Effective humidification balances indoor moisture levels to enhance comfort and protect your home's structure from dryness-related damage. Proper humidity control can reduce respiratory irritation and improve overall air quality, contributing to a healthier living environment. Discover how optimal humidification can transform your indoor space by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
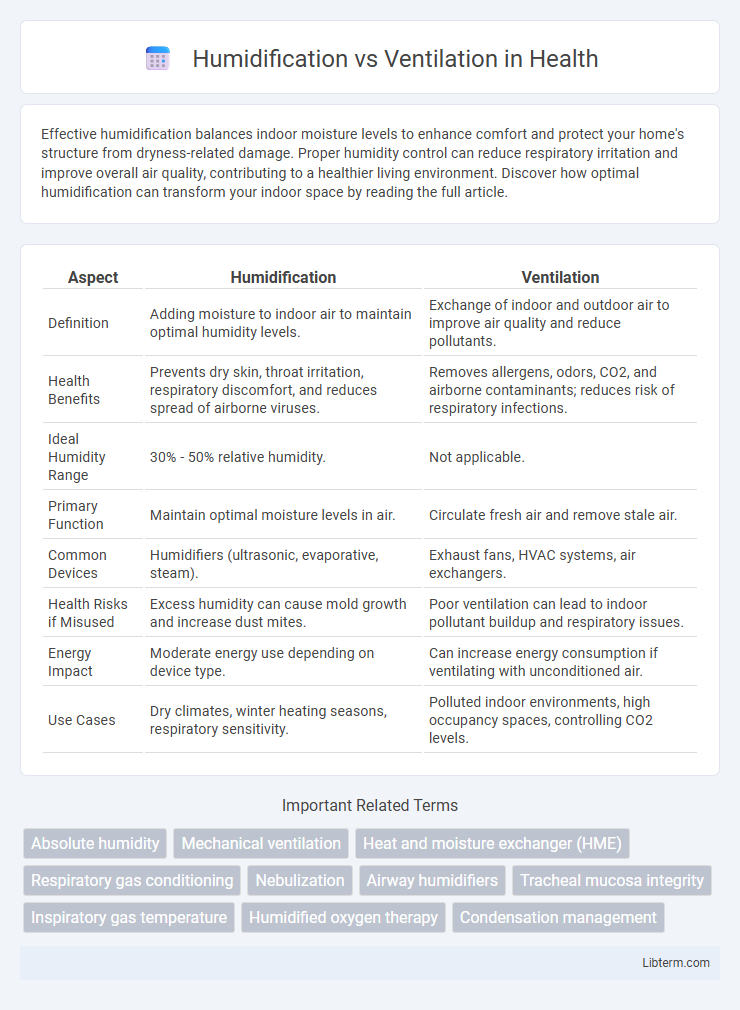
| Aspect | Humidification | Ventilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding moisture to indoor air to maintain optimal humidity levels. | Exchange of indoor and outdoor air to improve air quality and reduce pollutants. |
| Health Benefits | Prevents dry skin, throat irritation, respiratory discomfort, and reduces spread of airborne viruses. | Removes allergens, odors, CO2, and airborne contaminants; reduces risk of respiratory infections. |
| Ideal Humidity Range | 30% - 50% relative humidity. | Not applicable. |
| Primary Function | Maintain optimal moisture levels in air. | Circulate fresh air and remove stale air. |
| Common Devices | Humidifiers (ultrasonic, evaporative, steam). | Exhaust fans, HVAC systems, air exchangers. |
| Health Risks if Misused | Excess humidity can cause mold growth and increase dust mites. | Poor ventilation can lead to indoor pollutant buildup and respiratory issues. |
| Energy Impact | Moderate energy use depending on device type. | Can increase energy consumption if ventilating with unconditioned air. |
| Use Cases | Dry climates, winter heating seasons, respiratory sensitivity. | Polluted indoor environments, high occupancy spaces, controlling CO2 levels. |
Introduction to Humidification and Ventilation
Humidification involves adding moisture to the air to maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, which prevents dry skin, respiratory issues, and static electricity while protecting wooden furniture and musical instruments. Ventilation refers to the process of exchanging indoor air with outdoor air to control indoor air quality, remove pollutants, reduce humidity, and regulate temperature. Proper balance between humidification and ventilation is crucial for creating a healthy and comfortable indoor environment in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Defining Humidification: Purpose and Principles
Humidification involves adding moisture to the air to maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, typically between 30% and 50%, to enhance comfort and prevent respiratory issues. Its purpose is to counteract the drying effects of heating systems and dry climates, which can cause dry skin, irritation, and static electricity buildup. Humidification operates on principles of evaporation or steam generation, ensuring controlled moisture dispersion without promoting mold or condensation.
