Parsing involves analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language or computer languages, to identify its grammatical structure or syntactic components. This process is essential for understanding and interpreting the meaning behind data, enabling more accurate communication between humans and machines. Explore the rest of this article to discover how parsing techniques enhance language processing and data analysis.
Table of Comparison
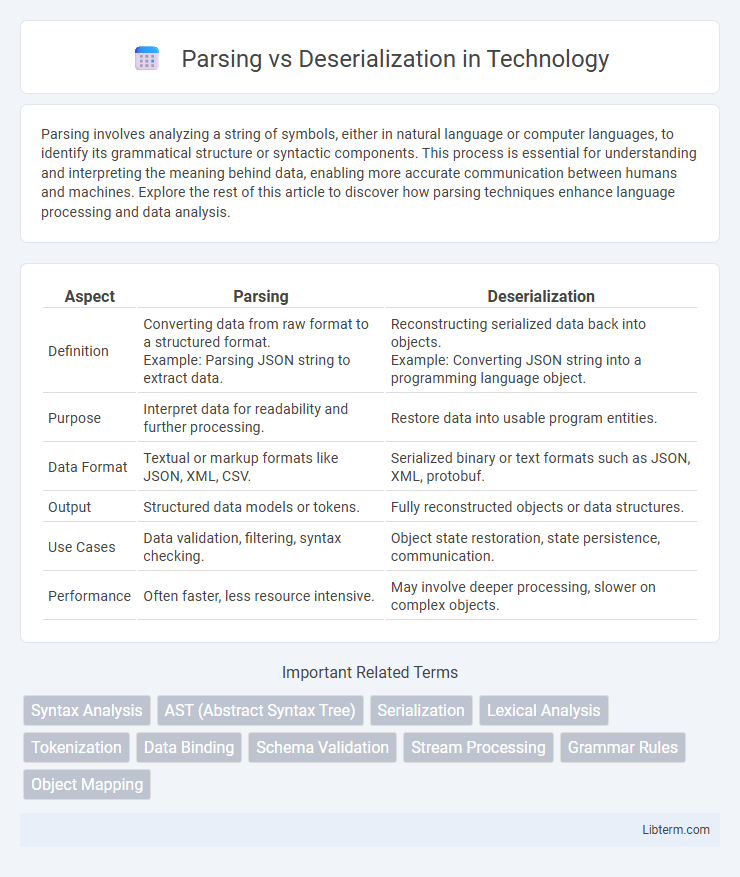
| Aspect | Parsing | Deserialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converting data from raw format to a structured format. Example: Parsing JSON string to extract data. |
Reconstructing serialized data back into objects. Example: Converting JSON string into a programming language object. |
| Purpose | Interpret data for readability and further processing. | Restore data into usable program entities. |
| Data Format | Textual or markup formats like JSON, XML, CSV. | Serialized binary or text formats such as JSON, XML, protobuf. |
| Output | Structured data models or tokens. | Fully reconstructed objects or data structures. |
| Use Cases | Data validation, filtering, syntax checking. | Object state restoration, state persistence, communication. |
| Performance | Often faster, less resource intensive. | May involve deeper processing, slower on complex objects. |
Introduction to Parsing and Deserialization
Parsing involves analyzing a string of data to extract meaningful information based on a specific grammar or format, enabling the transformation of raw input into a structured representation. Deserialization converts serialized byte streams or strings back into objects or data structures, facilitating data exchange between systems or storage formats. Both processes are fundamental in programming for handling data formats like JSON, XML, and binary protocols.
Defining Parsing
Parsing involves analyzing a string or data format to identify and extract its structural components based on a defined grammar or syntax. It transforms raw input, such as JSON or XML text, into a tree-like or hierarchical representation that reflects the data's organization. This process enables subsequent data processing or interpretation by converting unstructured or semi-structured text into a structured format.
Understanding Deserialization
Deserialization is the process of converting data from a byte stream or encoded format back into a usable object or data structure within a program, enabling easier manipulation and access. Unlike parsing, which involves analyzing and interpreting raw data or text to understand its structure, deserialization reconstructs objects by reading serialized data formats like JSON, XML, or binary. Understanding deserialization is crucial for effectively handling data exchange, ensuring security against injection attacks, and maintaining data integrity during application communication.
Key Differences: Parsing vs Deserialization
Parsing involves analyzing a string or text input to convert it into a structured format such as a syntax tree, often used in programming languages and data serialization. Deserialization specifically refers to the process of converting serialized data, like JSON or XML, back into an object or data structure that a program can manipulate. The key difference lies in parsing focusing on the syntactic structure extraction, while deserialization emphasizes reconstructing objects from serialized byte streams or text.
Core Use Cases for Parsing
Parsing primarily involves analyzing and converting data formats like JSON, XML, or CSV into a structured representation, enabling efficient data manipulation and validation. Core use cases for parsing include syntax checking in compilers, extracting relevant content from web pages, and transforming unstructured text into structured data for applications like search engines or data integration tools. Deserialization specifically refers to converting serialized data back into objects or data structures, commonly used in data exchange and storage scenarios.
Common Applications of Deserialization
Deserialization is commonly used in applications such as data exchange between microservices, restoring objects from storage, and communication protocols like JSON, XML, or binary formats. Unlike parsing, which converts raw data into a structured format, deserialization reconstructs complex objects and data structures to their original state for use in software applications. This process is essential in frameworks like REST APIs, message queues, and distributed systems where data integrity and object fidelity are critical.
Security Implications: Parsing and Deserialization Risks
Parsing and deserialization both involve transforming data formats but carry distinct security implications. Parsing risks often include injection attacks and buffer overflows due to improper input handling, while deserialization vulnerabilities can lead to remote code execution, object manipulation, and privilege escalation when untrusted data is reconstructed into objects. Secure coding practices must enforce strict validation, use safe libraries, and avoid deserializing from untrusted sources to mitigate these threats effectively.
Performance Considerations in Parsing and Deserialization
Parsing performance relies heavily on the complexity of the data format and the efficiency of the parser algorithm, with binary formats generally enabling faster parsing than text-based formats. Deserialization performance depends on the mapping complexity between raw data structures and in-memory objects, often influenced by serialization frameworks and object graph sizes. Optimizing parsing can reduce CPU overhead, while efficient deserialization minimizes memory allocation and latency during object reconstruction.
Popular Tools and Libraries
Popular parsing tools include ANTLR, a powerful parser generator for reading, processing, and translating structured text or binary files, and JSON.parse, widely used for parsing JSON strings in JavaScript applications. Deserialization libraries such as Jackson for Java and Newtonsoft.Json for .NET enable converting data formats like JSON or XML back into objects, efficiently handling complex data structures. These tools optimize data handling workflows by automating the conversion between raw data streams and in-memory objects, crucial for web development, API integration, and data exchange processes.
Choosing Between Parsing and Deserialization
Choosing between parsing and deserialization depends on the data format and intended use. Parsing is ideal for extracting specific information from structured text such as JSON or XML, enabling fine-grained control over data handling. Deserialization converts entire data streams into objects, making it efficient for reconstructing complex data structures from formats like binary or JSON for application use.
Parsing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com