Accreditation ensures that institutions and programs meet rigorous quality standards, providing assurance of educational excellence and credibility. It enhances your confidence in choosing the right school or course, supporting your academic and professional goals. Explore the full article to understand how accreditation impacts your educational journey and career success.
Table of Comparison
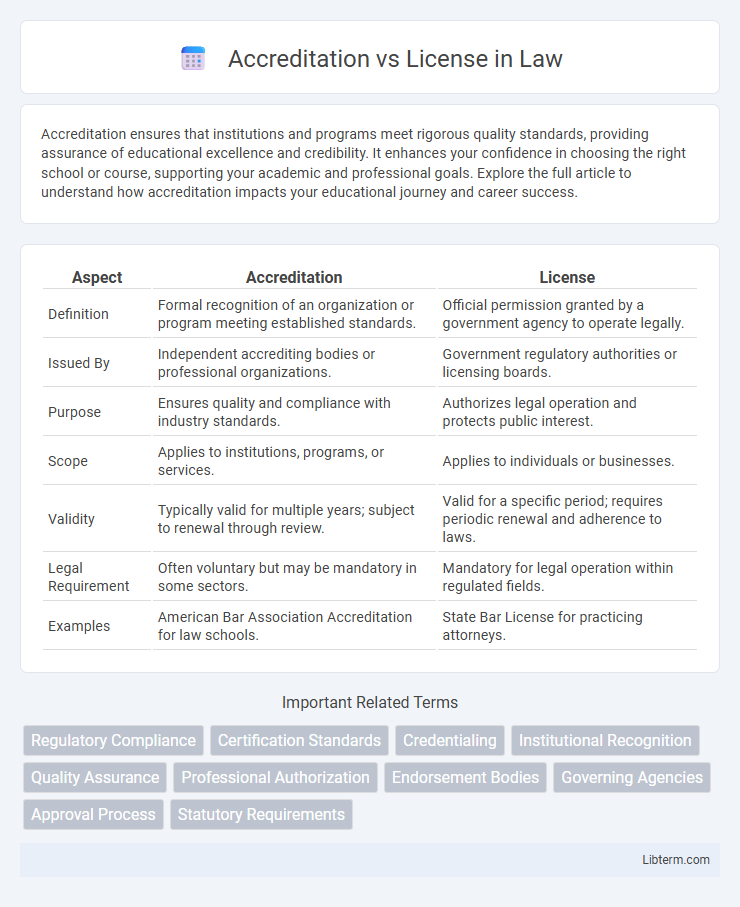
| Aspect | Accreditation | License |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal recognition of an organization or program meeting established standards. | Official permission granted by a government agency to operate legally. |
| Issued By | Independent accrediting bodies or professional organizations. | Government regulatory authorities or licensing boards. |
| Purpose | Ensures quality and compliance with industry standards. | Authorizes legal operation and protects public interest. |
| Scope | Applies to institutions, programs, or services. | Applies to individuals or businesses. |
| Validity | Typically valid for multiple years; subject to renewal through review. | Valid for a specific period; requires periodic renewal and adherence to laws. |
| Legal Requirement | Often voluntary but may be mandatory in some sectors. | Mandatory for legal operation within regulated fields. |
| Examples | American Bar Association Accreditation for law schools. | State Bar License for practicing attorneys. |
Introduction to Accreditation and Licensing
Accreditation is a formal recognition granted by a reputable organization confirming that an institution or program meets established quality standards. Licensing is a mandatory authorization issued by governmental agencies that permits individuals or entities to legally operate within a specific profession or industry. Both accreditation and licensing serve to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and maintain high levels of professional competence and safety.
Defining Accreditation
Accreditation is a formal, third-party evaluation process that ensures an organization, institution, or program meets specific quality standards established by an accrediting body. It validates the credibility, competence, and performance of the entity, promoting continuous improvement and public trust. Unlike a license, which is a mandatory legal authorization to operate, accreditation is often voluntary and focused on quality assurance and enhancement.
What Is a License?
A license is an official authorization granted by a governmental or regulatory body that permits an individual or organization to legally perform specific activities or operate within a particular industry. It ensures compliance with established laws, safety standards, and professional qualifications, serving as a legal requirement for practicing professions such as healthcare, education, or business operations. Licenses are mandatory for legal operation and are subject to renewal and regulatory oversight to maintain legitimacy and public trust.
Key Differences Between Accreditation and Licensing
Accreditation is a voluntary process in which an organization or institution is evaluated by an external body to verify it meets established standards of quality and performance, often in education or healthcare sectors. Licensing is a mandatory legal requirement granted by governmental agencies that authorizes an individual or organization to operate within specific regulatory parameters, ensuring compliance with statutory regulations. The key difference lies in accreditation being a quality assurance mechanism focused on excellence, while licensing serves as a regulatory permission to legally conduct business or practice.
Importance of Accreditation in Education and Industry
Accreditation validates the quality and standards of educational institutions and industry programs, ensuring they meet rigorous criteria set by authoritative bodies. It enhances credibility, facilitates student and consumer trust, and often influences eligibility for funding, certifications, and employment opportunities. Unlike licensing, which permits legal operation, accreditation drives continuous improvement and benchmarking against industry best practices.
The Role of Licensing in Professional Practice
Licensing plays a critical role in professional practice by legally authorizing individuals or organizations to perform specific tasks or services, ensuring adherence to established standards and protection of public safety. Unlike accreditation, which typically evaluates the quality of institutions or programs, licensing directly regulates practitioners' qualifications and competence within a profession. Compliance with licensing requirements is mandatory for lawful operation and often influences employment opportunities and professional credibility.
Accreditation Process: Steps and Standards
The accreditation process involves a thorough evaluation of an organization's quality standards, typically conducted by an independent accrediting body based on predefined criteria such as performance, safety, and ethical compliance. Key steps include a self-assessment report, onsite evaluation, and continuous monitoring to ensure adherence to industry-specific standards. This process not only validates the institution's credibility but also promotes ongoing improvement and accountability.
Licensing Requirements and Procedures
Licensing requirements typically involve meeting established state or local government standards that regulate businesses, professionals, or institutions to ensure public safety and compliance with legal mandates. The licensing process often includes submitting an application, passing examinations, undergoing background checks, and obtaining necessary permits or inspections from regulatory authorities. Unlike accreditation, which is usually a voluntary evaluation by independent organizations assessing quality and performance, licensing is mandatory and legally binding for operating within specific jurisdictions.
Benefits of Accreditation vs. License
Accreditation offers enhanced credibility and demonstrates a commitment to meeting high industry standards, which can improve stakeholder trust and customer confidence compared to a basic license. It often opens access to broader funding opportunities, partnerships, and market advantages that are not available through licensing alone. Unlike licenses, accreditation involves rigorous evaluation and continuous improvement, driving higher quality and operational excellence.
Choosing What’s Right: Accreditation or Licensing
Choosing between accreditation and licensing depends on the purpose and requirements of your organization or profession. Accreditation demonstrates adherence to industry-specific standards and enhances credibility, while licensing is a mandatory legal requirement ensuring compliance with governmental regulations. Evaluating your goals and regulatory environment helps determine whether accreditation or licensing best supports your operational and reputational needs.
Accreditation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com