Decentralized identity empowers individuals with full control over their personal data by eliminating reliance on centralized authorities. This approach enhances privacy, security, and user autonomy through blockchain and distributed ledger technologies. Discover how your digital identity can be transformed and secured by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
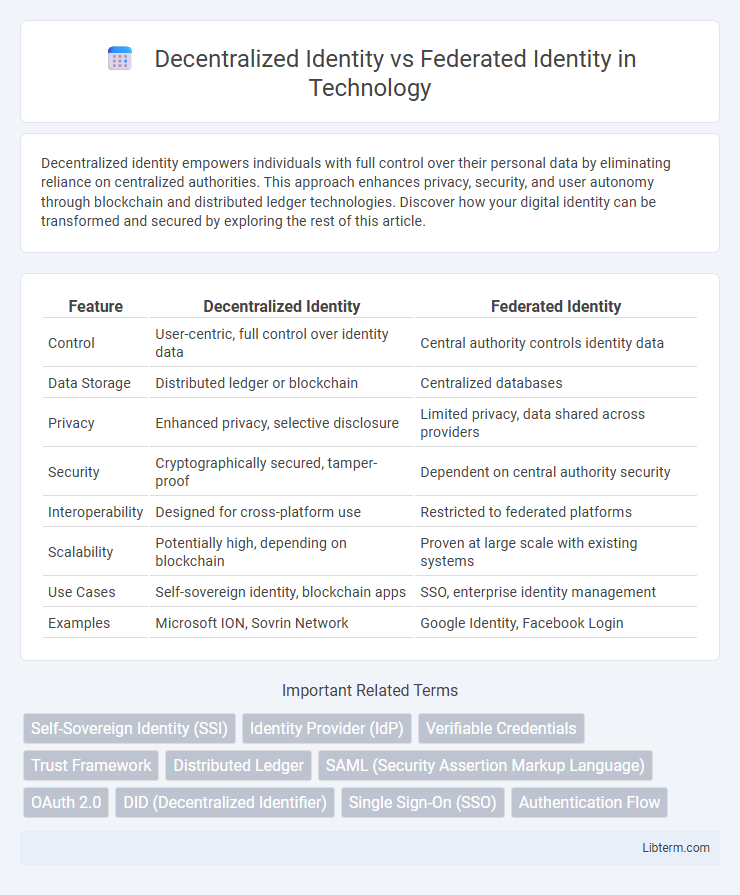
| Feature | Decentralized Identity | Federated Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Control | User-centric, full control over identity data | Central authority controls identity data |
| Data Storage | Distributed ledger or blockchain | Centralized databases |
| Privacy | Enhanced privacy, selective disclosure | Limited privacy, data shared across providers |
| Security | Cryptographically secured, tamper-proof | Dependent on central authority security |
| Interoperability | Designed for cross-platform use | Restricted to federated platforms |
| Scalability | Potentially high, depending on blockchain | Proven at large scale with existing systems |
| Use Cases | Self-sovereign identity, blockchain apps | SSO, enterprise identity management |
| Examples | Microsoft ION, Sovrin Network | Google Identity, Facebook Login |
Introduction to Digital Identity Systems
Digital identity systems enable secure authentication and personalized access across online platforms. Decentralized identity empowers users with control over their own credentials via blockchain or distributed ledger technologies, reducing reliance on central authorities. Federated identity allows multiple systems to share authentication via a trusted intermediary, simplifying user sign-on but creating dependency on a central identity provider.
What is Decentralized Identity?
Decentralized Identity (DID) is a digital identity model where individuals control their own identity data without reliance on a central authority, using blockchain or distributed ledger technology for secure, tamper-proof verification. Unlike Federated Identity, which depends on third-party providers like Google or Facebook to authenticate users across multiple platforms, DID enables peer-to-peer identity verification and enhances privacy by minimizing data sharing. This self-sovereign identity approach empowers users with greater control over personal information and reduces risks associated with centralized data breaches.
Understanding Federated Identity
Federated Identity enables users to access multiple systems using a single authentication credential managed by a trusted identity provider, streamlining login processes and reducing password fatigue. This approach centralizes user identity management across different organizations or platforms, improving convenience and security through established protocols like SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect. Organizations deploying Federated Identity benefit from simplified user provisioning, single sign-on (SSO), and enhanced control over user access without managing separate credentials for each service.
Key Components of Decentralized Identity
Decentralized Identity relies on blockchain technology, self-sovereign identity, and verifiable credentials to enable users to control their own digital identities without a central authority. Key components include decentralized identifiers (DIDs), which serve as unique, user-controlled identifiers, and cryptographic proofs that verify identity claims securely. Unlike federated identity systems that depend on third-party providers for authentication, decentralized identity empowers individuals by eliminating intermediaries and enhancing privacy and security.
Core Features of Federated Identity
Federated Identity enables users to access multiple applications using a single set of credentials managed by a trusted identity provider, streamlining authentication and reducing password fatigue. Core features include Single Sign-On (SSO), centralized identity and access management, and standardized protocols like SAML and OAuth for secure data exchange. This model enhances user convenience but relies on a centralized authority, which can create single points of failure and potential privacy concerns.
Security Implications: Decentralized vs Federated
Decentralized identity enhances security by allowing users to control their own credentials through blockchain technology, reducing risks of centralized data breaches and identity theft. Federated identity relies on third-party providers for authentication, creating single points of failure susceptible to hacking and unauthorized access. The distributed nature of decentralized identities offers stronger privacy guarantees and resilience against attacks compared to the centralized management in federated systems.
Privacy Considerations and User Control
Decentralized identity offers enhanced privacy by enabling users to store and manage their credentials directly on their devices or secure wallets, reducing reliance on centralized authorities and minimizing data exposure risks. Federated identity involves third-party providers who authenticate users across multiple services, increasing convenience but potentially creating privacy vulnerabilities due to centralized data aggregation and tracking. User control is significantly higher in decentralized systems, as individuals decide which attributes to share and with whom, whereas federated identity often limits transparency and user autonomy over personal data management.
Real-world Use Cases and Adoption
Decentralized identity enables individuals to control personal data through blockchain technology, with real-world use cases in healthcare for secure patient records and finance for streamlined KYC processes. Federated identity simplifies user access across multiple platforms by linking credentials, widely adopted in corporate environments like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 for seamless single sign-on (SSO). Adoption of decentralized identity is growing in sectors demanding privacy and data ownership, while federated identity remains dominant in enterprise and consumer applications for convenience and efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Decentralized Identity faces challenges such as scalability issues, lack of widespread adoption, and the complexity of user management without a central authority. Federated Identity struggles with centralized data control, privacy concerns, and vulnerability to single points of failure that can lead to security breaches. Both approaches require robust trust frameworks and interoperability standards to address their inherent limitations effectively.
Future Trends in Identity Management
Decentralized identity leverages blockchain technology to enhance user control and privacy by eliminating reliance on centralized authorities, promoting greater security and data ownership. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid models combining decentralized identifiers (DIDs) with federated identity systems to balance interoperability and user autonomy across platforms. Advances in zero-knowledge proofs and self-sovereign identity (SSI) frameworks are expected to drive widespread adoption, enabling seamless and secure identity verification in digital ecosystems.
Decentralized Identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com