Understanding administrative law interpretation is crucial for navigating government regulations and ensuring compliance with legal standards. This process involves analyzing statutes, agency rules, and court decisions to determine the scope of administrative authority and protect your rights. Explore the full article to deepen your knowledge of how administrative law impacts you and your legal responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
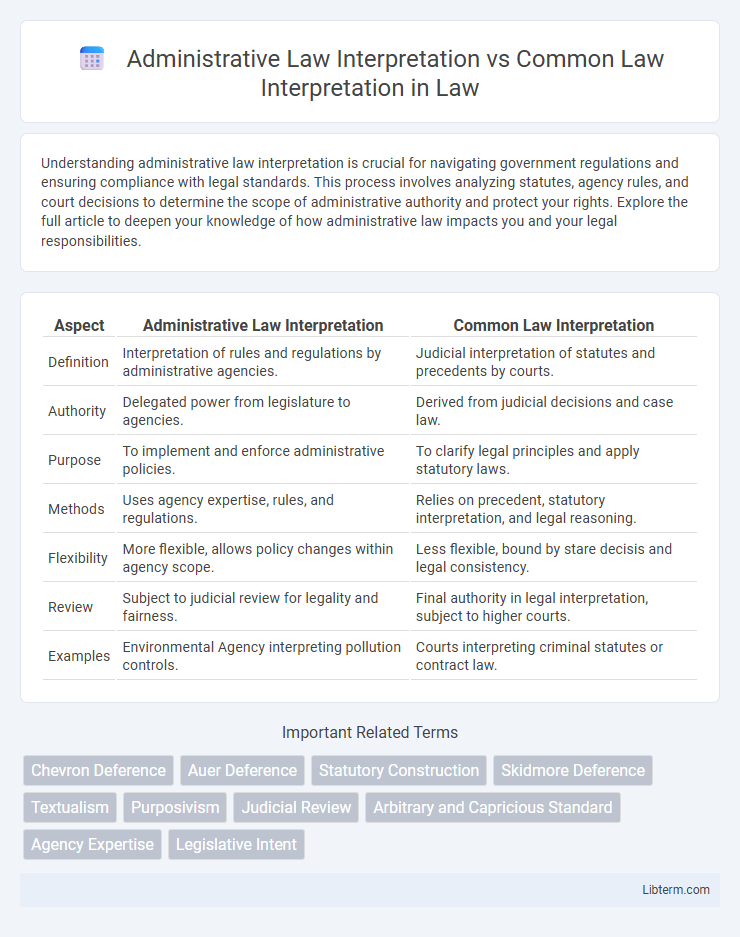
| Aspect | Administrative Law Interpretation | Common Law Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpretation of rules and regulations by administrative agencies. | Judicial interpretation of statutes and precedents by courts. |
| Authority | Delegated power from legislature to agencies. | Derived from judicial decisions and case law. |
| Purpose | To implement and enforce administrative policies. | To clarify legal principles and apply statutory laws. |
| Methods | Uses agency expertise, rules, and regulations. | Relies on precedent, statutory interpretation, and legal reasoning. |
| Flexibility | More flexible, allows policy changes within agency scope. | Less flexible, bound by stare decisis and legal consistency. |
| Review | Subject to judicial review for legality and fairness. | Final authority in legal interpretation, subject to higher courts. |
| Examples | Environmental Agency interpreting pollution controls. | Courts interpreting criminal statutes or contract law. |
Understanding Administrative Law Interpretation
Administrative law interpretation centers on understanding statutes and regulations based on the intent of administrative agencies and the practical implications for public policy enforcement. It emphasizes deference to agency expertise and seeks to balance statutory language with legislative purpose, often applying doctrines like Chevron deference. This approach contrasts with common law interpretation, which relies more heavily on judicial precedent and the literal meaning of legal texts.
Defining Common Law Interpretation
Common law interpretation relies on judicial decisions and precedents to ascertain the meaning of legal texts, emphasizing stability and predictability in legal outcomes. It prioritizes the original intent and historical context of statutes while allowing gradual evolution through case law. Unlike administrative law interpretation, common law interpretation resists expansive readings, focusing instead on the plain meaning and established legal principles derived from courts.
