Watchful waiting involves carefully monitoring a medical condition without immediate intervention, allowing time to assess whether symptoms worsen or improve. This approach is often recommended for slow-progressing or mild conditions where treatment risks may outweigh potential benefits. Discover how watchful waiting can impact your health and when it's the best strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
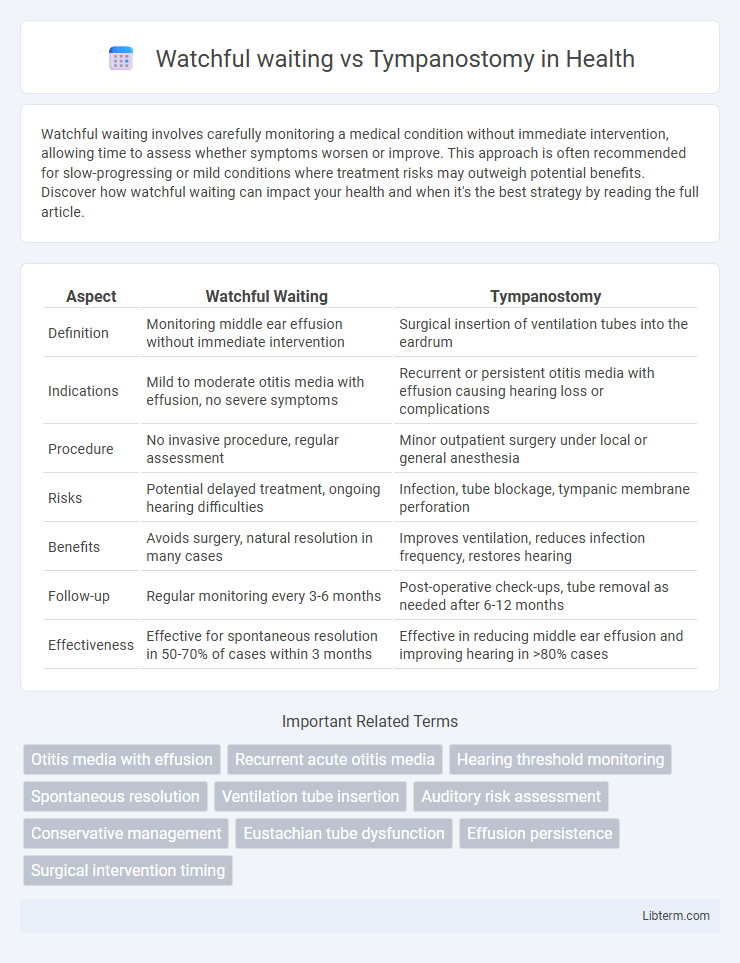
| Aspect | Watchful Waiting | Tympanostomy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitoring middle ear effusion without immediate intervention | Surgical insertion of ventilation tubes into the eardrum |
| Indications | Mild to moderate otitis media with effusion, no severe symptoms | Recurrent or persistent otitis media with effusion causing hearing loss or complications |
| Procedure | No invasive procedure, regular assessment | Minor outpatient surgery under local or general anesthesia |
| Risks | Potential delayed treatment, ongoing hearing difficulties | Infection, tube blockage, tympanic membrane perforation |
| Benefits | Avoids surgery, natural resolution in many cases | Improves ventilation, reduces infection frequency, restores hearing |
| Follow-up | Regular monitoring every 3-6 months | Post-operative check-ups, tube removal as needed after 6-12 months |
| Effectiveness | Effective for spontaneous resolution in 50-70% of cases within 3 months | Effective in reducing middle ear effusion and improving hearing in >80% cases |
Understanding Otitis Media: A Common Childhood Issue
Otitis media, a frequent childhood ear infection, often prompts decisions between watchful waiting and tympanostomy to manage symptoms and complications. Watchful waiting involves monitoring the condition without immediate intervention, appropriate for cases where symptoms are mild and expected to resolve spontaneously. Tympanostomy, the surgical insertion of ear tubes, is recommended for recurrent or persistent otitis media, enhancing middle ear ventilation and fluid drainage to prevent hearing loss and further infections.
What is Watchful Waiting?
