Efficient packing techniques save time and reduce travel stress by maximizing luggage space and protecting your belongings. Using rolling methods and packing cubes helps organize your items and prevents wrinkles in clothing. Discover expert tips and strategies to make your packing effortless in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
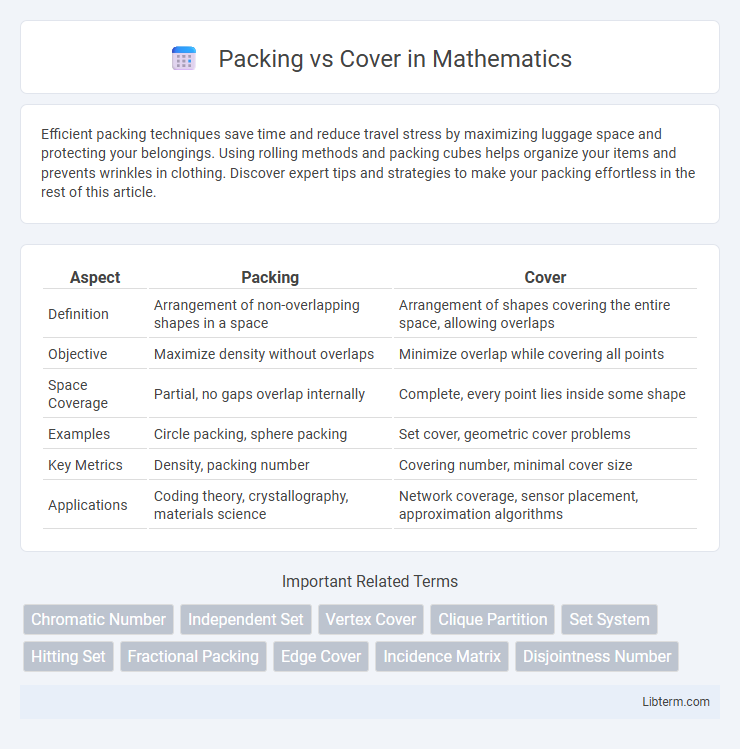
| Aspect | Packing | Cover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Arrangement of non-overlapping shapes in a space | Arrangement of shapes covering the entire space, allowing overlaps |
| Objective | Maximize density without overlaps | Minimize overlap while covering all points |
| Space Coverage | Partial, no gaps overlap internally | Complete, every point lies inside some shape |
| Examples | Circle packing, sphere packing | Set cover, geometric cover problems |
| Key Metrics | Density, packing number | Covering number, minimal cover size |
| Applications | Coding theory, crystallography, materials science | Network coverage, sensor placement, approximation algorithms |
Introduction to Packing and Cover
Packing refers to selecting disjoint subsets of elements in a set, ensuring no overlap among chosen components, commonly used in combinatorial optimization and graph theory. Cover involves choosing a collection of subsets that collectively include all elements of the original set, critical in applications like set cover problems and resource allocation. Both concepts play fundamental roles in mathematical optimization, algorithm design, and computational complexity analysis.
Defining Packing: What Does It Mean?
Packing refers to a collection of disjoint or non-overlapping subsets within a given set or space, where no two subsets share common elements. In graph theory, packing involves selecting vertex-disjoint or edge-disjoint subgraphs to maximize the number or size of these independent structures. This concept contrasts with covering, which aims to include all elements of a set, while packing emphasizes the arrangement of non-overlapping components for optimization.
Understanding Cover: Key Concepts
Cover refers to the minimum number of smaller sets required to completely contain all elements of a given set, playing a crucial role in optimization and combinatorial problems. In graph theory, the vertex cover problem specifically seeks the smallest subset of vertices that touch every edge, directly impacting network security and resource allocation tasks. Understanding cover enables efficient problem-solving strategies in fields like data compression, sensor placement, and computational biology.
Core Differences Between Packing and Cover
Packing involves placing items inside containers or boxes to securely organize and protect them, while cover refers to an external layer or material wrapped around an object for protection or concealment. The core difference lies in packing's function of containment and organization versus cover's role as a protective barrier or shield. Packing typically addresses spatial arrangement and cushioning, whereas cover primarily prevents exposure to external elements like dust, moisture, or damage.
Practical Applications of Packing
Packing involves arranging non-overlapping objects within a container to maximize density, commonly applied in logistics for efficient space utilization in shipping and storage. Practical applications include stacking boxes on pallets to minimize transportation costs and optimizing warehouse layout for increased inventory capacity. This technique improves material handling efficiency and reduces overall operational expenses.
Common Uses of Cover in Various Industries
Cover is widely used in industries such as construction for protective sheeting, agriculture for crop protection, and publishing for book jackets. In automotive manufacturing, covers protect vehicles during transport and storage, while in electronics, protective covers shield devices from dust and damage. The versatility of cover materials enables applications in healthcare for surgical drapes and in hospitality with bed and furniture covers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Packing
Packing provides efficient data compression by minimizing storage requirements and speeding up data transmission. Its main advantages include reduced file size and faster backup and restore processes, but disadvantages involve potential data loss in lossy packing methods and increased CPU usage during compression and decompression. Unlike covering, which focuses on data arrangement, packing directly affects resource consumption and performance in storage systems.
Benefits and Limitations of Using Cover
Using cover offers several benefits such as ease of application, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in protecting surfaces from environmental damage or contamination. However, its limitations include potential insufficient sealing compared to packing methods, reduced durability under heavy mechanical stress, and limited suitability for applications requiring airtight or leak-proof performance. Choosing cover over packing depends on the specific protection requirements and environmental conditions of the task.
Choosing Between Packing and Cover: Decision Factors
Choosing between packing and cover depends on the nature of the items and protection needs; packing is ideal for organizing and securing multiple smaller objects, while cover provides a protective layer against external elements. Factors such as fragility, exposure to weather, long-term storage, and transportation influence the decision, with packing offering cushioning and compartmentalization and cover offering moisture and dust resistance. Assessing material durability, item value, and intended handling conditions ensures the optimal choice between packing and cover for preservation and safety.
Conclusion: Packing vs Cover – Which Suits Your Needs?
Packing measures the maximum number of disjoint sets selected from a family, optimizing for distinct, non-overlapping elements, while covering focuses on the minimal collection of sets that encompass all elements, ensuring completeness. Choosing between packing and cover depends on whether the priority is maximizing independence or minimizing redundancy in your application. For problems demanding efficient resource allocation and conflict avoidance, packing is ideal, whereas covering suits scenarios requiring thorough inclusion and comprehensive oversight.
Packing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com