Core Principles of Administrative Law Interpretation
Administrative law interpretation centers on upholding statutory purpose, deference to agency expertise, and ensuring procedural fairness, reflecting the balance between governmental authority and individual rights. It emphasizes the application of the Chevron deference, where courts defer to reasonable agency interpretations of ambiguous statutes within their scope of authority. Common law interpretation prioritizes judicial precedent, literal statutory meanings, and the principles of stare decisis, seeking consistency and predictability in judicial decisions.
Key Features of Common Law Interpretation
Common law interpretation relies on judicial precedents, emphasizing the consistency and predictability of legal decisions through the doctrine of stare decisis. It prioritizes the literal meaning of statutory language while also considering legislative intent and the broader context of established case law. This interpretative approach allows courts to adapt legal principles over time by refining rules through incremental judicial decisions.
Sources of Authority in Administrative vs Common Law
Administrative law interpretation derives its authority primarily from statutes, regulations, and delegated legislative powers that empower administrative agencies to enforce specific legal frameworks. Common law interpretation, in contrast, is grounded in judicial decisions, precedents, and the doctrine of stare decisis, where courts interpret laws based on previous rulings and legal principles established over time. The distinction between statutory authority in administrative law and case law authority in common law underscores the different foundations and methodologies guiding legal interpretation in these two domains.
Role of Courts in Interpreting Administrative and Common Law
Courts play a crucial role in interpreting both administrative and common law by ensuring that administrative agencies adhere to statutory mandates while safeguarding individual rights. In administrative law interpretation, courts often apply the Chevron deference, upholding reasonable agency interpretations of ambiguous statutes, whereas in common law interpretation, courts emphasize precedent and judicial reasoning to evolve legal principles. This judicial oversight balances agency expertise with legal consistency, reinforcing the rule of law across both domains.
Statutory Interpretation in Administrative Law
Statutory interpretation in administrative law emphasizes deference to agency expertise and the purpose of the statute, often guided by principles such as Chevron deference or the "reasonableness" standard. Unlike common law interpretation, which relies heavily on judicial precedent and textualist or purposivist methods, administrative law prioritizes the agency's regulatory context and policy objectives within legislative intent. This approach ensures flexibility in applying statutes to complex and technical regulatory frameworks managed by specialized agencies.
Judicial Precedent in Common Law Interpretation
Judicial precedent in common law interpretation serves as a fundamental mechanism by which courts apply previous rulings to ensure consistency and predictability in legal decisions. Unlike administrative law interpretation, which often relies on statutes, regulations, and agency expertise, common law interpretation centers on the doctrine of stare decisis, compelling courts to follow established case law. This reliance on judicial precedent anchors the common law system, allowing judges to interpret laws within the context of historical rulings and adapt legal principles to evolving societal norms.
Impacts on Legal Outcomes and Precedents
Administrative law interpretation prioritizes the intent and purpose of statutes, often granting deference to agency expertise, which shapes regulatory enforcement and policy implementation with more flexible legal outcomes. Common law interpretation relies on judicial precedents and the principle of stare decisis, creating consistent and predictable decisions by adhering to established case law and legal doctrines. The contrast between these interpretive methods significantly influences the development of legal precedents, affecting how courts balance statutory mandates against evolving social and economic contexts.
Comparative Analysis: Strengths and Limitations
Administrative law interpretation emphasizes explicit statutory language and legislative intent, ensuring agency decisions align with legal frameworks but may limit flexibility in novel contexts. Common law interpretation relies on judicial precedents and evolving case law, providing adaptability and nuanced rulings but sometimes leading to inconsistencies or ambiguity in application. Balancing administrative precision with common law adaptability highlights strengths in regulatory clarity versus judicial flexibility, while their limitations stem from rigidity in administrative rules and unpredictability in common law evolution.
Administrative Law Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com