A subpoena is a legal document that compels an individual to provide testimony or produce evidence in a court case or legal investigation. Understanding the types, requirements, and consequences of ignoring a subpoena is essential to protect your legal rights. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to respond effectively to a subpoena and navigate the legal process with confidence.
Table of Comparison
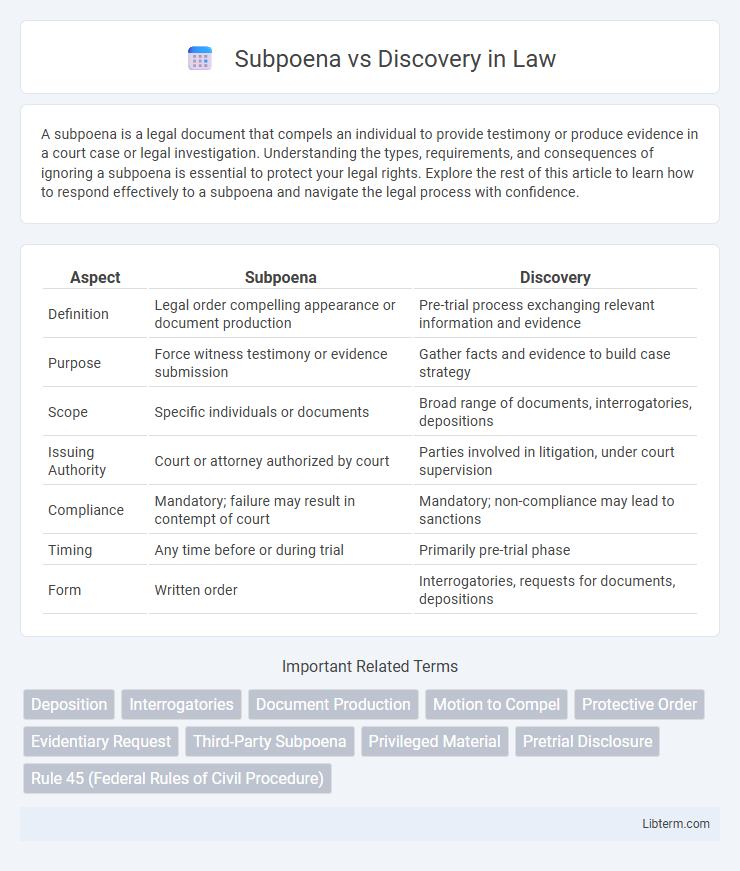
| Aspect | Subpoena | Discovery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal order compelling appearance or document production | Pre-trial process exchanging relevant information and evidence |
| Purpose | Force witness testimony or evidence submission | Gather facts and evidence to build case strategy |
| Scope | Specific individuals or documents | Broad range of documents, interrogatories, depositions |
| Issuing Authority | Court or attorney authorized by court | Parties involved in litigation, under court supervision |
| Compliance | Mandatory; failure may result in contempt of court | Mandatory; non-compliance may lead to sanctions |
| Timing | Any time before or during trial | Primarily pre-trial phase |
| Form | Written order | Interrogatories, requests for documents, depositions |
Introduction to Subpoena vs Discovery
A subpoena is a legal document that commands an individual or organization to produce evidence or testify in a legal proceeding, serving as a tool for collecting specific information. Discovery refers to the pre-trial phase in civil litigation where parties exchange relevant information and evidence to prepare their cases. Both subpoena and discovery play crucial roles in gathering facts but differ in scope, with subpoenas being directed to third parties and discovery involving mutual information exchange between litigants.
Defining Subpoena in Legal Context
A subpoena is a legally binding document that compels an individual to testify as a witness or produce evidence in a legal proceeding. It serves as a crucial tool for gathering information, ensuring parties comply with court orders during litigation. Unlike discovery, which involves a broader pre-trial exchange of documents and information, a subpoena specifically mandates appearance or submission of specified evidence.
Understanding the Discovery Process
The discovery process in litigation involves the exchange of relevant information between parties to build evidence for a case, whereas a subpoena is a legal document compelling someone to produce documents or testify. Discovery includes methods such as interrogatories, depositions, requests for production, and requests for admission to uncover facts and clarify issues before trial. Effective use of discovery tools allows attorneys to gather critical evidence, assess the strength of the opposing party's case, and prepare for negotiation or trial strategies.
Key Differences Between Subpoena and Discovery
A subpoena is a legal document compelling a person to produce evidence or testify, typically issued by a court or attorney, while discovery is a pre-trial process allowing parties to exchange information and evidence relevant to the case. Subpoenas target non-parties or witnesses outside the litigation, whereas discovery involves formal requests between the parties involved. Discovery methods include interrogatories, depositions, and requests for documents, contrasting the subpoena's authority to enforce compliance through the court system.
Types of Subpoenas in Legal Proceedings
Subpoenas in legal proceedings primarily include Subpoenas Ad Testificandum, which require a witness to testify, and Subpoenas Duces Tecum, mandating the production of documents or evidence. Each subpoena type serves distinct functions in both civil and criminal cases, facilitating the gathering of testimony and evidence crucial for case development. Understanding the scope and limitations of these subpoenas is essential for effective legal strategy and compliance.
Methods of Discovery in Civil and Criminal Cases
Methods of discovery in civil cases primarily include depositions, interrogatories, requests for production of documents, and requests for admissions, enabling parties to gather evidence before trial. In criminal cases, discovery often involves the subpoena of witnesses and documents, along with the defendant's right to access evidence held by the prosecution, such as police reports and witness statements. Subpoenas serve as a legal tool to compel witness testimony or document production in both civil and criminal proceedings, facilitating comprehensive evidence collection.
Legal Requirements for Issuing a Subpoena
Issuing a subpoena requires strict adherence to legal requirements, including proper jurisdiction, specific identification of the documents or testimony sought, and timely service to the recipient. Courts mandate that subpoenas be issued by authorized parties such as attorneys or clerks, and often require notice to all involved parties to ensure due process. Failure to comply with these legal standards can render the subpoena invalid and subject to challenges or sanctions.
Responding to Discovery Requests
Responding to discovery requests requires timely, thorough, and accurate production of relevant documents, information, and testimonies to comply with legal standards. Unlike subpoenas, which are often directed toward third parties, discovery requests involve parties within the litigation and aim to obtain evidence critical to case strategy and preparation. Failure to adequately respond to discovery requests can lead to sanctions, motions to compel, or adverse inferences during trial.
Common Challenges with Subpoena and Discovery
Common challenges with subpoena and discovery include issues of non-compliance, where parties may fail to provide requested documents or testimony in a timely manner, leading to delays and potential legal sanctions. Privacy concerns and relevance disputes often arise, as parties resist disclosing sensitive or unrelated information, complicating the scope and effectiveness of discovery. Managing the volume of data and ensuring proper preservation of evidence also pose significant obstacles, increasing costs and prolonging litigation processes.
Best Practices for Managing Subpoena and Discovery
Effective management of subpoena and discovery requires clear coordination between legal counsel and compliance teams to ensure timely and accurate document production. Implementing centralized tracking systems helps monitor deadlines, custodians, and responses, reducing risks of non-compliance and data spoliation. Best practices include consistent employee training on legal obligations and maintaining detailed records of all communications and evidence preserved during the discovery process.
Subpoena Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com