Interactive processing enables real-time engagement between users and systems, enhancing the responsiveness and accuracy of data handling. It allows your applications to adapt instantly based on user input, improving overall efficiency and user satisfaction. Explore the full article to understand how interactive processing can transform your operations.
Table of Comparison
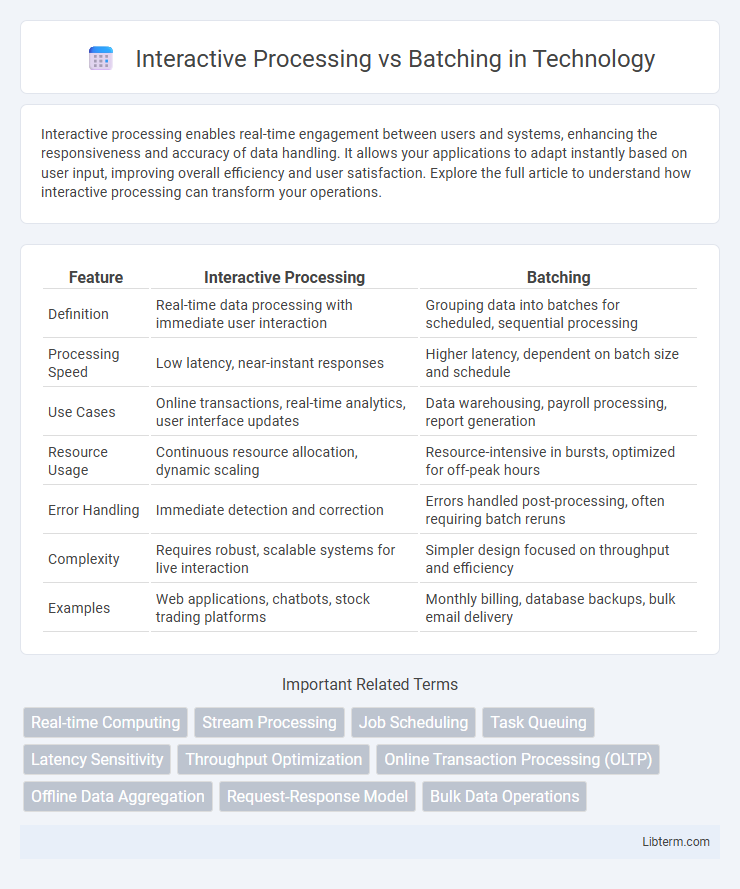
| Feature | Interactive Processing | Batching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time data processing with immediate user interaction | Grouping data into batches for scheduled, sequential processing |
| Processing Speed | Low latency, near-instant responses | Higher latency, dependent on batch size and schedule |
| Use Cases | Online transactions, real-time analytics, user interface updates | Data warehousing, payroll processing, report generation |
| Resource Usage | Continuous resource allocation, dynamic scaling | Resource-intensive in bursts, optimized for off-peak hours |
| Error Handling | Immediate detection and correction | Errors handled post-processing, often requiring batch reruns |
| Complexity | Requires robust, scalable systems for live interaction | Simpler design focused on throughput and efficiency |
| Examples | Web applications, chatbots, stock trading platforms | Monthly billing, database backups, bulk email delivery |
Understanding Interactive Processing
Interactive processing enables real-time data analysis and immediate response, making it ideal for applications requiring quick feedback such as online transactions and live monitoring systems. It processes small amounts of data continuously, ensuring low latency and high user engagement. This approach contrasts with batching, which accumulates data for periodic processing, sacrificing immediacy for efficiency in handling large datasets.
Overview of Batching Systems
Batching systems efficiently group multiple data or task units into a single processing job, reducing overhead and improving throughput for large-scale operations. These systems optimize resource utilization by minimizing context switching and enabling parallel execution on distributed computing frameworks like Apache Hadoop or Spark. Ideal for workloads requiring high-volume data processing, batching systems contrast with interactive processing by prioritizing throughput over immediate response times.
Key Differences Between Interactive and Batch Processing
Interactive processing handles data in real-time, providing immediate feedback and enabling dynamic user interaction, crucial for applications requiring low latency and continuous input. Batch processing executes large volumes of data simultaneously at scheduled intervals, optimizing resource use for tasks like payroll or data aggregation without user intervention. Key differences include processing speed, user involvement, and workload management, with interactive processing emphasizing responsiveness while batch processing prioritizes efficiency and throughput.
Performance Comparison
Interactive processing delivers low-latency responses by handling data in real-time, making it ideal for applications requiring immediate feedback. Batching processes large volumes of data collectively, maximizing throughput but increasing latency due to queued execution. Performance comparisons show interactive processing excels in responsiveness, while batching provides superior efficiency for large-scale data workloads.
User Experience: Interactivity vs. Automation
Interactive processing enhances user experience by enabling real-time responses and dynamic feedback, fostering greater engagement and immediate decision-making. Batching automates repetitive tasks, improving efficiency by processing large volumes of data without user intervention but sacrificing instant interactivity. Balancing interactivity with automation optimizes user satisfaction by combining responsiveness with streamlined workflows.
Scalability and Resource Utilization
Interactive processing enables real-time data analysis with low latency, optimizing resource utilization by dynamically allocating compute power based on workload demand. Batching processes large volumes of data in scheduled intervals, improving scalability through parallel execution but often at the cost of higher latency and resource idle time. Efficient scalability requires balancing these approaches, leveraging interactive processing for time-sensitive tasks while using batching to maximize throughput during off-peak periods.
Typical Use Cases for Interactive Processing
Interactive processing is ideal for real-time analytics, online transaction processing (OLTP), and dynamic data-driven applications where immediate response and low latency are critical. Common use cases include fraud detection in financial services, customer support chatbots, and personalized recommendation systems. These scenarios require continuous input from users and rapid processing to deliver timely, accurate results.
Common Applications of Batch Processing
Batch processing is commonly used in applications such as payroll systems, where large volumes of employee data are processed together to calculate salaries and tax deductions efficiently. It is also prevalent in data warehousing and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations, enabling the aggregation and transformation of extensive datasets during off-peak hours. Other typical batch processing applications include end-of-day financial transactions and billing systems that require handling vast amounts of records without immediate user interaction.
When to Choose Interactive Over Batch Processing
Interactive processing excels when real-time data analysis and immediate user feedback are critical, such as in fraud detection or live customer support. Batch processing is ideal for handling large volumes of data efficiently during off-peak hours, like end-of-day financial reporting or large-scale data transformations. Choose interactive processing for low-latency requirements and dynamic decision-making, ensuring timely and responsive actions.
Future Trends in Processing Approaches
Future trends in processing approaches emphasize the integration of interactive processing with batch processing to enhance real-time analytics and large-scale data handling. Advancements in in-memory computing and edge computing technologies are driving this convergence, enabling faster data access and reduced latency. Machine learning algorithms increasingly optimize task scheduling between interactive and batch systems for improved efficiency and scalability.
Interactive Processing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com