Sporadic events occur irregularly, often without a predictable pattern, making them challenging to anticipate or plan for. This unpredictability can affect various aspects of life, from weather phenomena to social interactions. Explore the article to understand how sporadic occurrences impact different fields and your strategies for dealing with them effectively.
Table of Comparison
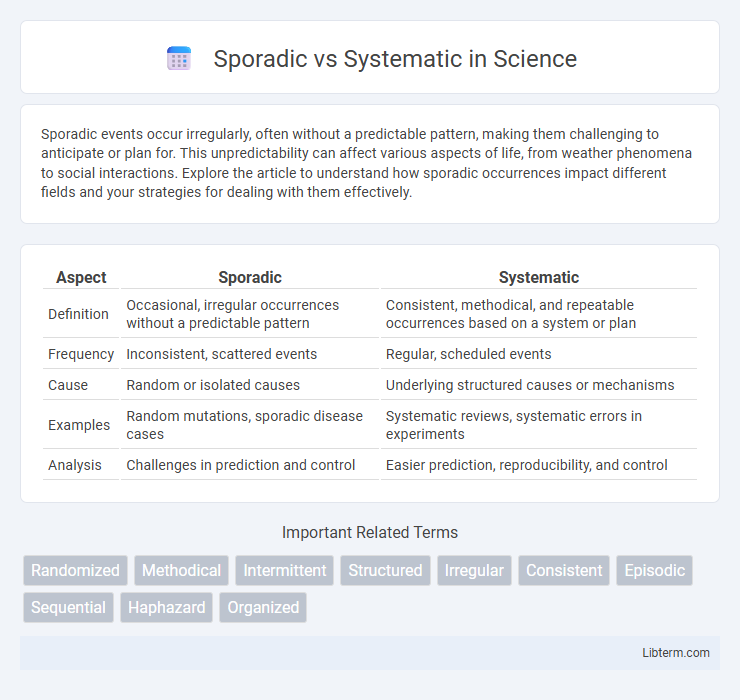
| Aspect | Sporadic | Systematic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Occasional, irregular occurrences without a predictable pattern | Consistent, methodical, and repeatable occurrences based on a system or plan |
| Frequency | Inconsistent, scattered events | Regular, scheduled events |
| Cause | Random or isolated causes | Underlying structured causes or mechanisms |
| Examples | Random mutations, sporadic disease cases | Systematic reviews, systematic errors in experiments |
| Analysis | Challenges in prediction and control | Easier prediction, reproducibility, and control |
Understanding Sporadic and Systematic Approaches
Sporadic approaches involve irregular, infrequent actions often triggered by specific events, leading to unpredictable outcomes and limited consistency. Systematic approaches utilize structured, repeatable processes designed to ensure consistent results and efficient resource management. Understanding the distinction between sporadic and systematic methods enhances decision-making by aligning actions with strategic goals and improving overall operational effectiveness.
Defining Sporadic Actions
Sporadic actions refer to irregular, infrequent behaviors or events that occur unpredictably without a set pattern or schedule. These actions contrast with systematic actions, which follow a structured, consistent, and repeatable process designed for efficiency and reliability. Understanding sporadic actions is essential in fields like quality control and behavior analysis, where identifying unpredictable occurrences helps improve systems and responses.
What Does Systematic Mean?
Systematic refers to actions or processes carried out according to a fixed plan or system, ensuring consistency and order. In various fields like research or problem-solving, systematic methods involve structured, repeatable steps designed to minimize errors and biases. This approach contrasts with sporadic occurrences, which are irregular and lack an organized framework.
Key Differences: Sporadic vs Systematic
Sporadic issues occur irregularly and unpredictably, making them challenging to diagnose and often linked to random events or external factors. Systematic problems arise consistently due to inherent flaws or design errors within a system, allowing for easier identification and targeted solutions. The key difference lies in their frequency and root cause, with sporadic being incidental and systematic stemming from structural or procedural defects.
Pros and Cons of Sporadic Methods
Sporadic methods offer flexibility and adaptability, making them useful for addressing unpredictable or unique cases without requiring extensive planning or resources. However, their inconsistency can lead to gaps in data collection, reduced reliability, and difficulty in establishing long-term patterns or trends compared to systematic approaches. The lack of structure may also result in inefficiencies and challenges in replicability or scalability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Systematic Methods
Systematic methods offer consistent and unbiased data collection, enhancing reproducibility and allowing for more accurate trend analysis in research and quality control. They require more planning and resources compared to sporadic approaches, potentially limiting flexibility in dynamic or unpredictable environments. However, systematic methods can reduce errors and improve decision-making by ensuring comprehensive and structured data coverage.
Real-World Examples: Sporadic vs Systematic
Sporadic errors, such as occasional software glitches in consumer apps, occur unpredictably and lack consistent patterns, making them difficult to reproduce and fix. Systematic errors, like measurement biases in scientific instruments or consistent coding flaws in financial software, arise from inherent faults in processes or systems and can be identified through thorough analysis and corrective action. Real-world examples include sporadic network outages caused by environmental interference versus systematic errors in manufacturing sensors consistently producing faulty readings.
Impact on Productivity and Results
Sporadic efforts often lead to inconsistent productivity and unpredictable results, causing delays and reduced efficiency in project completion. Systematic approaches streamline workflows through standardized processes, enhancing productivity by minimizing errors and improving time management. Organizations adopting systematic methods typically experience higher quality outcomes and sustained performance improvements compared to those relying on sporadic actions.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between sporadic and systematic methods depends on project scope, resource availability, and desired outcomes. Sporadic approaches suit creative tasks requiring flexibility and innovation, while systematic methods excel in complex projects needing consistency and thorough analysis. Evaluating time constraints, risk tolerance, and team expertise ensures informed decision-making for optimal results.
Integrating Sporadic and Systematic Strategies
Integrating sporadic and systematic strategies enhances project adaptability and consistency by combining flexibility with structured planning. Sporadic approaches allow for rapid response to unforeseen challenges, while systematic strategies ensure thorough analysis and methodical execution. Leveraging both methods maximizes efficiency and improves decision-making across dynamic and stable phases of a workflow.
Sporadic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com