Modular architecture enhances flexibility and scalability by breaking down complex systems into interchangeable, independent components. This design approach streamlines maintenance and promotes rapid development, adapting seamlessly to evolving user needs. Explore the rest of the article to discover how modular architecture can transform your projects.
Table of Comparison
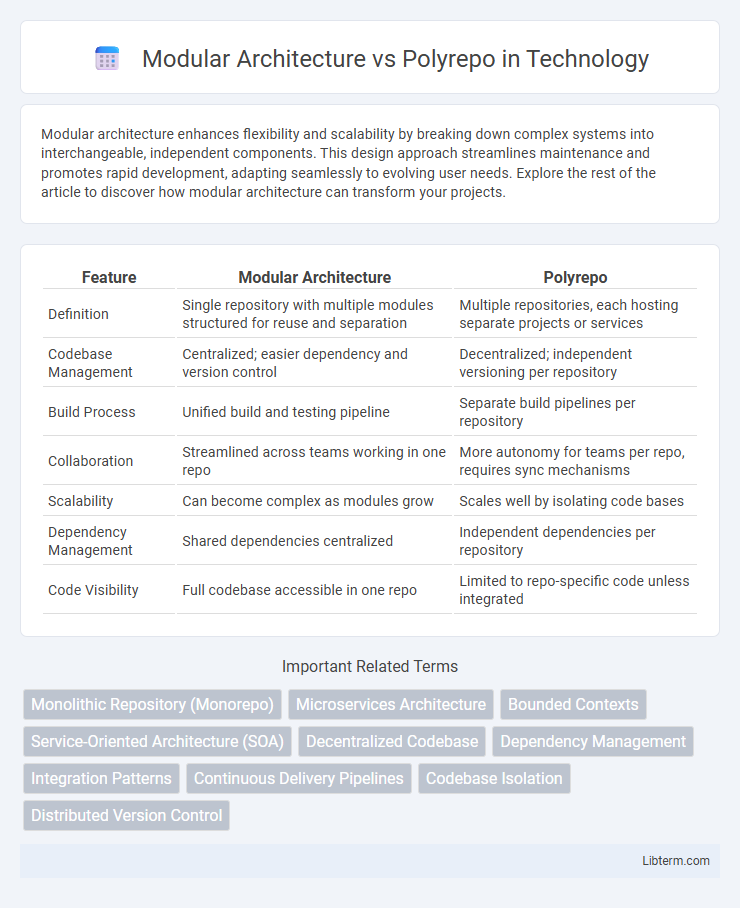
| Feature | Modular Architecture | Polyrepo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single repository with multiple modules structured for reuse and separation | Multiple repositories, each hosting separate projects or services |
| Codebase Management | Centralized; easier dependency and version control | Decentralized; independent versioning per repository |
| Build Process | Unified build and testing pipeline | Separate build pipelines per repository |
| Collaboration | Streamlined across teams working in one repo | More autonomy for teams per repo, requires sync mechanisms |
| Scalability | Can become complex as modules grow | Scales well by isolating code bases |
| Dependency Management | Shared dependencies centralized | Independent dependencies per repository |
| Code Visibility | Full codebase accessible in one repo | Limited to repo-specific code unless integrated |
Introduction to Modular Architecture and Polyrepo
Modular architecture divides a software system into distinct, self-contained modules that encapsulate functionality, promoting scalability and maintainability. Polyrepo refers to the practice of managing multiple independent repositories for different components or services within a system, enabling granular version control and autonomous development. Both approaches offer unique advantages in organizing complex software projects, with modular architecture emphasizing internal code organization and polyrepo focusing on external repository management.
Core Concepts: Defining Modular Architecture
Modular architecture organizes software into independent, interchangeable modules that encapsulate specific functionalities, enabling easier maintenance and scalability. Each module operates as a self-contained unit with well-defined interfaces and responsibilities, facilitating parallel development and clear separation of concerns. Unlike polyrepo, which manages multiple repositories, modular architecture emphasizes internal structure and component reusability within a single codebase.
Core Concepts: Understanding Polyrepo
Polyrepo architecture organizes codebases into multiple independent repositories, allowing teams to work autonomously and enforce clear boundaries between services or components. This approach contrasts with modular architecture's single repository housing multiple modules, which shares dependencies and configuration. Understanding polyrepo's core concept highlights advantages in scalability, version control granularity, and flexible deployment pipelines.
Key Differences Between Modular Architecture and Polyrepo
Modular architecture organizes code into self-contained, reusable modules within a single repository, enhancing maintainability and scalability by enabling isolated development and testing. Polyrepo manages multiple repositories, each housing distinct projects or services, which offers clear separation of concerns and independent deployment cycles but can complicate dependency management. Key differences include repository structure, with modular architecture favoring a unified codebase versus polyrepo's distributed repositories, and the impact on build processes, where modular setups often leverage integrated build tools, while polyrepo relies on coordinating separate pipelines.
Pros and Cons of Modular Architecture
Modular architecture enhances code maintainability and scalability by organizing software into independent, reusable components, which improves parallel development and simplifies debugging. However, it can introduce complexity in dependency management and increase initial setup time due to the need for clearly defined module boundaries. Despite these challenges, modular architecture facilitates easier testing and better team collaboration compared to monolithic or polyrepo approaches.
Pros and Cons of Polyrepo
Polyrepo structure offers clear separation of individual projects, enabling independent versioning and deployment, which enhances flexibility for diverse teams and technology stacks. It simplifies access control and reduces the risk of unintentional code dependencies, supporting more granular ownership across repositories. However, polyrepo can introduce complexity in managing cross-repository changes, increased overhead for consistent tooling, and challenges in maintaining synchronized documentation and testing environments.
Impact on Codebase Scalability
Modular architecture enhances codebase scalability by breaking down the system into independently deployable modules, enabling teams to work in parallel and reducing code interdependencies. Polyrepo structures further improve scalability by isolating modules into separate repositories, facilitating easier version control, targeted updates, and clearer ownership. Together, these approaches minimize merge conflicts and accelerate development cycles in large, evolving codebases.
Team Collaboration and Workflow Implications
Modular architecture enhances team collaboration by enabling independent development, testing, and deployment of distinct components, allowing parallel workflows and reducing merge conflicts. Polyrepo structures support decentralized version control with separate repositories per module, which can simplify permissions management but may increase overhead in coordinating cross-repository changes. Effective workflow integration relies on automation tools like CI/CD pipelines and clear interface contracts to synchronize efforts between modular components in both architectures.
Best Use Cases for Modular Architecture and Polyrepo
Modular architecture excels in large-scale projects requiring clear separation of concerns, scalability, and independent module deployment, such as enterprise-level applications and microservices ecosystems. Polyrepo structures are ideal for teams managing multiple repositories with distinct codebases or services, facilitating isolated version control and targeted collaboration in heterogeneous environments. Use modular architecture when unified integration and consistent versioning across modules are critical, and opt for polyrepo when autonomy and flexibility of individual components outweigh centralized dependency management.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Modular architecture enhances code maintainability by dividing a project into loosely coupled, reusable modules within a single repository, streamlining dependency management and version control. Polyrepo structures keep each module in separate repositories, offering better autonomy, granular access control, and independent deployment cycles, which can benefit large, cross-functional teams. Selecting between modular architecture and polyrepo depends on project scale, collaboration needs, and deployment frequency, with modular architecture ideal for smaller teams seeking simplicity and polyrepo suiting complex projects requiring isolated module development.
Modular Architecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com