Actual damages refer to the real, quantifiable losses a person suffers due to another party's actions, including medical expenses, property repairs, and lost wages. These damages are calculated based on concrete evidence, ensuring fair compensation for the direct impact on your finances and well-being. Explore the full article to understand how actual damages are determined and applied in various legal contexts.
Table of Comparison
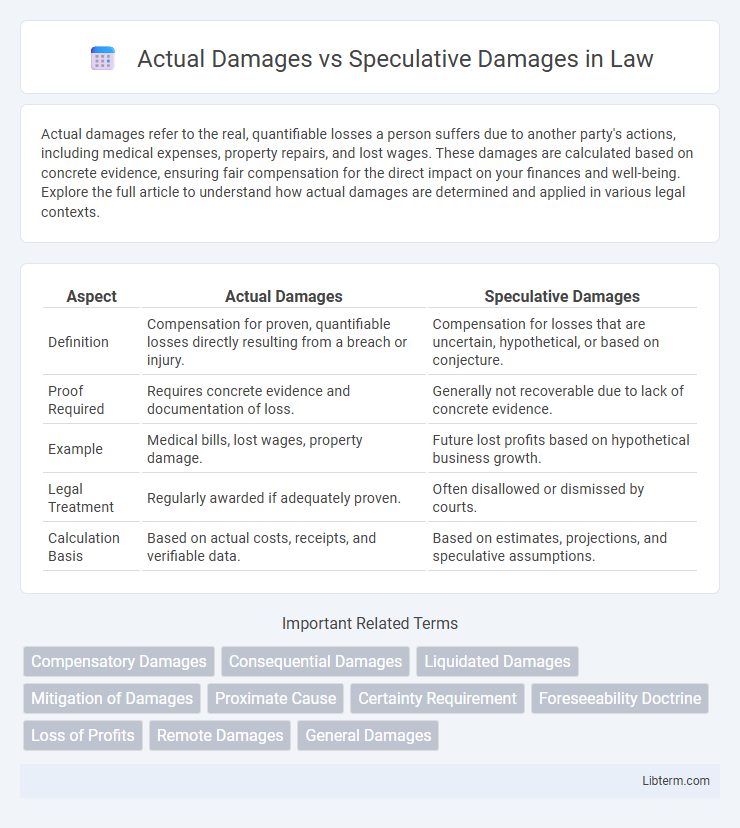
| Aspect | Actual Damages | Speculative Damages |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compensation for proven, quantifiable losses directly resulting from a breach or injury. | Compensation for losses that are uncertain, hypothetical, or based on conjecture. |
| Proof Required | Requires concrete evidence and documentation of loss. | Generally not recoverable due to lack of concrete evidence. |
| Example | Medical bills, lost wages, property damage. | Future lost profits based on hypothetical business growth. |
| Legal Treatment | Regularly awarded if adequately proven. | Often disallowed or dismissed by courts. |
| Calculation Basis | Based on actual costs, receipts, and verifiable data. | Based on estimates, projections, and speculative assumptions. |
Introduction to Actual and Speculative Damages
Actual damages refer to quantifiable monetary compensation awarded for proven losses directly caused by a defendant's actions, such as medical expenses, property repair costs, and lost wages. Speculative damages involve potential future losses that are uncertain or difficult to calculate with precision, often requiring expert testimony to establish probable outcomes. Understanding the distinction is crucial for accurately assessing claims and ensuring fair legal remedies.
Defining Actual Damages
Actual damages refer to compensation awarded for quantifiable losses directly resulting from a defendant's wrongful act, including medical expenses, property repair costs, and lost wages. Courts require plaintiffs to provide concrete evidence supporting these damages to ensure the award reflects real financial harm. Unlike speculative damages, actual damages must be proven with reasonable certainty and cannot be based on conjecture or potential future losses.
Understanding Speculative Damages
Speculative damages refer to potential losses that are uncertain and not proven with reasonable certainty in a legal claim, often based on future possibilities rather than past or present facts. Courts generally require concrete evidence and reasonable calculations to award damages, making speculative damages difficult to recover unless supported by credible expert testimony. Understanding the difference between actual damages, which are quantifiable and directly linked to a breach or injury, and speculative damages is crucial for accurately assessing potential legal remedies.
Key Differences Between Actual and Speculative Damages
Actual damages refer to compensation awarded for quantifiable losses directly resulting from an injury or breach, such as medical bills, lost wages, and property repair costs. Speculative damages involve compensation for potential future losses that are uncertain or difficult to quantify, often lacking concrete evidence to prove their likelihood. The key difference lies in the evidentiary basis: actual damages require demonstrable proof of loss, whereas speculative damages are based on conjecture and future possibilities.
Legal Standards for Proving Actual Damages
Actual damages require concrete evidence demonstrating a quantifiable loss directly caused by the defendant's actions, typically supported by documentation such as receipts, invoices, or expert testimony. Legal standards mandate that plaintiffs prove the damages are certain and not speculative, establishing a clear causal link between the misconduct and the financial harm. Courts reject claims based on conjecture or hypothetical scenarios, emphasizing the necessity of precise and verifiable injury to recover actual damages.
Challenges in Proving Speculative Damages
Proving speculative damages presents significant challenges due to the necessity of establishing a clear causal link between the injury and the claimed losses, which often lack concrete evidence or quantifiable metrics. Courts require precise documentation and expert testimony to substantiate future losses, making it difficult to validate estimates based on hypothetical scenarios or assumptions. Actual damages rely on verifiable data such as invoices and receipts, while speculative damages depend heavily on the predictability of future events, increasing the risk of dismissal due to uncertainty.
Importance of Documentation in Damage Claims
Actual damages require precise evidence documenting direct losses, such as receipts, invoices, and contracts, to establish the exact monetary harm incurred. Speculative damages, being uncertain and based on projections, demand rigorous and credible forecasting supported by expert analysis and thorough records to avoid dismissal. Proper documentation ensures the legitimacy of damage claims, strengthens legal arguments, and enhances the likelihood of successful compensation awards.
Case Law Examples: Actual vs Speculative Damages
Actual damages are awarded based on concrete, provable losses as demonstrated in landmark cases such as *Hadley v. Baxendale*, where damages must be a foreseeable result of the breach. Speculative damages, by contrast, involve uncertain or hypothetical losses and are generally rejected, as seen in *Story Parchment Co. v. Paterson Parchment Paper Co.*, where courts emphasized the necessity of reasonable certainty. These case law examples establish the critical distinction that actual damages require tangible evidence, while speculative damages lack sufficient factual basis to support recovery.
Impact on Compensation and Settlements
Actual damages represent quantifiable financial losses, including medical expenses, lost wages, and property damage, ensuring precise compensation in settlements. Speculative damages involve uncertain future losses, such as potential earning capacity or emotional distress, often leading to disputes and reduced settlement certainty. Courts and insurers prioritize actual damages to minimize ambiguity and secure fair compensation for proven harm.
Conclusion: Implications for Plaintiffs and Defendants
Actual damages represent quantifiable losses directly caused by a defendant's actions, providing plaintiffs with concrete compensation based on provable evidence, while speculative damages involve uncertain or hypothetical losses that courts often reject due to their lack of factual support. Plaintiffs must therefore present clear, measurable evidence to succeed in damage claims, whereas defendants can challenge claims lacking concrete proof to avoid unwarranted liability. Understanding these distinctions impacts litigation strategies, evidentiary requirements, and the likelihood of award recovery in civil lawsuits.
Actual Damages Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com