Emotion shapes human experience by influencing thoughts, behaviors, and decision-making processes. Understanding different emotional responses enhances your ability to navigate relationships and improve mental well-being. Explore the rest of the article to discover how emotions impact everyday life and strategies to manage them effectively.
Table of Comparison
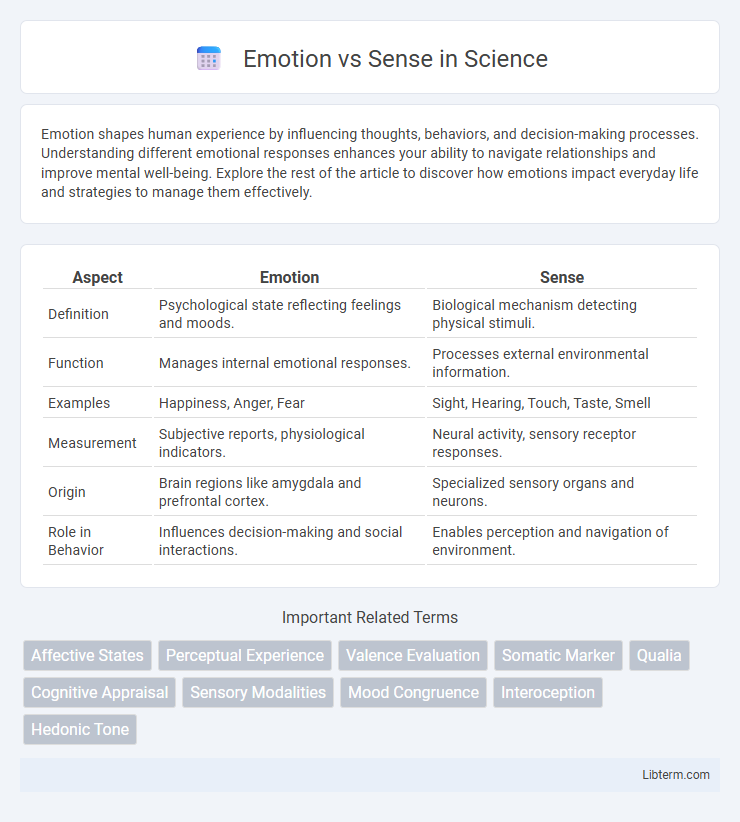
| Aspect | Emotion | Sense |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Psychological state reflecting feelings and moods. | Biological mechanism detecting physical stimuli. |
| Function | Manages internal emotional responses. | Processes external environmental information. |
| Examples | Happiness, Anger, Fear | Sight, Hearing, Touch, Taste, Smell |
| Measurement | Subjective reports, physiological indicators. | Neural activity, sensory receptor responses. |
| Origin | Brain regions like amygdala and prefrontal cortex. | Specialized sensory organs and neurons. |
| Role in Behavior | Influences decision-making and social interactions. | Enables perception and navigation of environment. |
Understanding Emotion and Sense: Key Definitions
Emotion refers to complex psychological states involving subjective experiences, physiological responses, and behavioral expressions, while sense pertains to the physiological capacity to perceive stimuli through sensory organs. Understanding emotion involves recognizing feelings such as happiness, sadness, anger, and fear, which influence cognition and decision-making. Sense encompasses the reception and processing of external information through sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell, forming the basis for perception and interaction with the environment.
The Science Behind Emotions: How Feelings Emerge
Emotions emerge from complex interactions between the brain's limbic system, particularly the amygdala and hypothalamus, and sensory inputs that trigger physiological responses. Neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin regulate mood and emotional intensity, linking biochemical processes to subjective feelings. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how the brain integrates external stimuli and internal states to produce distinct emotional experiences.
Decoding the Five Senses: The Human Sensory System
The human sensory system decodes environmental stimuli through five primary senses: sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch, each processed by specialized organs and neural pathways. Sensory receptors convert external signals into electrical impulses that the brain interprets, allowing perception and response to surroundings. Understanding the distinction between emotion and sense involves recognizing that sensory input triggers emotional reactions, yet emotions emerge from complex brain processes beyond mere sensory decoding.
Emotion vs Sense: Core Differences Explained
Emotion and sense represent distinct cognitive processes; emotion involves subjective feelings triggered by internal or external stimuli, while sense pertains to the physical perception of the environment through sensory organs. Emotions influence decision-making and behavior by integrating past experiences, whereas senses provide immediate, objective data crucial for survival and interaction. Understanding the core differences clarifies how humans process experiences emotionally versus perceptually.
The Interplay Between Sensory Input and Emotional Response
Sensory input from the environment triggers neural pathways that directly influence emotional responses in the brain, particularly within the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. The intensity and quality of sensory stimuli, such as colors, sounds, or textures, modulate feelings like fear, joy, or discomfort, creating a feedback loop between perception and emotion. This dynamic interplay enables humans to interpret and react to their surroundings with both instinctive and nuanced emotional experiences.
The Role of the Brain in Processing Emotion and Sense
The brain processes emotion primarily through the amygdala, which evaluates threats and triggers emotional responses, while the sensory cortex interprets sensory input from the environment. Neural pathways in the limbic system integrate emotional data with sensory information, enabling a cohesive perception of stimuli. This complex interaction allows the brain to respond adaptively by linking emotional significance to sensory experiences.
Cultural Influences on Emotion and Sensory Perception
Cultural influences shape both emotion and sensory perception by determining the expression, interpretation, and valuation of feelings and sensory experiences. Different cultures emphasize distinct emotional responses and sensory priorities, affecting how individuals perceive and react to stimuli such as color, taste, and sound. Understanding these cultural variations is essential for cross-cultural communication, psychological research, and marketing strategies targeting diverse populations.
How Emotions Shape Our Sensory Experiences
Emotions profoundly influence sensory experiences by altering perception, intensity, and focus, enhancing or dulling stimuli based on emotional state. Neurobiological research shows that the amygdala modulates sensory processing centers, heightening responses to emotionally charged stimuli such as fear or pleasure. This dynamic interaction means that sensations are not purely objective but are intricately colored by the emotional context, shaping how reality is interpreted and responded to.
Practical Implications: Emotion vs Sense in Daily Life
Emotion and sense play distinct roles in daily decision-making, where emotions often drive quick, intuitive responses while senses provide concrete data for rational analysis. Practical implications arise when balancing emotional impulses with sensory information enhances judgment, such as in risk assessment or interpersonal communication. Understanding the interplay between emotion and sense improves problem-solving efficiency and emotional intelligence in everyday situations.
Bridging the Gap: Integrating Emotion and Sense for Wellbeing
Bridging the gap between emotion and sense is crucial for holistic wellbeing, as it fosters balanced decision-making and resilience. Integrating emotional intelligence with sensory awareness enhances mindfulness practices, reducing stress and improving mental health outcomes. Studies show that combining cognitive clarity with emotional insight leads to greater self-regulation and overall life satisfaction.
Emotion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com