Efficient database storage is essential for optimizing data access speed and ensuring reliable data management across applications. Proper organization and indexing techniques significantly improve query performance and reduce storage costs. Explore the full article to discover how you can enhance your database storage strategy effectively.
Table of Comparison
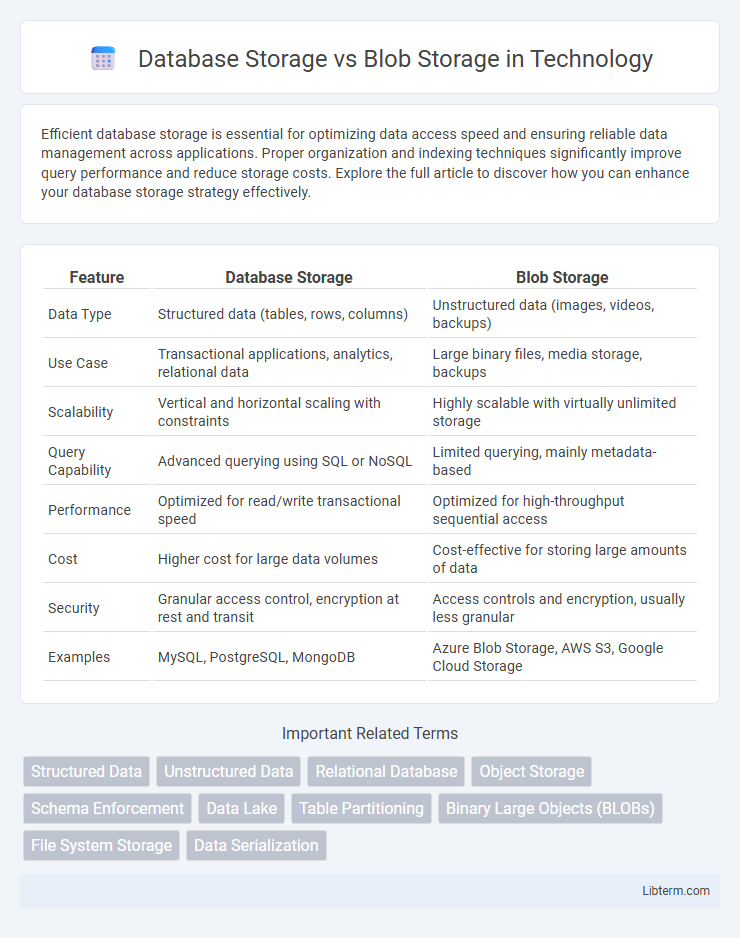
| Feature | Database Storage | Blob Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured data (tables, rows, columns) | Unstructured data (images, videos, backups) |
| Use Case | Transactional applications, analytics, relational data | Large binary files, media storage, backups |
| Scalability | Vertical and horizontal scaling with constraints | Highly scalable with virtually unlimited storage |
| Query Capability | Advanced querying using SQL or NoSQL | Limited querying, mainly metadata-based |
| Performance | Optimized for read/write transactional speed | Optimized for high-throughput sequential access |
| Cost | Higher cost for large data volumes | Cost-effective for storing large amounts of data |
| Security | Granular access control, encryption at rest and transit | Access controls and encryption, usually less granular |
| Examples | MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB | Azure Blob Storage, AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage |
Introduction to Database Storage vs Blob Storage
Database storage organizes structured data into tables with defined schemas, enabling efficient querying and transaction management for applications requiring relational data integrity. Blob storage is designed to handle unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups, providing scalable, cost-effective, and high-availability object storage in the cloud. Choosing between database and blob storage depends on the nature of the data and access patterns, with databases optimizing complex queries and blobs catering to large binary or unstructured data needs.
Key Concepts: Structured vs Unstructured Data
Database storage excels in managing structured data through tables and schemas, enabling efficient querying and data relationships. Blob storage is optimized for unstructured data such as images, videos, and documents, offering scalable, cost-effective storage without rigid schema requirements. Understanding the distinction between structured and unstructured data is crucial for selecting the appropriate storage solution based on data type and access patterns.
Storage Architecture Overview
Database storage organizes data into structured tables with defined schemas, enabling efficient querying and transactional consistency for relational data. Blob storage is designed for unstructured data, storing large binary objects like images, videos, and backups in scalable, flat containers without rigid schema requirements. Database storage uses row or column-based storage engines optimized for ACID compliance, whereas blob storage relies on distributed object storage systems to ensure high availability and durability across multiple geographic locations.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Database storage offers optimized query performance through indexing and structured data organization, enabling rapid transactional processing for complex relational datasets. Blob storage excels in scalability by managing vast unstructured data volumes with distributed architecture, providing high availability and cost-effective storage for large files like images or videos. Performance-wise, database storage is ideal for operations requiring low latency and consistency, while blob storage is better suited for scalable, high-throughput workloads with less stringent latency requirements.
Cost Considerations: Database vs Blob
Database storage typically incurs higher costs due to structured data management, indexing, and transaction support, leading to increased expenses for compute and storage resources. Blob storage offers a cost-effective alternative for unstructured data, with lower pricing based on capacity and access frequency, making it ideal for large-scale, infrequently accessed datasets. Choosing between database and blob storage depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints, where blob storage reduces costs for archival and multimedia files while databases justify higher costs with advanced query capabilities.
Security and Compliance Differences
Database storage offers structured data management with robust access controls, encryption at rest and in transit, and detailed auditing capabilities, making it ideal for compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Blob storage, while scalable for unstructured data such as media files and backups, often relies on container-level access policies and simpler encryption mechanisms, which may require additional measures for strict compliance standards. Enterprises must evaluate the specific security features and compliance certifications of each storage type to ensure data protection and regulatory adherence.
Backup, Recovery, and Durability
Database storage provides structured backup options with point-in-time recovery and transaction consistency, ensuring data integrity during rollback scenarios. Blob storage offers scalable, cost-effective backup solutions with high durability through geo-replication and automatic data redundancy across multiple data centers. Durability in databases is reinforced by write-ahead logging and snapshots, while blob storage leverages erasure coding and multiple replicas to protect against hardware failures.
Use Cases for Database Storage
Database storage is ideal for structured data requiring complex queries, transactions, and relationships, such as customer records, financial data, and inventory management systems. It supports ACID compliance, ensuring data integrity and consistency in applications like online banking and e-commerce platforms. Use cases often include real-time analytics, CRM systems, and enterprise resource planning where rapid access and modification of related data sets are critical.
Use Cases for Blob Storage
Blob Storage is ideal for storing unstructured data such as images, videos, backups, and large binary files that require scalable and cost-effective storage solutions. It supports massive data volumes with high availability and durability, making it suitable for content delivery, archiving, and big data analytics workloads. Unlike database storage optimized for structured data and complex queries, Blob Storage excels in scenarios needing efficient storage and retrieval of large files without the need for transactional consistency.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
When choosing the right storage solution, database storage offers structured data management with powerful querying capabilities, ideal for transactional data and relationships. Blob storage excels at handling unstructured data such as images, videos, and backups, providing scalable and cost-efficient large object storage. Evaluate data type, access patterns, scalability needs, and cost to determine whether database storage or blob storage best fits your application requirements.
Database Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com