Constitutional amendments are formal changes or additions to a country's constitution, designed to address evolving legal, social, or political needs. These amendments often reflect significant shifts in governance, rights, or public policy, requiring careful consideration and often a rigorous approval process. Explore this article to understand the impact and procedure of constitutional amendments on Your nation's legal framework.
Table of Comparison
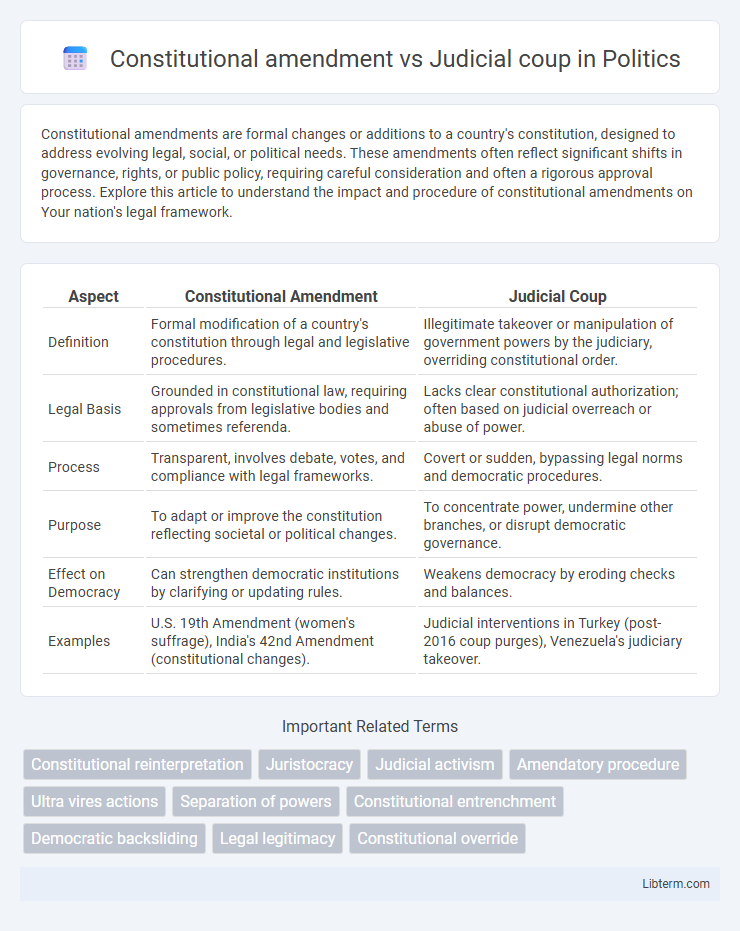
| Aspect | Constitutional Amendment | Judicial Coup |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal modification of a country's constitution through legal and legislative procedures. | Illegitimate takeover or manipulation of government powers by the judiciary, overriding constitutional order. |
| Legal Basis | Grounded in constitutional law, requiring approvals from legislative bodies and sometimes referenda. | Lacks clear constitutional authorization; often based on judicial overreach or abuse of power. |
| Process | Transparent, involves debate, votes, and compliance with legal frameworks. | Covert or sudden, bypassing legal norms and democratic procedures. |
| Purpose | To adapt or improve the constitution reflecting societal or political changes. | To concentrate power, undermine other branches, or disrupt democratic governance. |
| Effect on Democracy | Can strengthen democratic institutions by clarifying or updating rules. | Weakens democracy by eroding checks and balances. |
| Examples | U.S. 19th Amendment (women's suffrage), India's 42nd Amendment (constitutional changes). | Judicial interventions in Turkey (post-2016 coup purges), Venezuela's judiciary takeover. |
Understanding Constitutional Amendments: Definition and Process
Constitutional amendments are formal changes or additions to a nation's constitution, typically requiring a rigorous process such as legislative approval, public referendum, or both to ensure democratic legitimacy. Judicial coups occur when courts illegitimately alter constitutional meanings or usurp political authority, bypassing established amendment procedures. Understanding this distinction highlights the importance of adhering to constitutional processes to maintain the rule of law and prevent judicial overreach.
