid |
| Purpose | Prevent middle ear infections and improve hearing | Relieve persistent ear infections and chronic fluid buildup |
| Procedure | Insertion of small ventilation tubes (grommets) under general anesthesia | Incision in the tympanic membrane to allow fluid escape, sometimes with tube placement |
| Duration | Tubes remain for 6-12 months, usually falling out naturally | Opening may be temporary; if tubes placed, same duration as ear tube insertion |
| Benefits | Reduces ear infections, improves hearing, restores middle ear ventilation | Immediate relief from fluid pressure and infections, improved hearing |
| Risks | Infection, persistent perforation, tube blockage, eardrum scarring | Bleeding, infection, perforation risk, need for repeat surgery |
| Typical Candidates | Children with recurrent otitis media or chronic middle ear effusion | Patients with chronic ear infections unresponsive to medication |
| Recovery | Generally quick; most resume normal activities within days | Short recovery; mild discomfort and ear drainage common initially |
Understanding Ear Tube Insertion
Ear tube insertion, also known as tympanostomy, involves placing small tubes in the eardrum to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid buildup. This procedure is commonly performed to treat chronic otitis media with effusion and recurrent ear infections, improving hearing and reducing discomfort. Understanding ear tube insertion highlights its role in maintaining middle ear pressure and preventing complications related to prolonged fluid retention.
What Is Tympanostomy?
Tympanostomy is a surgical procedure that involves creating a small incision in the eardrum to insert a tiny tube, known as an ear tube, which helps ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid buildup. This intervention is commonly used to treat recurrent ear infections or chronic otitis media with effusion, enhancing hearing and reducing discomfort. The terms ear tube insertion and tympanostomy often refer to the same treatment, with tympanostomy emphasizing the surgical aspect of placing the ear tube.
Indications for Ear Tube Placement
Ear tube insertion, also known as tympanostomy, is primarily indicated for recurrent otitis media with effusion lasting more than three months and associated hearing loss exceeding 20 dB. It is recommended for children with persistent middle ear fluid causing speech delay or balance problems, as well as adults experiencing chronic eustachian tube dysfunction. Indications also include frequent acute otitis media episodes, typically defined as three infections in six months or four infections in one year.
Common Causes for Tympanostomy
Ear tube insertion and tympanostomy both address middle ear problems by facilitating fluid drainage and pressure equalization. Common causes for tympanostomy include recurrent otitis media with effusion, chronic middle ear infections, and persistent hearing loss due to fluid buildup. This procedure effectively reduces the risk of complications and improves auditory function in affected patients.
Ear Tube Insertion Procedure Overview
Ear tube insertion, also known as tympanostomy, involves placing small tubes into the eardrum to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid accumulation. The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia, where a tiny incision (myringotomy) is made in the eardrum followed by the insertion of the tube to maintain aeration. This method effectively treats recurrent otitis media and chronic middle ear effusion by equalizing pressure and reducing infection risk.
Tympanostomy: Step-by-Step Process
Tympanostomy involves creating a small incision in the eardrum to insert a tiny tube, allowing air to enter the middle ear and prevent fluid buildup. The process begins with local or general anesthesia, followed by careful incision and fluid suction if present, then placement of the ventilation tube. This procedure effectively reduces recurrent ear infections and improves hearing by maintaining proper ear ventilation.
Benefits of Ear Tube Insertion
Ear tube insertion offers significant relief from chronic otitis media by ventilating the middle ear and preventing fluid accumulation, which reduces the frequency and severity of ear infections. This procedure improves hearing and speech development in children by maintaining proper ear pressure and reducing the risk of hearing loss. Ear tube insertion is minimally invasive with quick recovery, making it a preferred treatment for persistent middle ear issues compared to traditional tympanostomy.
Risks and Complications of Tympanostomy
Tympanostomy, also known as ear tube insertion, carries risks such as infection, persistent ear drainage, and possible eardrum scarring. Complications may include tympanic membrane perforation and temporary hearing loss. Close monitoring after the procedure is essential to manage adverse effects and ensure proper healing.
Aftercare and Recovery for Both Procedures
Ear tube insertion and tympanostomy involve placing small tubes in the eardrum to drain fluid and equalize pressure. Aftercare requires keeping water out of the ears, avoiding ear infections, and monitoring for signs of complications such as persistent pain or discharge. Recovery typically takes a few days, with normal activities resumed quickly, but follow-up appointments are essential to ensure proper tube function and healing.
Comparing Outcomes: Ear Tube Insertion vs Tympanostomy
Ear tube insertion and tympanostomy are often used interchangeably, yet the latter specifically refers to the surgical procedure creating an incision in the eardrum to insert the tubes. Outcomes of ear tube insertion typically show significant improvement in middle ear ventilation and recurrent otitis media reduction, with success rates exceeding 80%. Tympanostomy outcomes emphasize rapid symptom relief and low complication rates, with both procedures demonstrating comparable efficacy in restoring hearing function and preventing middle ear infections.
Ear tube insertion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com