Theoretical concepts form the foundation for understanding complex subjects and drive innovation across various fields. Mastery of theories allows you to apply knowledge effectively and solve practical problems with confidence. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how theoretical insights can enhance your expertise.
Table of Comparison
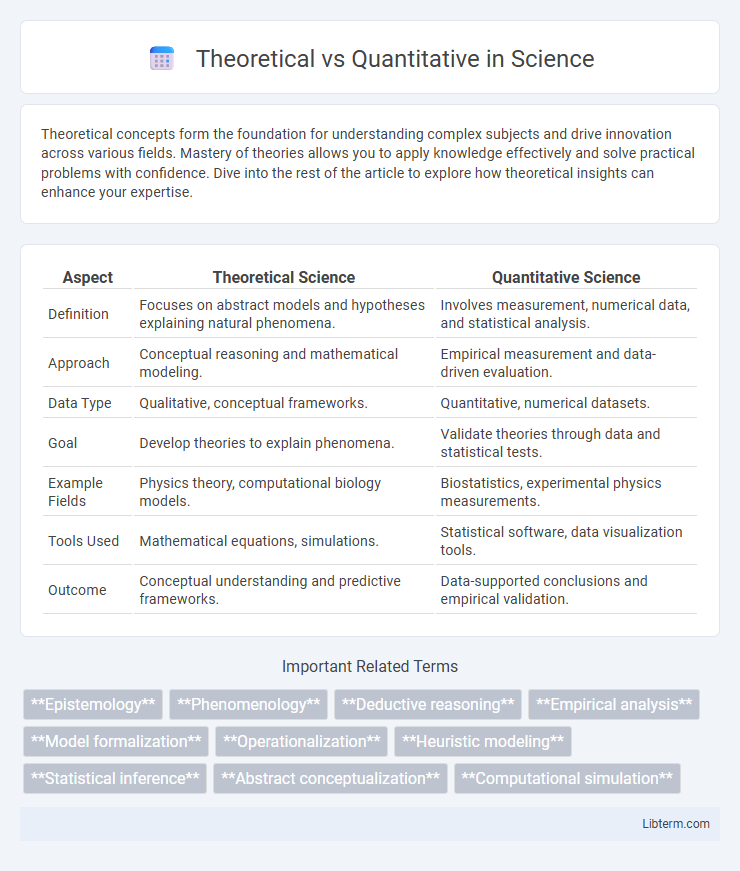
| Aspect | Theoretical Science | Quantitative Science |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on abstract models and hypotheses explaining natural phenomena. | Involves measurement, numerical data, and statistical analysis. |
| Approach | Conceptual reasoning and mathematical modeling. | Empirical measurement and data-driven evaluation. |
| Data Type | Qualitative, conceptual frameworks. | Quantitative, numerical datasets. |
| Goal | Develop theories to explain phenomena. | Validate theories through data and statistical tests. |
| Example Fields | Physics theory, computational biology models. | Biostatistics, experimental physics measurements. |
| Tools Used | Mathematical equations, simulations. | Statistical software, data visualization tools. |
| Outcome | Conceptual understanding and predictive frameworks. | Data-supported conclusions and empirical validation. |
Introduction to Theoretical and Quantitative Approaches
Theoretical approaches in research develop frameworks and hypothesize underlying principles to explain phenomena, emphasizing conceptual clarity and abstraction. Quantitative approaches focus on numerical data collection and statistical analysis to test hypotheses and measure variables objectively. Both methodologies complement each other by enhancing the rigor and depth of scientific inquiry across disciplines like social sciences, economics, and natural sciences.
Defining Theoretical Analysis
Theoretical analysis involves constructing abstract models to understand complex systems or phenomena by identifying underlying principles and relationships. It relies on logical reasoning, mathematical frameworks, and hypotheses to predict outcomes without immediate reliance on empirical data. This form of analysis forms the foundation for developing quantitative methods that validate or refine theoretical predictions through numerical measurement and statistical evaluation.
Understanding Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods emphasize numerical data collection and statistical analysis to identify patterns and test hypotheses in research. These methods rely on structured surveys, experiments, and computational models to ensure objective measurement and reproducibility. Understanding quantitative techniques enhances the ability to analyze complex datasets and derive evidence-based conclusions in various academic and professional fields.
Historical Development of Theoretical and Quantitative Approaches
The historical development of theoretical and quantitative approaches in research reflects distinct yet complementary paradigms shaped by evolving academic disciplines. Theoretical approaches originated in philosophy and social sciences, emphasizing conceptual frameworks and abstract reasoning to explain phenomena, while quantitative methods emerged with the rise of statistics and empirical sciences, focusing on numerical data and statistical analysis for validation. Over time, advancements in computing and data availability have further integrated these approaches, fostering a comprehensive understanding through model-building and empirical testing.
Key Differences Between Theoretical and Quantitative Research
Theoretical research centers on developing abstract concepts and models to explain phenomena without relying on numerical data, emphasizing hypotheses and frameworks. Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data using statistical methods to test hypotheses and measure variables objectively. Key differences include the nature of data used--conceptual vs. numerical--and the focus on model development in theoretical research versus empirical measurement in quantitative studies.
Advantages of Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks provide a structured approach to understanding complex phenomena by offering clear concepts and relationships that guide research design and interpretation. They allow researchers to build on existing knowledge, facilitating hypothesis development and deeper insight into causal mechanisms. This foundational clarity enhances the coherence and rigor of studies, making theoretical frameworks indispensable for advancing scientific inquiry.
Benefits of Quantitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis offers precise, data-driven insights by utilizing statistical methods and numerical data, enhancing decision-making accuracy in business and scientific research. It enables the identification of patterns, trends, and correlations that support predictive modeling and hypothesis testing. This approach increases objectivity, reduces bias, and allows for scalable analysis across large datasets, driving evidence-based strategies and measurable outcomes.
Limitations of Theoretical and Quantitative Methods
Theoretical methods often face limitations due to assumptions and simplifications that may not capture real-world complexities, leading to reduced applicability in practical scenarios. Quantitative methods rely heavily on data quality and availability, where inadequate or biased datasets can impair the accuracy and reliability of results. Both approaches struggle with modeling dynamic systems where variables change unpredictably, highlighting the need for integrative strategies combining theory and empirical data.
Integrating Theoretical and Quantitative Approaches
Integrating theoretical and quantitative approaches enhances research by combining conceptual frameworks with empirical data analysis, enabling more robust models and predictive accuracy. Theoretical insights guide hypothesis formation and variable selection, while quantitative methods validate these theories through statistical testing and data-driven evidence. This synergy supports comprehensive understanding and effective decision-making across scientific disciplines.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting between theoretical and quantitative approaches depends on research goals and data availability. Theoretical methods excel in developing frameworks and hypotheses, while quantitative techniques provide empirical validation and measurable insights. Balancing both approaches enhances comprehensive understanding and robust conclusions across disciplines.
Theoretical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com