Individualistic action emphasizes personal initiative and self-reliance, driving innovation and unique problem-solving approaches. Understanding the impact of acting independently can enhance your ability to make decisions aligned with your values and goals. Discover how embracing individualistic behavior can transform your personal and professional life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
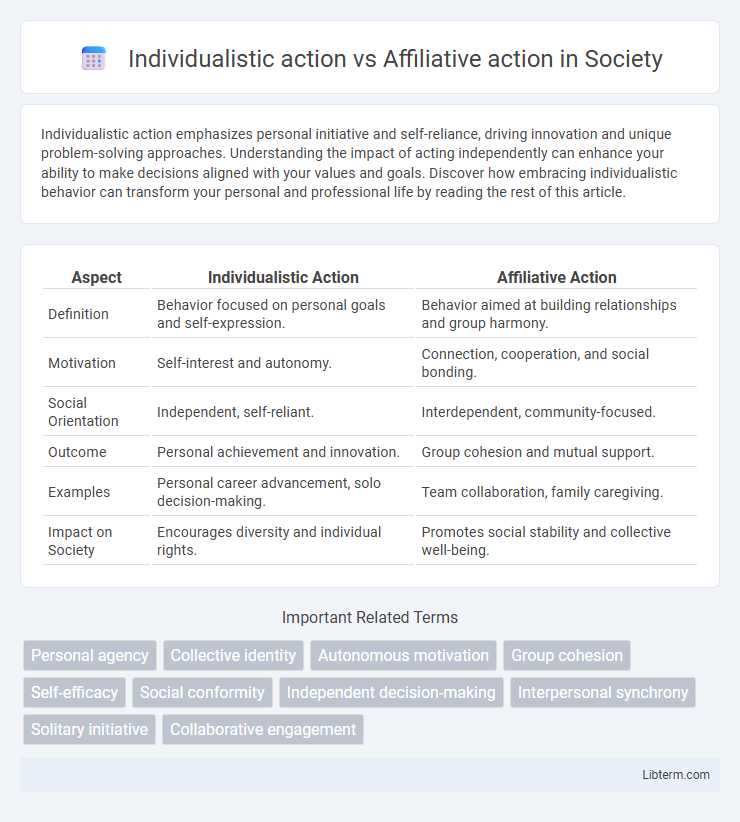
| Aspect | Individualistic Action | Affiliative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Behavior focused on personal goals and self-expression. | Behavior aimed at building relationships and group harmony. |
| Motivation | Self-interest and autonomy. | Connection, cooperation, and social bonding. |
| Social Orientation | Independent, self-reliant. | Interdependent, community-focused. |
| Outcome | Personal achievement and innovation. | Group cohesion and mutual support. |
| Examples | Personal career advancement, solo decision-making. | Team collaboration, family caregiving. |
| Impact on Society | Encourages diversity and individual rights. | Promotes social stability and collective well-being. |
Understanding Individualistic Action
Individualistic action emphasizes self-reliance, personal goals, and independent decision-making, prioritizing individual benefits over group interests. It is driven by personal autonomy and intrinsic motivation, often leading to innovation and unique problem-solving approaches. Understanding individualistic action requires analyzing how personal values and identity shape behavior distinct from social conformity or collective influence.
Defining Affiliative Action
Affiliative action involves behaviors aimed at forming or maintaining social bonds, emphasizing cooperation, empathy, and group harmony. This type of action prioritizes collective goals and interpersonal connections over personal gains. Unlike individualistic action, which focuses on personal achievement and autonomy, affiliative action fosters collaboration and mutual support within social groups.
Core Differences: Individual vs. Affiliative Approaches
Individualistic actions prioritize personal goals, autonomy, and self-expression, emphasizing independence and self-reliance. Affiliative actions focus on social harmony, group cohesion, and relational interdependence, highlighting cooperation and collective well-being. The core difference lies in the motivation behind behavior: individualistic approaches seek personal achievement, while affiliative approaches aim to strengthen social bonds.
Psychological Foundations of Individualistic Action
Psychological foundations of individualistic action emphasize autonomy, self-expression, and personal achievement as key motivators driving behavior. Research highlights intrinsic motivation, intrinsic goals, and self-concept clarity as critical factors fostering individualistic tendencies in decision-making and goal pursuit. Neuropsychological studies link individualistic action to brain regions involved in self-referential processing, such as the medial prefrontal cortex, underscoring the importance of self-identity in shaping behavior.
Social Dynamics in Affiliative Action
Affiliative action enhances social cohesion by promoting cooperation, trust, and group solidarity, which are essential for effective social dynamics. These actions facilitate stronger interpersonal connections and collective identity, reducing conflict and fostering mutual support within groups. Social dynamics in affiliative action are characterized by increased empathy, shared norms, and collaborative problem-solving that drive group harmony and resilience.
Benefits of Individualistic Behavior
Individualistic behavior enhances personal autonomy and encourages innovation by allowing individuals to pursue unique goals and ideas without constraints. This type of action fosters self-reliance and boosts intrinsic motivation, leading to greater confidence and problem-solving skills. Empirical studies show that individualistic actions contribute to higher creativity levels and improved personal achievement in competitive environments.
Advantages of Affiliative Behavior
Affiliative behavior enhances social bonding and fosters cooperative relationships, leading to increased group cohesion and collective problem-solving efficiency. It promotes emotional support and trust, which significantly improve mental health and reduce stress levels among group members. Affiliative actions contribute to creating a positive social environment that boosts motivation and resilience in both personal and professional contexts.
Challenges and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Individualistic action often faces challenges such as limited support networks and a higher risk of isolation, which can hinder problem-solving and reduce emotional resilience. Affiliative action may result in groupthink, where the desire for harmony suppresses critical thinking and innovation, leading to suboptimal decisions. Balancing autonomy and collaboration is difficult, as excessive individualism can fragment efforts, while too much affiliation might stifle creativity and personal accountability.
Contexts Favoring Individualism or Affiliation
Contexts favoring individualism often emphasize personal goals, autonomy, and self-expression, such as competitive workplaces or creative industries where innovation and unique contributions are valued. Affiliative actions thrive in environments prioritizing group harmony, social support, and collective well-being, commonly seen in close-knit communities or collaborative team settings. Cultural norms and situational demands strongly influence whether individuals lean toward individualistic or affiliative behaviors in social interactions.
Striking a Balance: Integrating Individualistic and Affiliative Actions
Striking a balance between individualistic action, which emphasizes personal goals and independence, and affiliative action, which focuses on group harmony and collaboration, is essential for effective decision-making and leadership. Integrating these approaches enhances self-expression while fostering social cohesion, enabling adaptive responses to diverse social contexts. Optimal performance often arises when individuals assert autonomy without compromising the benefits of cooperative engagement.
Individualistic action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com