Watchful waiting is a conservative approach primarily used to monitor children with otitis media with effusion (OME) or mild recurrent ear infections without immediate surgical intervention. This strategy involves regular medical evaluations to track symptom progression and decide if tympanostomy, the surgical insertion of ear tubes, becomes necessary. Research indicates that many cases resolve spontaneously within 3 months, reducing the need for tympanostomy and associated risks.
Tympanostomy Tubes: An Overview
Tympanostomy tubes, also known as ear tubes, are small cylinders inserted into the eardrum to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid accumulation, commonly used in children with recurrent otitis media or persistent middle ear effusion. This surgical intervention offers faster relief from symptoms such as hearing loss and ear pain compared to watchful waiting, which involves monitoring without immediate medical treatment. Clinical outcomes demonstrate that tympanostomy tubes reduce infection frequency and improve hearing, making them a preferred option when conservative management fails.
Indications for Each Treatment Approach
Watchful waiting is indicated for children with acute otitis media (AOM) presenting mild symptoms, age over 6 months, and uncertain diagnosis, allowing spontaneous recovery without immediate intervention. Tympanostomy tubes are recommended for recurrent AOM (three or more episodes in six months or four within a year) or persistent middle ear effusion lasting more than three months with hearing loss or balance issues. Clinical guidelines emphasize tympanostomy when AOM negatively impacts quality of life or causes complications, while watchful waiting prioritizes minimizing surgical risks in less severe cases.
Effectiveness: Comparing Outcomes
Watchful waiting effectively manages many cases of otitis media with effusion, showing spontaneous resolution in approximately 80% of children within three months. Tympanostomy tube insertion offers faster symptom relief and improved hearing by facilitating fluid drainage, with success rates exceeding 90% in reducing recurrent infections and hearing loss. Comparing outcomes, tympanostomy demonstrates superior short-term effectiveness, but watchful waiting remains a recommended initial approach for mild or non-severe cases to avoid surgical risks.
Risks and Benefits of Watchful Waiting
Watchful waiting for otitis media with effusion avoids surgical risks such as anesthesia complications, infection, and tympanostomy tube extrusion but carries the risk of prolonged hearing loss and potential speech delays in young children. This approach reduces unnecessary surgeries and associated healthcare costs while allowing many effusions to resolve spontaneously within three months. However, persistent effusion beyond 3 months or worsening symptoms may necessitate tympanostomy tube insertion for improved middle ear ventilation and hearing outcomes.
Risks and Benefits of Tympanostomy Tubes
Tympanostomy tubes offer significant benefits for children with recurrent otitis media by improving middle ear ventilation and reducing the frequency of infections, potentially preventing hearing loss and speech delays. Risks include possible complications such as persistent perforation, otorrhea, and the need for additional surgeries, though these are generally infrequent and manageable. Watchful waiting avoids surgical risks but may prolong symptoms and delay resolution of middle ear effusion, impacting hearing and quality of life.
Impact on Hearing and Child Development
Watchful waiting in cases of otitis media with effusion often results in spontaneous resolution, minimizing unnecessary interventions but may delay hearing improvement, potentially affecting speech and language development in children. Tympanostomy tubes facilitate immediate middle ear ventilation, which can rapidly restore hearing and reduce the risk of developmental delays related to auditory deficits. Studies indicate that early tympanostomy placement is linked to improved auditory outcomes and better language acquisition milestones in children with persistent effusions.
Parental Preferences and Informed Decision-Making
Parental preferences play a critical role in choosing between watchful waiting and tympanostomy for managing recurrent otitis media, with many parents favoring minimally invasive options to avoid surgical risks. Informed decision-making hinges on clear communication from healthcare providers about the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of both approaches to align treatment with family values and lifestyle. Studies indicate that parents who receive comprehensive counseling are more confident and satisfied with their choice, ultimately improving adherence and health outcomes for their children.
Current Guidelines and Best Practices
Current guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend watchful waiting as the first-line management for children with uncomplicated otitis media with effusion lasting less than three months, emphasizing careful monitoring for spontaneous resolution. Tympanostomy tube insertion is advised for persistent effusion beyond three months accompanied by hearing loss or structural changes in the tympanic membrane. Best practices prioritize individualized decision-making based on severity, duration, and impact on hearing, balancing risks and benefits of surgical intervention versus observation.
Watchful waiting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com