Judicial Coup: Meaning and Historical Context
A judicial coup occurs when a court, typically a supreme or constitutional court, unlawfully oversteps its constitutional mandate to seize political power or override democratic processes, undermining the separation of powers and democratic governance. Historically, judicial coups have taken place in countries like Pakistan during General Zia-ul-Haq's regime (1977-1988), where courts legitimized military takeovers by validating unconstitutional acts. Unlike constitutional amendments, which are legal modifications to a constitution through established procedures, judicial coups represent subversions of constitutional order driven by judicial overreach.
Key Differences Between Constitutional Amendments and Judicial Coups
Constitutional amendments involve a formal, legal process to modify or add to the constitution with legitimate authority, typically requiring approval from legislative bodies or public referenda. In contrast, judicial coups occur when courts overstep their constitutional role by effectively nullifying or rewriting laws and policies without proper constitutional mandate, undermining democratic processes. Key differences include legality, procedural adherence, and respect for separation of powers, with amendments reflecting democratic consent and judicial coups representing judicial overreach.
Legal Frameworks Governing Constitutional Changes
Legal frameworks governing constitutional changes vary significantly between constitutional amendments and judicial coups. Constitutional amendments involve formal procedures defined by the constitution itself, often requiring legislative approval, referenda, or supermajority votes to ensure legitimacy and adherence to rule of law. Judicial coups bypass these legal protocols, as courts or judges unlawfully invalidate or alter constitutional provisions without prescribed procedures, undermining democratic principles and the separation of powers.
The Role of the Judiciary in Democratic Governance
The role of the judiciary in democratic governance is to uphold constitutional principles and protect the rule of law through interpreting and applying amendments according to legal frameworks. A constitutional amendment represents a formal, democratic process for change, whereas a judicial coup occurs when courts override democratic decisions without legal basis, undermining constitutional authority. The judiciary must balance preserving democratic legitimacy with constitutional fidelity to maintain public trust and democratic stability.
Implications of Judicial Overreach on Constitutional Order
Judicial overreach disrupts the constitutional order by allowing courts to exceed their interpretive role, potentially undermining the separation of powers and eroding democratic principles. When judicial bodies alter constitutional provisions without proper legislative processes, it challenges the legitimacy of constitutional amendments and can lead to a crisis in governance and public trust. This imbalance risks weakening the rule of law and destabilizing established constitutional frameworks.
Case Studies: Constitutional Amendments vs Judicial Coups
Case studies reveal that constitutional amendments involve formal, legal changes to a country's constitution, exemplified by the 1978 Indian amendment introducing the right to education, reflecting a transparent, democratic process. In contrast, judicial coups occur when courts overstep their mandate, undermining elected governments without constitutional backing, as seen in Pakistan 2007 when the judiciary invalidated a civilian government's actions, effectively seizing power. These case studies highlight the distinction between lawful structural reforms and illegitimate power grabs under the guise of judicial authority.
Safeguarding the Constitution: Checks and Balances
Constitutional amendments represent a formal and democratic process of modifying the foundational legal framework, ensuring changes align with the people's will and maintain institutional balance. Judicial coups occur when courts overreach their authority, undermining the separation of powers and threatening democratic governance by manipulating constitutional interpretation for political ends. Safeguarding the Constitution relies on robust checks and balances between legislative, executive, and judicial branches to prevent abuses and uphold the rule of law.
Public Perception and Political Ramifications
Public perception of a constitutional amendment often centers on legality and democratic process, reflecting a formal, institutional change endorsed by elected representatives. In contrast, a judicial coup is widely viewed as an illegitimate seizure of power by the judiciary, undermining the rule of law and provoking political instability. The political ramifications of a constitutional amendment usually involve structured policy shifts and legal adjustments, while a judicial coup can trigger widespread protests, erosion of public trust, and potential authoritarianism.
Paths Forward: Strengthening Constitutional Democracy
Strengthening constitutional democracy requires transparent amendments that respect the rule of law and reflect broad public consensus, ensuring legal frameworks evolve legitimately. Judicial coups undermine democratic institutions by subverting constitutional norms through illegal seizures of power, necessitating robust judicial independence and accountability mechanisms. Emphasizing civic education, institutional checks and balances, and international support can help safeguard democratic processes and prevent authoritarian backsliding.
Constitutional amendment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com