Maintaining high levels of alertness is essential for optimal performance and safety in daily tasks. Your ability to stay focused can significantly reduce the risk of errors and improve decision-making processes. Discover effective strategies to enhance your alertness throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
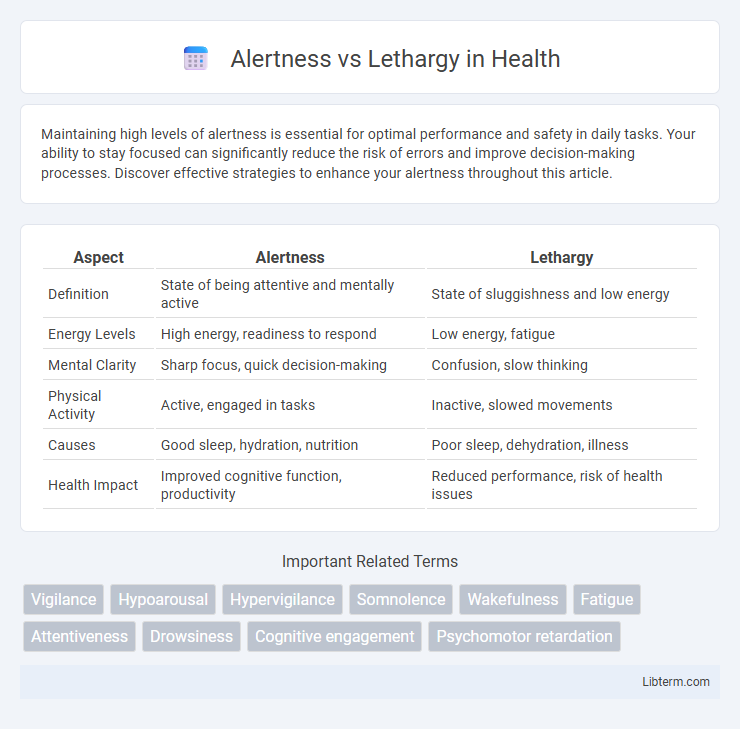
| Aspect | Alertness | Lethargy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | State of being attentive and mentally active | State of sluggishness and low energy |
| Energy Levels | High energy, readiness to respond | Low energy, fatigue |
| Mental Clarity | Sharp focus, quick decision-making | Confusion, slow thinking |
| Physical Activity | Active, engaged in tasks | Inactive, slowed movements |
| Causes | Good sleep, hydration, nutrition | Poor sleep, dehydration, illness |
| Health Impact | Improved cognitive function, productivity | Reduced performance, risk of health issues |
Understanding Alertness and Lethargy
Alertness refers to a heightened state of cognitive and sensory awareness, characterized by quick reaction times, enhanced concentration, and responsiveness to stimuli, which is crucial for effective decision-making and safety in daily activities. Lethargy, on the other hand, denotes a diminished level of energy and mental alertness, often manifesting as fatigue, sluggishness, and impaired cognitive functions that can negatively impact productivity and overall well-being. Understanding the neurobiological mechanisms, including neurotransmitter activity and circadian rhythms, helps distinguish between transient alertness fluctuations and chronic lethargy linked to medical conditions or lifestyle factors.
The Science Behind Alertness
Alertness is regulated by the brain's reticular activating system, which controls wakefulness and attention by modulating neural activity and neurotransmitter release such as dopamine and norepinephrine. Circadian rhythms and sleep homeostasis also impact alertness by balancing the body's internal clock and sleep debt, influencing cognitive performance and reaction times. Chronic lethargy often results from disruptions in these systems, leading to diminished neural responsiveness and impaired executive function.
Causes of Lethargy
Lethargy often results from factors such as inadequate sleep, poor nutrition, dehydration, and underlying medical conditions like hypothyroidism, anemia, or infections. Mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety, can also significantly contribute to feelings of prolonged lethargy. Chronic stress and sedentary lifestyles exacerbate physical and mental fatigue, reducing overall alertness and vitality.
Symptoms: How Alertness and Lethargy Manifest
Alertness manifests through heightened sensory awareness, quick cognitive responses, and sustained attention, often accompanied by physical signs such as increased heart rate and pupil dilation. Lethargy presents as persistent fatigue, slowed reaction times, diminished motivation, and reduced physical energy, frequently coupled with cognitive cloudiness and difficulty concentrating. Distinguishing these symptoms aids in recognizing underlying health conditions affecting mental and physical performance.
Psychological Impacts of Alertness vs Lethargy
Alertness enhances cognitive functions such as memory, decision-making, and problem-solving by increasing neural activity and improving information processing speed. Lethargy, characterized by low energy and reduced mental responsiveness, is linked to diminished executive function, slower reaction times, and increased vulnerability to depression and anxiety. Psychological impacts of sustained alertness include heightened emotional regulation and resilience, while chronic lethargy often correlates with impaired motivation and greater risk of mood disorders.
Physical Health Factors Influencing Energy Levels
Physical health factors significantly influence alertness and lethargy through aspects such as sleep quality, nutrition, and hydration. Consistent sleep patterns enhance cognitive function and energy, while poor sleep leads to fatigue and reduced focus. Balanced nutrition rich in vitamins and minerals supports metabolic processes vital for sustained energy, and adequate hydration prevents early onset of lethargy caused by dehydration.
Lifestyle Choices: Boosting Alertness and Battling Lethargy
Regular physical activity and sufficient sleep significantly enhance alertness by improving blood flow and cognitive function, while poor lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior and inconsistent sleep patterns contribute to lethargy. Nutrient-rich diets high in antioxidants, vitamins B and C, and magnesium support energy metabolism and brain health, reducing feelings of fatigue. Mindful practices such as stress management and hydration further optimize mental clarity and combat lethargy effectively.
Nutrition’s Role in Mental and Physical Energy
Balanced nutrition rich in complex carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals supports sustained alertness by providing steady energy release and essential nutrients for brain function. Deficiencies in key nutrients like iron, B vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to lethargy by impairing oxygen transport, neurotransmitter synthesis, and cellular energy metabolism. Proper hydration and regulation of blood sugar levels also play critical roles in maintaining mental clarity and physical stamina throughout the day.
How Sleep Patterns Affect Alertness and Lethargy
Irregular sleep patterns disrupt the brain's ability to maintain alertness, leading to increased lethargy and diminished cognitive performance. Consistent quality sleep restores the balance of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which enhance wakefulness and mental clarity. Studies show that circadian rhythm alignment directly improves sustained attention and reduces feelings of fatigue throughout the day.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Alertness Daily
Maintaining optimal alertness daily involves regular physical activity, balanced nutrition rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and consistent sleep patterns aligned with circadian rhythms. Hydration and short, strategic breaks during work enhance cognitive function and prevent lethargy. Incorporating mindfulness techniques and exposure to natural light can further support sustained mental clarity and energy levels throughout the day.
Alertness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com