Directed energy technology harnesses focused beams such as lasers or microwaves to deliver precise power for military, industrial, and communication applications. This emerging field promises enhanced accuracy, reduced collateral damage, and cost-effective solutions compared to traditional methods. Discover how directed energy can revolutionize your understanding of advanced technologies in the full article.
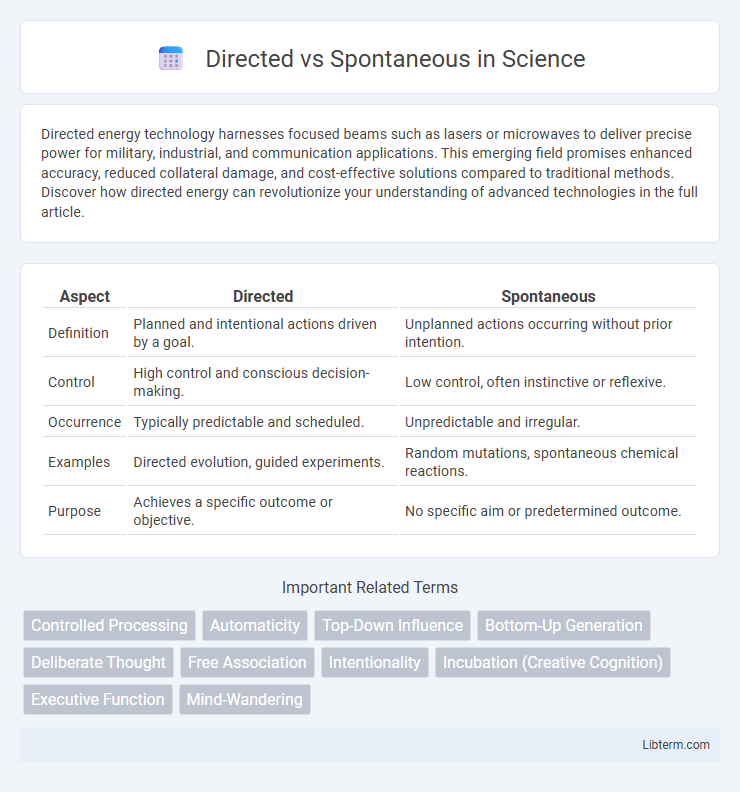
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Directed | Spontaneous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planned and intentional actions driven by a goal. | Unplanned actions occurring without prior intention. |
| Control | High control and conscious decision-making. | Low control, often instinctive or reflexive. |
| Occurrence | Typically predictable and scheduled. | Unpredictable and irregular. |
| Examples | Directed evolution, guided experiments. | Random mutations, spontaneous chemical reactions. |
| Purpose | Achieves a specific outcome or objective. | No specific aim or predetermined outcome. |
Understanding Directed and Spontaneous Processes
Directed processes involve controlled, goal-oriented actions guided by specific instructions or planning, ensuring predictable outcomes. Spontaneous processes arise naturally without external guidance, characterized by randomness and self-organization within a system. Understanding these processes is crucial in fields like thermodynamics, cognitive science, and organizational behavior to optimize efficiency and adaptability.
Key Differences Between Directed and Spontaneous Approaches
Directed approaches follow a structured plan with clear objectives and predefined steps, ensuring controlled execution and predictable outcomes. Spontaneous approaches emphasize improvisation and adaptability, allowing for creative problem-solving in dynamic or uncertain environments. Key differences include the level of planning, flexibility in response, and the predictability of results, with directed methods favoring consistency and spontaneous methods fostering innovation.
Advantages of Directed Methods
Directed methods in research offer precise control over experimental conditions, ensuring reproducibility and accuracy in data collection. These techniques enable targeted manipulation of variables, facilitating clear cause-and-effect analysis. The structured framework of directed methods enhances consistency and allows for systematic comparison across studies.
Benefits of Spontaneous Strategies
Spontaneous strategies enhance adaptability by allowing businesses to respond quickly to unexpected market changes, fostering innovation and creativity. These approaches encourage real-time decision-making, leading to opportunities that might be missed with rigid, directed plans. Embracing spontaneity in strategy can improve resilience and drive competitive advantage in dynamic environments.
Real-World Examples of Directed vs Spontaneous
Directed actions in real-world scenarios include scheduled public transportation systems like subways and buses, where routes and timings are predefined and strictly followed. Spontaneous actions often occur in social gatherings, such as impromptu dance sessions or unplanned conversations, where responses are immediate and unscripted. Urban planning also reflects the contrast, with directed elements like traffic signals regulating flow, while spontaneous pedestrian movements create dynamic, unpredictable patterns.
Impact on Creativity and Innovation
Directed creativity follows structured processes and specific goals, driving innovation through clear objectives and targeted problem-solving, which often results in efficient but potentially less diverse outcomes. Spontaneous creativity embraces unpredictability and free-flowing ideas, fostering innovation by encouraging divergent thinking and novel combinations that can lead to breakthrough discoveries. Balancing directed and spontaneous approaches enhances creative potential, leveraging both systematic execution and imaginative exploration to maximize innovation impact.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between directed and spontaneous approaches depends on project goals, team dynamics, and time constraints. Directed methods provide clear structure and control, ideal for risk-sensitive or complex tasks requiring precision. Spontaneous approaches foster creativity and adaptability, benefiting innovation-driven environments where flexibility enhances outcomes.
Challenges in Balancing Directed and Spontaneous Actions
Balancing directed and spontaneous actions presents challenges such as maintaining flexibility without sacrificing goal alignment or efficiency. Directed actions require structured planning and consistency, whereas spontaneous actions demand adaptability and creativity, often leading to conflicts in resource allocation and decision-making priorities. Effective management involves integrating real-time feedback systems and adaptive frameworks to harmonize intentional strategies with opportunistic behaviors.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies on directed versus spontaneous approaches reveal contrasting outcomes in organizational innovation. Directed innovation, characterized by structured processes and clear objectives, often leads to predictable and scalable successes such as Toyota's lean manufacturing system. In contrast, spontaneous innovation thrives in unpredictable environments exemplified by Google's 20% time policy, but carries risks highlighted by failures like Kodak's inability to adapt to digital transformation despite initial spontaneous creativity.
Future Trends in Directed and Spontaneous Methodologies
Future trends in directed methodologies emphasize increasing automation and AI integration to enhance precision and scalability in controlled environments. Spontaneous methodologies are evolving with adaptive learning algorithms and real-time data analytics that promote flexibility and responsiveness in dynamic contexts. Emerging hybrid models combine directed frameworks with spontaneous adjustments, optimizing innovation and efficiency across various industries.
Directed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com