Mens rea refers to the mental state or intent a person has when committing a crime, crucial for establishing criminal liability. Understanding mens rea helps distinguish between intentional wrongdoing and accidental actions, making it a key concept in criminal law. Explore the rest of the article to grasp how mens rea impacts legal outcomes and your rights.
Table of Comparison
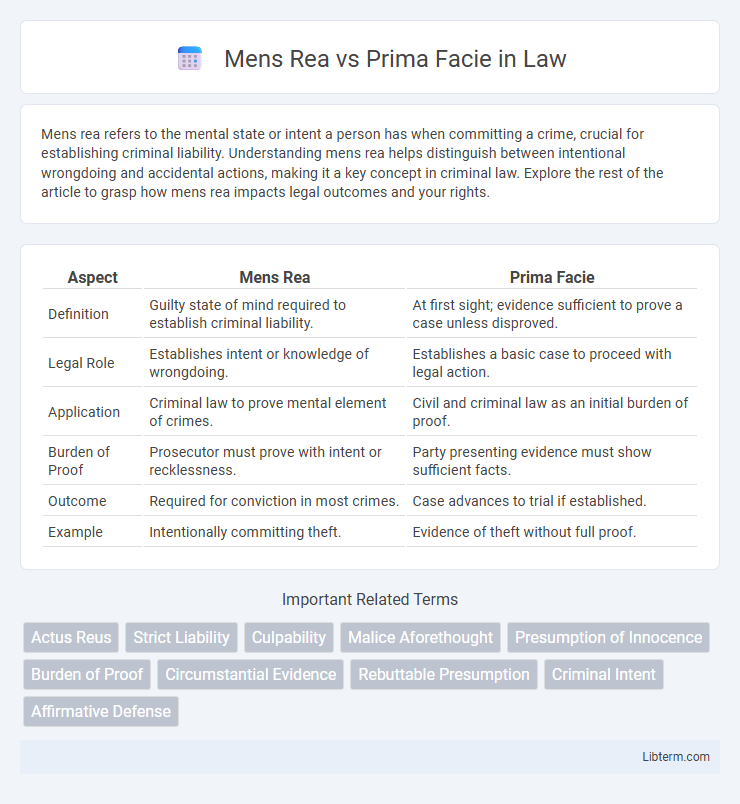
| Aspect | Mens Rea | Prima Facie |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guilty state of mind required to establish criminal liability. | At first sight; evidence sufficient to prove a case unless disproved. |
| Legal Role | Establishes intent or knowledge of wrongdoing. | Establishes a basic case to proceed with legal action. |
| Application | Criminal law to prove mental element of crimes. | Civil and criminal law as an initial burden of proof. |
| Burden of Proof | Prosecutor must prove with intent or recklessness. | Party presenting evidence must show sufficient facts. |
| Outcome | Required for conviction in most crimes. | Case advances to trial if established. |
| Example | Intentionally committing theft. | Evidence of theft without full proof. |
Introduction to Mens Rea and Prima Facie
Mens Rea, a fundamental concept in criminal law, refers to the mental state or intent behind committing a crime, crucial for establishing culpability. Prima Facie, meaning "at first sight," represents the initial evidence sufficient to prove a case unless disproven by further investigation. Understanding the distinction between Mens Rea and Prima Facie is essential for accurately assessing criminal liability and legal responsibility.
Defining Mens Rea: The Mental Element in Crime
Mens rea refers to the mental state or intent behind a criminal act, representing the defendant's awareness and purpose in committing the offense. It is a fundamental component in establishing criminal liability, distinguishing intentional wrongdoing from accidental acts. Understanding mens rea involves analyzing whether the accused possessed knowledge, recklessness, or negligence during the commission of the crime.
Understanding Prima Facie: Establishing Legal Sufficiency
Prima facie refers to evidence that is sufficient to establish a fact or raise a presumption unless disproved, serving as a preliminary threshold in legal proceedings. It establishes legal sufficiency by presenting enough credible evidence to support a claim or charge, prompting further examination or a trial. Unlike mens rea, which focuses on the defendant's mental state or intent, prima facie relates specifically to the adequacy of evidence at the initial stage of litigation.
Historical Roots and Legal Evolution
Mens Rea, rooted in common law traditions, emerged to establish the mental state necessary for criminal liability, emphasizing intentionality or recklessness as essential components. Prima facie, originating from Latin meaning "at first sight," functions as an evidentiary standard to present sufficient initial proof to support a legal claim or charge. The legal evolution of Mens Rea centers on refining the nuances of culpability, while Prima facie has developed as a procedural threshold to determine whether a case merits further examination.
Key Differences Between Mens Rea and Prima Facie
Mens Rea refers to the mental state or intent behind committing a crime, indicating the defendant's culpability or guilty mind. Prima Facie denotes the establishment of sufficient evidence to prove a case unless disproved, serving as the initial threshold in legal proceedings. The key difference lies in Mens Rea addressing subjective intent, while Prima Facie focuses on the objective evidence presented at the outset.
Mens Rea in Criminal Law: Types and Applications
Mens rea, a fundamental concept in criminal law, refers to the defendant's mental state or intent when committing a crime, distinguishing between intentional, reckless, negligent, and strict liability offenses. Understanding the types of mens rea is critical for determining criminal liability, as different crimes require varying levels of intent or knowledge, such as specific intent in burglary or general intent in assault. Legal applications of mens rea influence verdicts, sentencing, and defenses, ensuring that individuals are charged according to their culpability and mental awareness at the time of the offense.
Prima Facie Case: Structure and Importance in Trials
A prima facie case is established when the plaintiff presents sufficient evidence that, if uncontradicted, proves the claim and justifies proceeding to trial. Its structure includes the presentation of credible facts that satisfy each element of the cause of action, compelling the defendant to produce evidence to counter the claim. The importance of a prima facie case in trials lies in its role as a preliminary filter, ensuring only claims with adequate evidentiary foundation advance, thereby conserving judicial resources and promoting fair adjudication.
Role of Mens Rea in Proving Guilt
Mens rea, or the guilty mind, is essential in proving criminal liability as it establishes the defendant's intent or knowledge of wrongdoing, differentiating between accidental acts and deliberate crimes. It requires demonstrating that the accused had the mental state to commit the offense, which influences the degree and nature of the charge. Prima facie evidence, by contrast, refers to the initial facts that suggest guilt, but mens rea solidifies the prosecution's case by confirming the defendant's culpable state of mind.
Prima Facie Evidence: Analytical Perspectives
Prima facie evidence serves as the initial proof required to establish a legal case's validity, compelling courts to accept facts as true unless contradicted by rebuttal evidence. This type of evidence contrasts with mens rea, which concerns the defendant's mental state or intent, by focusing on tangible proof rather than subjective intent. Analytical perspectives on prima facie evidence emphasize its role in streamlining judicial processes by setting a preliminary burden of proof that shapes case progression and outcomes.
Comparative Analysis: Impact on Legal Proceedings
Mens Rea, referring to the mental state or intent behind a crime, significantly influences the determination of guilt and the severity of charges in legal proceedings. Prima Facie involves establishing sufficient evidence at first glance to support a case, guiding whether a case should proceed to trial without delving into intent. The comparative impact lies in Mens Rea shaping the qualitative assessment of culpability, while Prima Facie governs the procedural threshold for initiating or dismissing legal action.
Mens Rea Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com