Unite means to come together for a common purpose, fostering strength and collaboration among individuals or groups. This concept highlights the power of collective effort in overcoming challenges and achieving shared goals. Explore the rest of this article to discover how uniting can transform your personal or professional life.
Table of Comparison
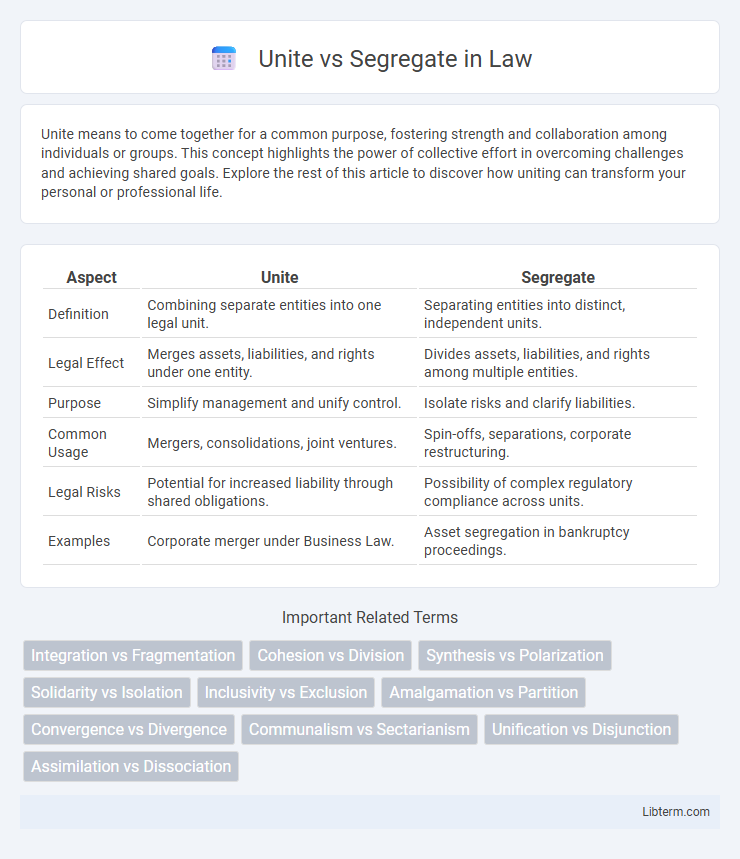
| Aspect | Unite | Segregate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining separate entities into one legal unit. | Separating entities into distinct, independent units. |
| Legal Effect | Merges assets, liabilities, and rights under one entity. | Divides assets, liabilities, and rights among multiple entities. |
| Purpose | Simplify management and unify control. | Isolate risks and clarify liabilities. |
| Common Usage | Mergers, consolidations, joint ventures. | Spin-offs, separations, corporate restructuring. |
| Legal Risks | Potential for increased liability through shared obligations. | Possibility of complex regulatory compliance across units. |
| Examples | Corporate merger under Business Law. | Asset segregation in bankruptcy proceedings. |
Introduction to Unity and Segregation
Unity represents the harmonious integration of diverse groups, fostering collaboration and shared purpose within communities or organizations. Segregation involves the systematic separation of people based on characteristics such as race, ethnicity, or social status, often leading to inequality and social division. Understanding the dynamics between unity and segregation is crucial for addressing social cohesion and creating inclusive environments.
Historical Perspectives on Social Cohesion
Historical perspectives on social cohesion reveal that societies emphasizing unity tend to foster stronger collective identities, enhancing stability and cooperation. Segregation often results in fragmented communities, increasing social tensions and inequalities, as evidenced by apartheid South Africa and segregated America. Social cohesion historically thrives when inclusive policies and shared goals bridge diverse groups, promoting resilience and peaceful coexistence.
The Psychology Behind Unity
The psychology behind unity reveals that individuals experience enhanced social cohesion and emotional well-being when they feel connected to a group, driven by humans' inherent need for belonging and acceptance. Neural mechanisms such as mirror neurons facilitate empathy and understanding, fostering collective identity and cooperation. Conversely, segregation often triggers social identity threat, increasing anxiety and reducing trust, which undermines collaborative potential and psychological security.
Causes and Consequences of Segregation
Segregation often arises from systemic discrimination, economic disparities, and social prejudices that enforce physical or social separation between groups based on race, ethnicity, or class. Consequences include entrenched inequality, reduced access to quality education and employment, and heightened social tensions that can perpetuate cycles of poverty and discrimination. Segregation undermines social cohesion and limits economic mobility, leading to fragmented communities and persistent socio-economic divides.
Economic Impacts: United vs Segregated Communities
United communities foster economic growth by pooling resources, encouraging diverse entrepreneurship, and attracting investment, leading to higher employment rates and improved local infrastructure. Segregated communities often experience economic disparities, limited access to quality education and jobs, and reduced consumer markets, perpetuating poverty cycles and stunting regional development. Studies show integrated economies benefit from increased innovation, social mobility, and a more resilient workforce, essential for sustainable urban growth.
Cultural Diversity: Strength in Unity
Cultural diversity fosters innovation and resilience by bringing varied perspectives and experiences together, enhancing problem-solving and creativity. Unite strategies emphasize collaboration across different cultural backgrounds, promoting mutual respect and shared goals that strengthen community bonds. Segregation limits these benefits by isolating groups, reducing opportunities for cultural exchange and collective growth.
Political Factors: Policies That Unite or Divide
Political factors significantly influence whether societies unite or segregate through policies promoting inclusion or exclusion. Inclusive policies, such as anti-discrimination laws and equitable resource distribution, foster national unity and social cohesion by reducing disparities. Conversely, divisive policies like gerrymandering, unequal voting rights, and ethnically biased legislation deepen societal fractures and perpetuate segregation.
Education Systems: Integration vs Separation
Education systems that prioritize integration promote diverse classrooms where students from various backgrounds learn together, fostering social cohesion and reducing prejudices. In contrast, segregated education systems often lead to unequal resource allocation and limit opportunities for marginalized groups, perpetuating systemic inequalities. Research shows integrated education improves academic outcomes and prepares students for multicultural societies by encouraging empathy and collaboration.
Technology’s Role in Connecting or Isolating
Technology amplifies both unity and segregation by shaping social interactions through digital platforms, where algorithms curate personalized content that can either foster inclusive communities or reinforce echo chambers. Communication tools like social media and video conferencing break geographical barriers, enabling global connectivity and collaborative innovation across diverse cultures and industries. However, these same technologies can deepen isolation by promoting filter bubbles and digital addiction, limiting exposure to differing perspectives and reducing face-to-face human contact.
Building a Balanced Future: Strategies for Unity
Building a balanced future requires implementing strategies that promote unity across diverse communities by fostering inclusive dialogue and equitable resource distribution. Prioritizing collaborative policymaking and cultural exchange programs enhances mutual understanding and reduces societal divisions. Effective leadership that emphasizes shared goals and collective responsibility strengthens social cohesion and paves the way for sustainable development.
Unite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com