Constructive feedback is essential for personal and professional growth, providing clear guidance that helps you improve skills and performance. Focusing on specific behaviors and offering actionable suggestions creates a positive environment that encourages continuous development. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective ways to give and receive constructive feedback for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
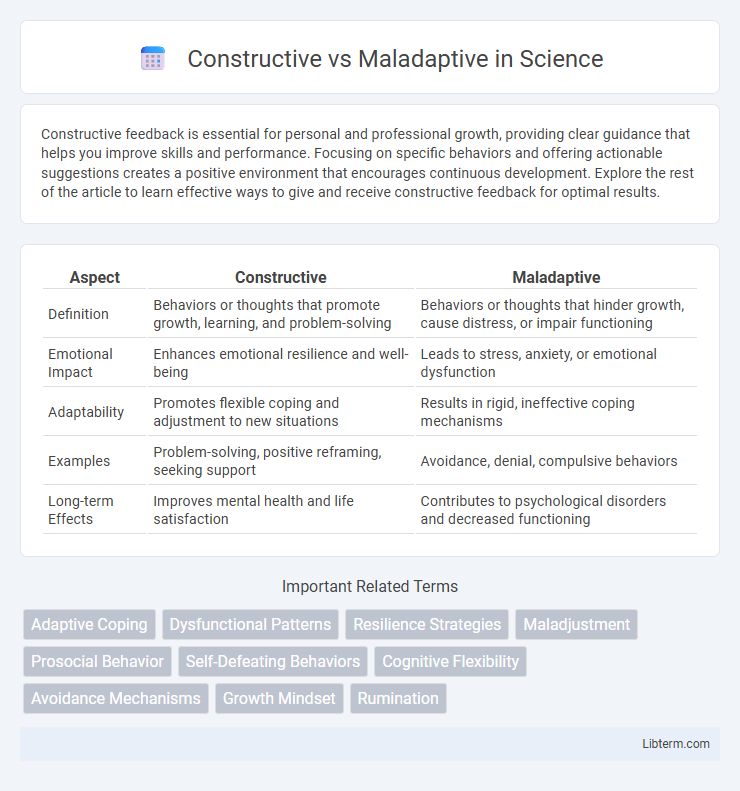
| Aspect | Constructive | Maladaptive |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behaviors or thoughts that promote growth, learning, and problem-solving | Behaviors or thoughts that hinder growth, cause distress, or impair functioning |
| Emotional Impact | Enhances emotional resilience and well-being | Leads to stress, anxiety, or emotional dysfunction |
| Adaptability | Promotes flexible coping and adjustment to new situations | Results in rigid, ineffective coping mechanisms |
| Examples | Problem-solving, positive reframing, seeking support | Avoidance, denial, compulsive behaviors |
| Long-term Effects | Improves mental health and life satisfaction | Contributes to psychological disorders and decreased functioning |
Understanding Constructive vs Maladaptive Behaviors
Constructive behaviors promote personal growth and effective problem-solving by fostering positive responses to stress and challenges. Maladaptive behaviors, in contrast, hinder emotional well-being and adaptability, often leading to increased anxiety or dysfunctional outcomes. Understanding these behavior types helps in developing healthier coping mechanisms and improving mental resilience.
Key Characteristics of Constructive Approaches
Constructive approaches emphasize proactive problem-solving, fostering resilience, and encouraging adaptive coping mechanisms that enhance emotional regulation and personal growth. These approaches prioritize positive communication, collaboration, and goal-oriented strategies to effectively manage stress and conflict. Key characteristics include flexibility, mindfulness, and the ability to transform challenges into opportunities for learning and development.
Signs of Maladaptive Patterns
Maladaptive patterns often manifest through chronic avoidance of challenges, persistent negative self-talk, and impulsive behaviors that hinder personal growth. These signs include excessive rumination, difficulty managing stress, and rigid thinking that prevents adaptive problem-solving. Recognizing such behaviors early is crucial for implementing effective strategies to promote constructive coping mechanisms.
Psychological Foundations of Constructive Strategies
Constructive strategies in psychology are rooted in adaptive cognitive and emotional processes that promote resilience, effective problem-solving, and emotional regulation. These strategies involve recognizing and reframing negative thoughts, fostering self-efficacy, and utilizing coping mechanisms aligned with positive behavioral outcomes. Maladaptive strategies, in contrast, often sustain psychological distress by reinforcing negative patterns and hindering adaptive adjustment.
Common Triggers for Maladaptive Responses
Common triggers for maladaptive responses include chronic stress, unresolved trauma, and negative thought patterns that overwhelm an individual's coping capacity. Environmental factors such as toxic relationships, high-pressure work environments, and lack of social support also significantly contribute to the development of maladaptive behaviors. Biological predispositions, including genetic vulnerabilities and neurological imbalances, further exacerbate these maladaptive reactions, impairing emotional regulation and decision-making processes.
Impact on Mental Health: Constructive vs Maladaptive
Constructive coping strategies enhance mental health by promoting resilience, emotional regulation, and problem-solving skills, leading to reduced stress and improved well-being. Maladaptive coping mechanisms, such as avoidance or substance abuse, exacerbate mental health issues by increasing anxiety, depression, and emotional distress. Effective mental health interventions prioritize developing constructive coping techniques to mitigate the negative effects of maladaptive behaviors.
Benefits of Embracing Constructive Choices
Embracing constructive choices enhances emotional resilience and fosters personal growth by promoting adaptive coping strategies that improve mental health. Constructive decisions lead to better problem-solving skills, increased self-awareness, and healthier relationships, contributing to overall well-being. Prioritizing constructive behaviors reduces stress and prevents the negative consequences associated with maladaptive patterns such as avoidance and self-sabotage.
Risks Associated with Maladaptive Coping
Maladaptive coping strategies, such as avoidance, substance abuse, and denial, significantly increase the risk of mental health disorders including anxiety, depression, and chronic stress. These ineffective responses often exacerbate emotional distress by preventing individuals from addressing the root causes of their problems, leading to impaired social relationships and reduced overall functioning. In contrast, constructive coping promotes resilience and problem-solving, minimizing long-term psychological and physical health risks.
Transforming Maladaptive Habits into Constructive Actions
Transforming maladaptive habits into constructive actions requires identifying negative behavioral patterns and consciously replacing them with positive, goal-oriented alternatives that enhance mental well-being. Techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based interventions help rewire thought processes, promoting adaptive responses to stress and challenges. Consistent practice, self-awareness, and reinforcement of new habits facilitate long-term behavioral change, improving overall emotional resilience and productivity.
Practical Tips for Fostering Constructive Behaviors
To foster constructive behaviors, prioritize clear communication, empathy, and goal-oriented problem-solving in daily interactions. Encourage consistent self-reflection and positive reinforcement to replace maladaptive responses with adaptive coping strategies. Implement structured routines and mindfulness techniques to enhance emotional regulation and resilience in challenging situations.
Constructive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com