Polygon is a leading blockchain platform designed to improve Ethereum's scalability and usability without compromising security. It offers a multi-chain system that supports faster transactions and lower fees, making decentralized applications more accessible to users like you. Explore the rest of this article to discover how Polygon can enhance your blockchain experience.
Table of Comparison
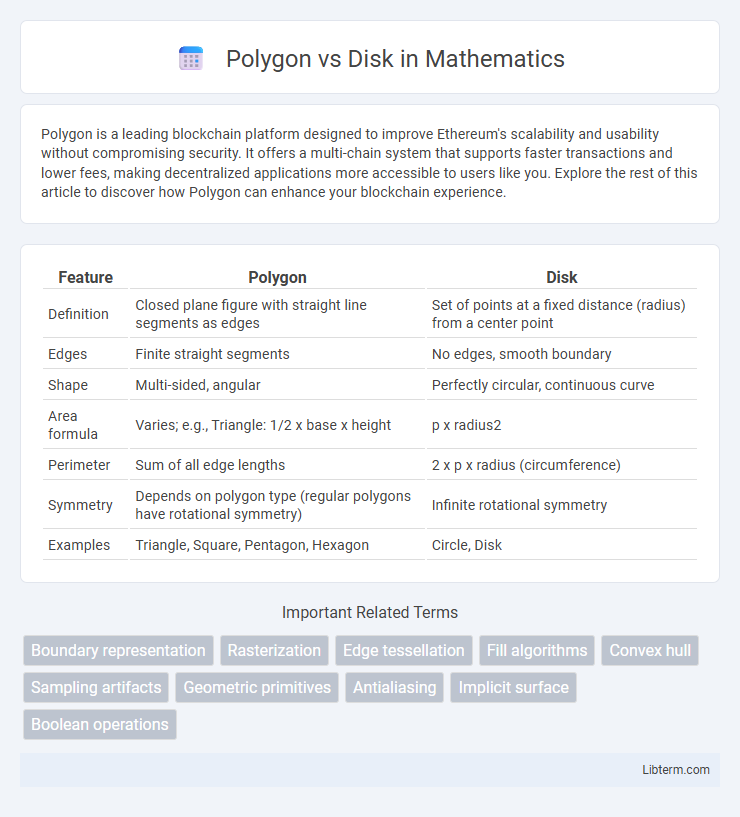
| Feature | Polygon | Disk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Closed plane figure with straight line segments as edges | Set of points at a fixed distance (radius) from a center point |
| Edges | Finite straight segments | No edges, smooth boundary |
| Shape | Multi-sided, angular | Perfectly circular, continuous curve |
| Area formula | Varies; e.g., Triangle: 1/2 x base x height | p x radius2 |
| Perimeter | Sum of all edge lengths | 2 x p x radius (circumference) |
| Symmetry | Depends on polygon type (regular polygons have rotational symmetry) | Infinite rotational symmetry |
| Examples | Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon | Circle, Disk |
Introduction to Polygon and Disk
Polygon and disk are fundamental geometric shapes used in mathematics and computer graphics, each serving distinct purposes. A polygon is a closed figure composed of a finite number of straight line segments connected end-to-end, forming vertices and edges, commonly used to represent complex shapes and surfaces. In contrast, a disk is a set of points in a plane that lie within a fixed radius from a central point, often utilized to model circular regions and smooth objects.
Overview of Polygon Network
Polygon Network is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum designed to enhance transaction speed and reduce costs by utilizing sidechains and a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. It supports interoperability across multiple blockchains, enabling seamless asset transfers and decentralized application (dApp) scalability. Polygon has gained significant adoption in the DeFi and NFT ecosystems due to its low fees and high throughput capabilities.
Overview of Disk Protocol
Disk Protocol is a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform that enables users to lend, borrow, and earn interest on digital assets through algorithmic money markets. It operates on multiple blockchains, offering scalable and secure financial services with native support for synthetic asset creation and smart contract automation. Polygon, in contrast, is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that enhances transaction speed and reduces costs, facilitating a broad ecosystem of dApps but does not natively provide lending or synthetic asset functionalities like Disk Protocol.
Key Differences Between Polygon and Disk
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure with straight sides and angles, defined by a closed chain of line segments, whereas a disk is a circular region in a plane enclosed by a single curved boundary with all points equidistant from the center. Polygons have vertices and edges that form various shapes such as triangles, squares, and hexagons, while disks are characterized by radius and center point with continuous, smooth curvature. Key differences include the polygon's segmented sides and angular corners contrasted with the disk's circular boundary and uniform curvature.
Consensus Mechanisms: Polygon vs Disk
Polygon employs a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism that enhances scalability and security by enabling validators to stake tokens and participate in block validation. Disk, in contrast, utilizes a delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) model, where token holders vote for a limited number of delegates responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the network integrity. The PoS approach in Polygon supports decentralization with a broader validator set, while Disk's DPoS mechanism emphasizes efficiency and faster block production through elected representatives.
Scalability and Throughput Comparison
Polygon leverages a multi-chain scaling framework that enhances scalability by enabling faster transaction processing across its sidechains and Layer 2 solutions, achieving throughput up to 65,000 transactions per second (TPS). In contrast, traditional disk storage systems do not directly impact blockchain transaction throughput but are critical for data persistence and retrieval speeds, which can indirectly affect performance in decentralized applications. Polygon's architecture prioritizes high scalability and throughput by offloading transactions from the main Ethereum chain, whereas disk systems primarily focus on storage capacity and input/output operations per second (IOPS).
Security Features: Polygon vs Disk
Polygon employs a robust security model with its Plasma framework and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, ensuring fast transaction finality and strong protection against double-spending and fraud. Disk protocol integrates end-to-end encryption and decentralized storage, prioritizing data confidentiality and tamper resistance through cryptographic proofs. While Polygon emphasizes network security and scalability, Disk focuses on secure data storage with cryptographic guarantees, making their security features complementary rather than directly comparable.
Developer Ecosystem and Tools
Polygon offers a robust developer ecosystem with comprehensive SDKs, APIs, and developer-friendly tools such as Polygon Studios and Polygon Edge that facilitate scalable dApp development on Ethereum-compatible chains. Disk, though emerging, specializes in decentralized data storage solutions with a narrower toolset primarily focused on integration with IPFS and blockchain-based file management, limiting its scope for broader dApp development. The extensive Polygon developer community and diverse tool availability provide greater resources and flexibility for developers compared to Disk's niche-focused platform.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Polygon excels in scalable Ethereum-compatible blockchain solutions, making it ideal for decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, NFT marketplaces, and gaming applications that require high throughput and low transaction fees. Disk, on the other hand, specializes in decentralized storage and data management, offering secure and censorship-resistant solutions for enterprises needing reliable off-chain data storage and retrieval. Use cases for Polygon prominently include layer 2 scaling to enhance blockchain efficiency, while Disk is predominantly applied in secure, distributed data storage and content delivery networks.
Future Prospects: Polygon vs Disk
Polygon's future prospects are promising due to its scalability solutions and strong developer ecosystem, which position it well for mainstream adoption in blockchain gaming and decentralized finance. Disk, by contrast, focuses on decentralized data storage with innovations targeting secure and efficient data retrieval, appealing to enterprises prioritizing privacy and data integrity. The evolving blockchain landscape suggests Polygon will dominate smart contract applications, while Disk may carve a niche within decentralized storage and data management sectors.
Polygon Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com