Understanding Ventilation: Key Concepts
Ventilation is the process of exchanging indoor air with outdoor air to control air quality, temperature, and moisture levels in a building environment. It involves mechanisms such as natural ventilation, using windows and vents, and mechanical ventilation systems like HVAC units equipped with fans and ducts. Proper ventilation reduces indoor pollutants, controls humidity, prevents mold growth, and ensures adequate oxygen supply for occupants, making it essential for maintaining healthy indoor air quality.
Humidification vs Ventilation: Core Differences
Humidification involves adding moisture to the air to maintain optimal indoor humidity levels, preventing dryness and improving comfort, while ventilation focuses on exchanging indoor air with fresh outdoor air to reduce pollutants and control temperature. Humidification primarily targets moisture balance, often achieved using ultrasonic or steam humidifiers, whereas ventilation systems rely on mechanical or natural airflow to regulate air quality. Understanding these core differences helps in designing HVAC solutions that optimize both air moisture and quality for healthier indoor environments.
Health Impacts of Humidification and Ventilation
Maintaining optimal humidification levels reduces respiratory issues by preventing dry air that can irritate mucous membranes and exacerbate conditions like asthma and sinusitis. Proper ventilation decreases indoor pollutant concentrations, limiting exposure to allergens, bacteria, and viruses, which supports cardiovascular and respiratory health. Balancing humidification and ventilation improves overall indoor air quality, enhancing immune function and reducing risks of infections and chronic respiratory diseases.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Spaces
Humidification enhances indoor air quality in residential and commercial spaces by maintaining optimal moisture levels, preventing dry air-related issues such as respiratory discomfort and static electricity. Ventilation systems improve air exchange, reducing pollutant concentrations and controlling humidity to prevent mold growth, crucial for health and structural integrity. Effective integration of humidification and ventilation supports energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and compliance with building codes in homes and office environments.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Humidification systems, while improving indoor air quality, often consume significant energy due to heating or steam generation, impacting overall efficiency. Ventilation strategies, particularly energy recovery ventilation (ERV), optimize energy use by exchanging heat between incoming and outgoing air, reducing heating and cooling loads. Balancing humidification needs with advanced ventilation technologies can lead to optimal energy savings in building climate control.
Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Humidification systems require regular cleaning and monitoring to prevent microbial growth and mineral buildup, posing significant maintenance challenges compared to ventilation systems, which mainly need filter replacements and duct inspections. Operational challenges in humidification include maintaining precise humidity levels to avoid excess moisture and potential mold growth, whereas ventilation focuses on ensuring adequate air exchange and controlling indoor contaminants. Both systems demand energy-efficient operation strategies to balance indoor air quality with cost management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Environment
Selecting the right solution between humidification and ventilation depends on your environment's specific humidity levels and air quality needs. Humidification adds moisture to dry air, preventing discomfort and static electricity in low-humidity conditions, while ventilation improves indoor air quality by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air. Assess factors like climate, existing HVAC systems, and occupant health to determine whether increased moisture, enhanced airflow, or a combination of both best supports a comfortable and healthy environment.
Future Trends in Indoor Air Quality Management
Future trends in indoor air quality management emphasize integrating advanced humidification systems with smart ventilation to create balanced environments that optimize moisture levels and airflow for health and comfort. Emerging technologies include AI-driven sensors that continuously monitor and adjust humidity and ventilation parameters, enhancing energy efficiency and preventing issues such as mold growth and respiratory discomfort. The adoption of IoT-enabled air quality solutions is expected to revolutionize commercial and residential HVAC systems by providing real-time data analytics and adaptive control for sustainable indoor environments.
Humidification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com