Horizontal layouts enhance visual balance and improve readability by organizing content side by side. This design approach is ideal for showcasing multiple elements simultaneously without overwhelming the viewer. Explore the rest of the article to discover how horizontal alignment can elevate your project's effectiveness.
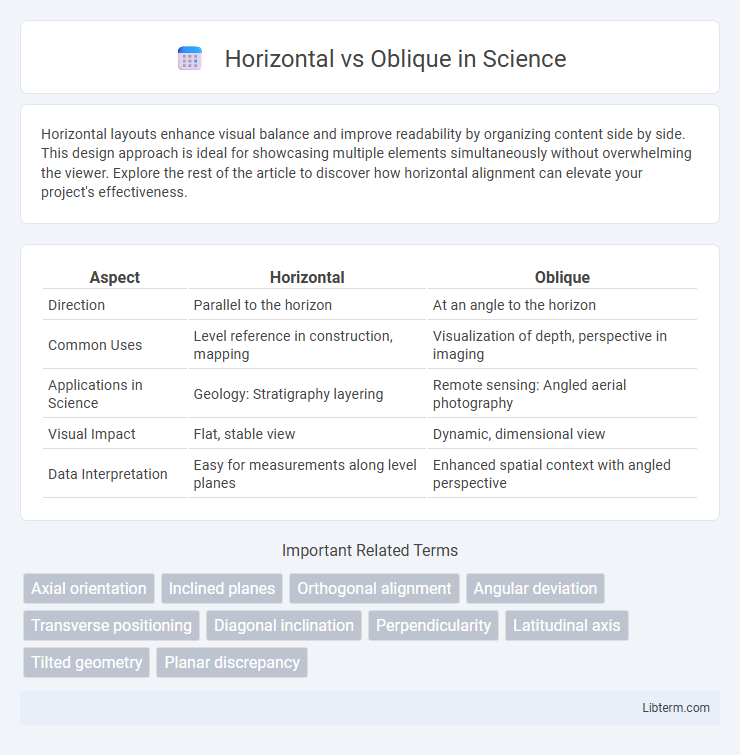
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Horizontal | Oblique |
|---|---|---|
| Direction | Parallel to the horizon | At an angle to the horizon |
| Common Uses | Level reference in construction, mapping | Visualization of depth, perspective in imaging |
| Applications in Science | Geology: Stratigraphy layering | Remote sensing: Angled aerial photography |
| Visual Impact | Flat, stable view | Dynamic, dimensional view |
| Data Interpretation | Easy for measurements along level planes | Enhanced spatial context with angled perspective |
Introduction to Horizontal and Oblique
Horizontal lines run parallel to the horizon, representing stability, calmness, and restfulness in design and composition. Oblique lines, angled and slanting, evoke movement, tension, and dynamism, often guiding the viewer's eye through a visual narrative. Understanding the contrast between horizontal and oblique lines is essential in fields like art, architecture, and graphic design for creating balanced or energetic aesthetics.
Defining Horizontal and Oblique
Horizontal lines run parallel to the horizon, creating a sense of stability and calmness in visual design. Oblique lines, also known as diagonal lines, are angled and convey movement, dynamism, and tension. Understanding the distinction between horizontal and oblique lines is essential in art, architecture, and graphic design for manipulating spatial perception and emotional impact.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Oblique
Horizontal lines run parallel to the horizon and represent stability and rest, commonly found in architectural designs and natural landscapes. Oblique lines, angled diagonally, suggest movement, dynamism, and tension, often used in artistic compositions to create a sense of depth or direction. The key difference lies in their orientation: horizontal lines are flat and level, while oblique lines incline or decline, influencing visual perception and emotional response.
Applications of Horizontal Orientation
Horizontal orientation finds widespread application in website design, enhancing user experience by facilitating easy navigation and natural eye movement across content. In photography and cinematography, horizontal frames capture expansive landscapes and group shots effectively, providing a wider field of view. Architecture often employs horizontal layouts to create a sense of stability and harmony, optimizing space utilization and aesthetic appeal.
Applications of Oblique Orientation
Oblique orientation is widely applied in fields such as architecture, graphic design, and manufacturing to create dynamic visual effects and enhance structural aesthetics. In medical imaging, oblique angles provide clearer views of anatomical structures by capturing planes that are not accessible through traditional horizontal or vertical orientations. Additionally, oblique scanning techniques improve the accuracy of geological surveys and remote sensing by capturing terrain features at diverse angles.
Advantages of Horizontal Arrangements
Horizontal arrangements offer improved visibility and accessibility by aligning components side-by-side, facilitating easier monitoring and maintenance. This layout enhances airflow and temperature management in equipment setups, reducing overheating risks and increasing operational efficiency. Space optimization in horizontal layouts supports scalable system expansion while maintaining organized cable management and streamlined workflow.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Oblique Approaches
Oblique approaches offer enhanced flexibility in accessing difficult-runway or terrain-challenged airports by allowing non-linear flight paths that improve obstacle clearance and optimize descent angles. They reduce pilot workload by providing clear visual cues for alignment, yet they demand higher pilot training and situational awareness due to their complexity compared to straightforward horizontal approaches. Limitations include potential increased fuel consumption and navigation challenges in adverse weather conditions or congested airspace, necessitating advanced avionics support for safe execution.
Common Mistakes in Identifying Horizontal vs Oblique
Common mistakes in identifying horizontal versus oblique lines often stem from misunderstanding their geometric definitions; horizontal lines run parallel to the x-axis, whereas oblique lines are slanted at any angle other than 0deg, 90deg, or 180deg. Confusing these lines occurs when angles or slopes are inaccurately measured or when visual perception is affected by perspective distortions. Accurate identification requires careful analysis of the line's slope, where horizontal lines have a slope of zero, and oblique lines have a non-zero, non-infinite slope.
Choosing Between Horizontal and Oblique: Factors to Consider
Choosing between horizontal and oblique cutting techniques depends on the specific tissue type and desired outcome of the procedure. Horizontal cuts are typically preferred for creating clean, parallel incisions that minimize damage to surrounding structures, ideal for muscle or tendon repair. Oblique cuts offer better surface area for healing and are often selected when optimizing tensile strength and promoting faster tissue integration is critical.
Conclusion: Horizontal vs Oblique in Practice
Horizontal drilling offers greater precision and efficiency for accessing reservoirs with extensive lateral spreads, improving well productivity and reducing surface impact. Oblique drilling provides flexibility in navigating complex geological formations, enabling optimal well placement in challenging environments. Selecting between horizontal and oblique drilling depends on subsurface conditions, reservoir characteristics, and project goals, with horizontal preferred for maximizing contact and oblique utilized for directional adjustment.
Horizontal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com