Immunostimulation enhances your immune system's ability to fight infections and diseases by activating immune cells and boosting their response. Various natural and synthetic agents can trigger this process, improving overall health and resilience. Discover how immunostimulation works and its benefits throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
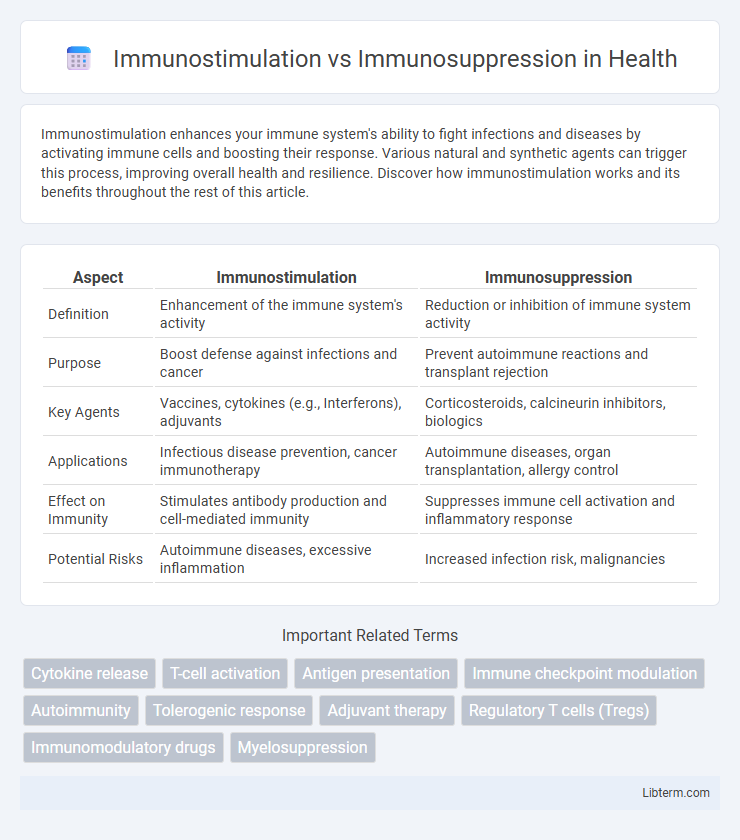
| Aspect | Immunostimulation | Immunosuppression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancement of the immune system's activity | Reduction or inhibition of immune system activity |
| Purpose | Boost defense against infections and cancer | Prevent autoimmune reactions and transplant rejection |
| Key Agents | Vaccines, cytokines (e.g., Interferons), adjuvants | Corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, biologics |
| Applications | Infectious disease prevention, cancer immunotherapy | Autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, allergy control |
| Effect on Immunity | Stimulates antibody production and cell-mediated immunity | Suppresses immune cell activation and inflammatory response |
| Potential Risks | Autoimmune diseases, excessive inflammation | Increased infection risk, malignancies |
Introduction to Immune System Modulation
Immune system modulation involves either immunostimulation or immunosuppression to regulate immune responses for therapeutic purposes. Immunostimulation enhances the activity of immune cells such as T lymphocytes, B cells, and macrophages to improve defense against infections and cancer. Immunosuppression reduces immune activity to prevent autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection, and chronic inflammatory conditions by targeting cytokines, signaling pathways, or immune checkpoints.
Defining Immunostimulation
Immunostimulation refers to the enhancement or activation of the immune system to improve its response against pathogens, cancer cells, or vaccines. It involves boosting innate and adaptive immune functions through agents like cytokines, adjuvants, or immune checkpoint inhibitors. This process contrasts with immunosuppression, where immune activity is deliberately reduced to prevent autoimmune reactions or transplant rejection.
What is Immunosuppression?
Immunosuppression refers to the reduction or inhibition of the immune system's activity, often achieved through medications or medical treatments to prevent the body from rejecting transplanted organs or to manage autoimmune diseases. Key immunosuppressive agents include corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors like cyclosporine, and biologics targeting specific immune cells or cytokines. This modulation lowers the immune response, decreasing inflammation and preventing tissue damage caused by an overactive immune system.
Key Mechanisms of Immunostimulation
Immunostimulation enhances the immune system by activating immune cells such as T lymphocytes, B cells, and macrophages through antigen presentation and cytokine release. Key mechanisms include the upregulation of co-stimulatory molecules, increased production of interleukins like IL-2, and enhanced natural killer (NK) cell activity. These processes lead to strengthened adaptive and innate immune responses, improving the body's ability to recognize and eliminate pathogens and cancer cells.
Main Pathways of Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression primarily involves pathways such as the inhibition of T-cell activation via CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors, the suppression of cytokine signaling through JAK-STAT pathway modulation, and the increased production of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-b. These mechanisms reduce immune responses, preventing excessive inflammation and autoimmunity. Therapeutic agents targeting these pathways, such as checkpoint inhibitors and cytokine blockers, are central to managing immune-related disorders.
Therapeutic Uses of Immunostimulants
Immunostimulants enhance the body's immune response, playing a crucial role in treating infections, cancer, and immunodeficiency disorders by activating immune cells such as macrophages, T-cells, and natural killer cells. Therapeutic uses of immunostimulants include vaccines, interferons, and colony-stimulating factors, which boost immune function to prevent disease progression and improve patient outcomes. These agents differ from immunosuppressants, which are used to reduce immune activity in conditions like autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation.
Clinical Applications of Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressants play a crucial role in clinical settings by preventing organ transplant rejection and treating autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. These agents, including corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and mTOR inhibitors, modulate the immune system to reduce hyperactive immune responses. Careful dosing and monitoring are essential to minimize side effects such as increased infection risk and malignancy while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.
Risks and Side Effects of Immunomodulation
Immunostimulation enhances immune system activity, potentially causing risks such as excessive inflammation, autoimmune reactions, and cytokine storms. Immunosuppression lowers immune responses, increasing susceptibility to infections, malignancies, and delayed wound healing. Immunomodulation therapies require careful risk assessment to balance efficacy with potential adverse effects on immune homeostasis.
Comparing Immunostimulation vs Immunosuppression
Immunostimulation enhances the body's immune response by activating immune cells such as T-cells and macrophages to fight infections and tumors, often used in vaccines and cancer therapies. Immunosuppression, in contrast, suppresses or inhibits immune activity to prevent autoimmune reactions or organ transplant rejection, commonly achieved through corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors. Comparing immunostimulation and immunosuppression highlights their opposite mechanisms: one promotes immune activation, while the other dampens immune responses to maintain homeostasis or prevent damage.
Future Directions in Immune System Therapies
Future directions in immune system therapies emphasize precision immunomodulation, leveraging advances in genomic editing and personalized medicine to enhance immunostimulation or immunosuppression as needed. Emerging therapies target specific immune checkpoints and cellular pathways, aiming to balance immune activation for cancer treatment or immune tolerance for autoimmune diseases and transplant acceptance. Integration of artificial intelligence and biomarker-driven approaches promises to optimize therapeutic efficacy and minimize adverse effects, driving innovation in immune system modulation.
Immunostimulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com