Transparency fosters trust and accountability by openly sharing information and decisions within organizations. It enhances collaboration and ensures that all stakeholders have access to clear, honest communication. Explore the rest of the article to discover how fostering transparency can benefit your personal and professional relationships.
Table of Comparison
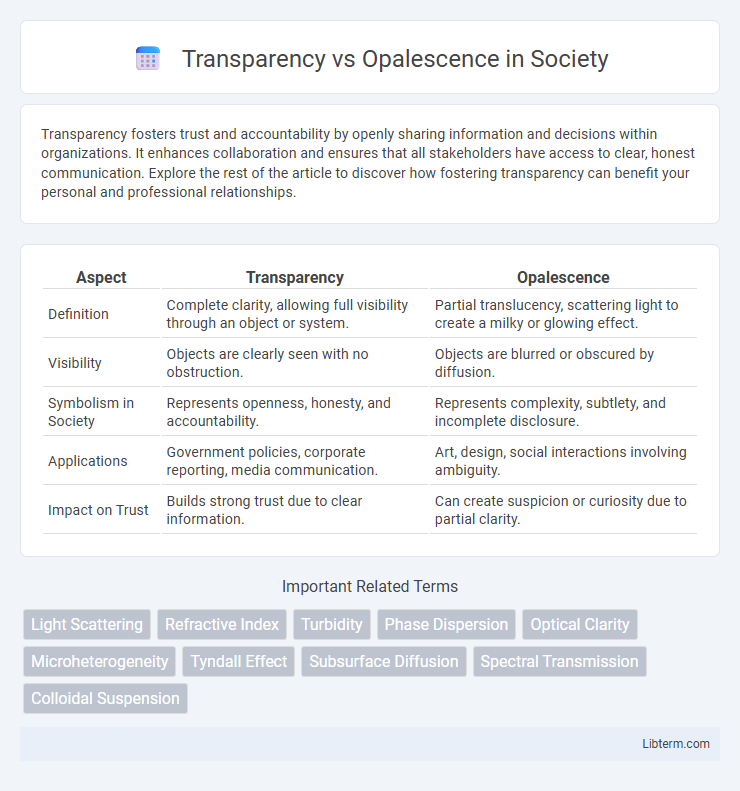
| Aspect | Transparency | Opalescence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete clarity, allowing full visibility through an object or system. | Partial translucency, scattering light to create a milky or glowing effect. |
| Visibility | Objects are clearly seen with no obstruction. | Objects are blurred or obscured by diffusion. |
| Symbolism in Society | Represents openness, honesty, and accountability. | Represents complexity, subtlety, and incomplete disclosure. |
| Applications | Government policies, corporate reporting, media communication. | Art, design, social interactions involving ambiguity. |
| Impact on Trust | Builds strong trust due to clear information. | Can create suspicion or curiosity due to partial clarity. |
Defining Transparency and Opalescence
Transparency in materials refers to their ability to transmit light without significant scattering, allowing objects behind them to be clearly seen. Opalescence, by contrast, describes a optical phenomenon where light is scattered and diffused within a material, creating a milky or bluish appearance especially under varying light conditions. Defining transparency and opalescence involves understanding how light interacts with microstructures, with transparency characterized by minimal light distortion and opalescence resulting from complex light scattering.
Physical Properties: Key Differences
Transparency allows light to pass through materials with minimal scattering, resulting in clear and distinct images, while opalescence causes light to scatter and diffuse, creating a milky or iridescent appearance. Transparent materials have a uniform structure that does not disrupt light waves, whereas opalescent substances contain microstructures or particles that alter light transmission by refracting and reflecting it in multiple directions. These fundamental differences in light interaction impact applications in optics, coatings, and materials science.
Scientific Principles Behind Transparency
Transparency in materials is primarily influenced by their atomic and molecular structure, which determines how light passes through without significant scattering or absorption. The uniform arrangement and minimal defects within transparent substances, such as glass or certain plastics, allow photons to transmit directly, maintaining clarity. In contrast, opalescence arises from micrometer-scale heterogeneities causing light to scatter, producing a milky or iridescent effect seen in opals and milk glass.
Opalescence: Causes and Effects
Opalescence occurs due to the scattering of light within a material, often caused by microscopic particles or structural inconsistencies that create a milky, iridescent appearance. This phenomenon is commonly seen in certain gemstones, such as opal, where the interplay of silica spheres diffracts light and produces vibrant color flashes. The effect enhances aesthetic qualities but can reduce optical clarity when opalescence dominates, impacting transparency and visual perception.
Applications in Everyday Materials
Transparency allows materials like glass and clear plastics to transmit light, making them essential for windows, lenses, and screens. Opalescence characterizes materials such as opal gemstones and some ceramics that scatter light to produce a milky, iridescent effect, used in jewelry and decorative tiles. Understanding the balance between transparency and opalescence guides the development of coatings, optical devices, and aesthetic finishes in consumer products.
Transparency in Technology and Design
Transparency in technology and design emphasizes clear visibility and understandable functionality, allowing users to see and comprehend the processes behind digital interfaces or products. This concept supports trust and accountability by making data flows, algorithms, and design decisions accessible and interpretable. Emphasizing transparency enhances user experience, facilitates ethical innovation, and promotes informed decision-making in complex technological landscapes.
The Role of Opalescence in Art and Nature
Opalescence in art and nature creates a unique visual phenomenon by scattering light to produce a play of colors, distinguishing it from mere transparency. This property enhances the depth and vibrancy of materials such as opal gemstones and certain paints, making them dynamic and captivating under varying light conditions. The interplay of opalescence contributes to a multidimensional aesthetic experience, highlighting the contrast to the clarity and straightforwardness of transparent surfaces.
Optical Advantages and Limitations
Transparency offers high clarity and sharpness by allowing maximum light transmission, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. Opalescence provides a unique play of light with a milky or iridescent effect, enhancing aesthetic appeal but reducing overall transparency. While transparency excels in optical accuracy, opalescence balances visual intrigue with modest light diffusion, limiting sharpness but enhancing depth perception.
Choosing Between Transparency and Opalescence
Choosing between transparency and opalescence hinges on the desired visual effect and material application. Transparency allows light to pass through clearly, making it ideal for windows and lenses where clarity is essential. Opalescence creates a milky, iridescent glow, often used in decorative glass and lighting to diffuse light and create aesthetic appeal.
Future Innovations in Material Science
Future innovations in material science are pushing the boundaries of transparency and opalescence by developing smart materials that dynamically adjust optical properties based on environmental stimuli. Nanotechnology enables the creation of ultra-clear polymers with enhanced durability and tunable light scattering, facilitating applications in advanced optics and display technologies. Researchers are also exploring bio-inspired materials that mimic natural opalescence to achieve energy-efficient light management for next-generation sensors and photovoltaic devices.
Transparency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com