Firewalling is a crucial network security measure designed to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules. It helps protect your systems from unauthorized access and cyber threats by filtering data packets and blocking malicious activity. Discover how effective firewalling can safeguard your digital environment by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
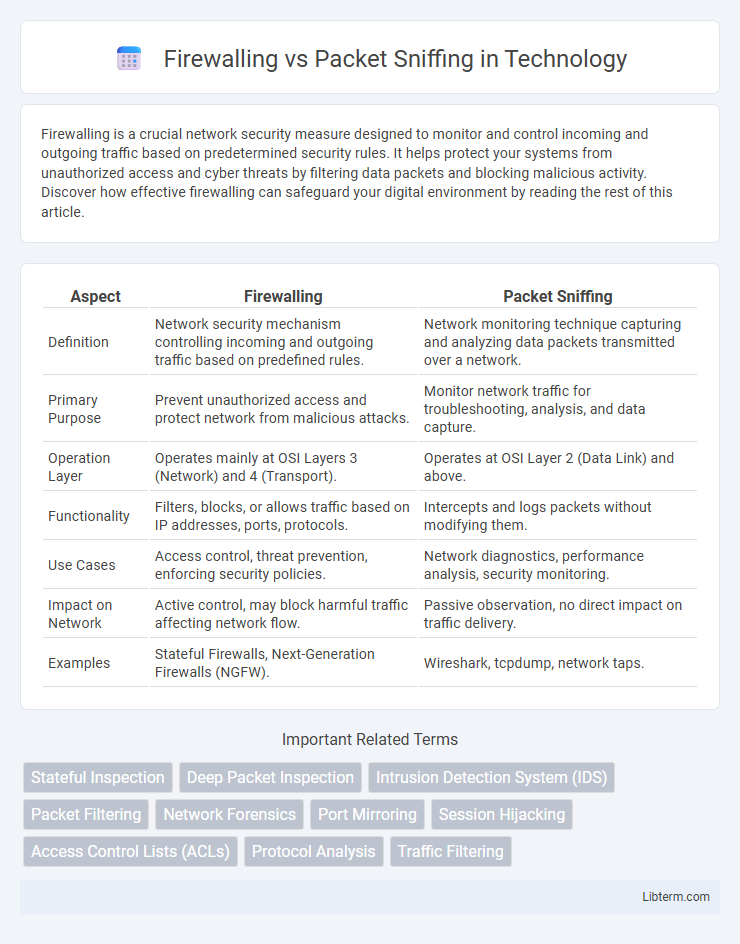
| Aspect | Firewalling | Packet Sniffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Network security mechanism controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. | Network monitoring technique capturing and analyzing data packets transmitted over a network. |
| Primary Purpose | Prevent unauthorized access and protect network from malicious attacks. | Monitor network traffic for troubleshooting, analysis, and data capture. |
| Operation Layer | Operates mainly at OSI Layers 3 (Network) and 4 (Transport). | Operates at OSI Layer 2 (Data Link) and above. |
| Functionality | Filters, blocks, or allows traffic based on IP addresses, ports, protocols. | Intercepts and logs packets without modifying them. |
| Use Cases | Access control, threat prevention, enforcing security policies. | Network diagnostics, performance analysis, security monitoring. |
| Impact on Network | Active control, may block harmful traffic affecting network flow. | Passive observation, no direct impact on traffic delivery. |
| Examples | Stateful Firewalls, Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW). | Wireshark, tcpdump, network taps. |
Introduction to Firewalling and Packet Sniffing
Firewalling controls network traffic by filtering incoming and outgoing packets based on predefined security rules to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Packet sniffing captures and analyzes network data packets in real time, enabling network monitoring, troubleshooting, and detecting suspicious activities. Both technologies complement each other in network security by providing proactive defense and detailed visibility.
Defining Firewalling: Purpose and Functionality
Firewalling is a network security measure designed to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Its primary purpose is to establish a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, such as the internet, to prevent unauthorized access and cyber threats. Firewalls function by filtering data packets, blocking malicious traffic, and allowing legitimate communication, thereby safeguarding network integrity.
Understanding Packet Sniffing: How It Works
Packet sniffing captures and analyzes data packets traveling through a network by intercepting the traffic at the data link layer. This process involves using specialized software or hardware tools to inspect packet headers and payloads, enabling the extraction of sensitive information like passwords or network configurations. Unlike firewalling, which actively blocks unauthorized access, packet sniffing passively monitors network communications for surveillance or troubleshooting purposes.
Key Differences Between Firewalling and Packet Sniffing
Firewalling controls network traffic by filtering incoming and outgoing packets based on predefined security rules to prevent unauthorized access and threats. Packet sniffing captures and analyzes data packets transmitted over a network, providing insights into communication but not actively blocking or filtering traffic. The key difference lies in the firewall's proactive defense mechanism versus the passive monitoring role of packet sniffing tools.
Advantages of Deploying Firewalls
Deploying firewalls enhances network security by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access while allowing legitimate communication. Firewalls provide real-time threat prevention against malware, hacking attempts, and data breaches, significantly reducing the risk of cyber attacks. Unlike packet sniffing, which passively monitors data, firewalls actively enforce security policies, offering a proactive defense mechanism to protect sensitive information and maintain network integrity.
Benefits and Risks of Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing enables network administrators to monitor traffic in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and detect unauthorized data transmissions, improving overall network security and performance. However, unauthorized packet sniffing poses significant risks, including data breaches, exposure of sensitive information, and increased vulnerability to cyberattacks. Unlike firewalling, which blocks unauthorized access, packet sniffing primarily focuses on traffic analysis, making it essential to implement strict access controls to prevent misuse.
Common Use Cases for Firewalling
Firewalling is primarily used to control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, making it essential for protecting sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, and blocking malicious attacks such as malware and ransomware. Common use cases include securing corporate networks, enforcing access policies in enterprise environments, and segmenting network zones to reduce the attack surface. Firewalls also help in monitoring and managing traffic to comply with regulatory requirements and ensure network reliability.
Packet Sniffing in Network Security Analysis
Packet sniffing plays a critical role in network security analysis by capturing and inspecting data packets transmitted over a network to identify malicious activities or unauthorized access. This technique enables security analysts to monitor real-time traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and perform deep packet inspection for threat intelligence and forensic investigations. Unlike firewalling, which primarily enforces access control, packet sniffing provides detailed packet-level visibility essential for proactive threat detection and incident response.
Firewalling vs. Packet Sniffing: Security Implications
Firewalling controls network traffic by filtering packets based on predetermined security rules, preventing unauthorized access and protecting systems from external threats. Packet sniffing involves intercepting and analyzing packets for monitoring or troubleshooting network communication but can expose sensitive data if used maliciously. Both techniques impact network security: firewalling actively blocks threats, while packet sniffing requires strict access control to avoid potential data breaches.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Network
Firewalling provides robust network security by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules, effectively blocking unauthorized access and threats. Packet sniffing allows detailed monitoring and analysis of network data packets for troubleshooting or performance evaluation but lacks proactive defense capabilities. Choosing the right approach depends on your network needs: prioritize firewalling for perimeter protection and packet sniffing for in-depth visibility and diagnostics.
Firewalling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com